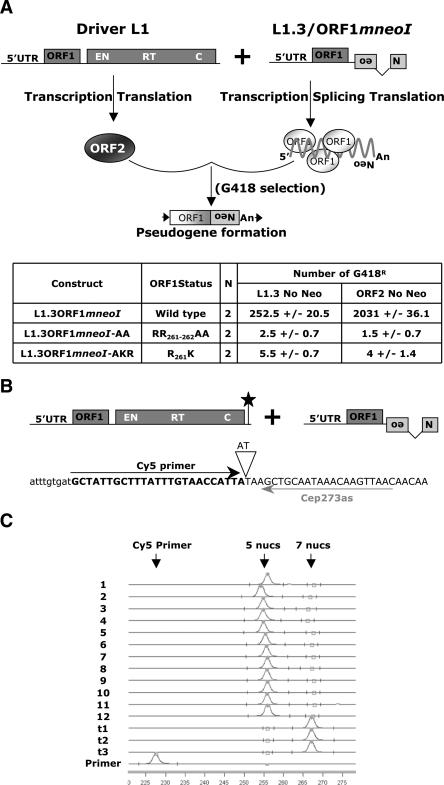
Figure 2.
ORF1p-dependent processed pseudogene formation occurs by template choice. (A) Rationale of the trans-complementation assay. A wild-type RC-L1 lacking the retrotransposition indicator cassette (pJM101/L1.3 No neo) or an ORF2 expression construct (ORF2 No neo) were cotransfected into HeLa cells with a construct consisting of the L1 5′UTR, ORF1, and the mneoI retrotransposition indicator cassette (ORF1mneoI or mutant derivatives), which is a preferential substrate for trans-complementation (Wei et al. 2001). The CMV immediate early promoter augments the expression of both the driver and reporter constructs. G418-resistant foci will arise only if ORF1mneoI RNA (i.e., the reporter mRNA) is trans-mobilized by ORF2p provided by the L1 lacking the indicator cassette (i.e., the driver L1). The inset Table indicates the names of the various reporter constructs (column 1), the status of ORF1 (column 2), the number of times the assay was conducted (column 3, N), and the number of G418-resistant foci obtained using either driver L1 (column 4). (B,C) Rationale and results of the fluorescent primer extension (FluPE) assay. The 3′ ends of the driver and reporter mRNAs were engineered so that the driver contains two extra nucleotides (indicated by the black star in the illustration of the driver construct and the inverted triangle in the depicted sequence). The driver and reporter constructs were cotransfected into HeLa cells and we isolated pools that contained ∼125–450 independent G418-resistant foci. Genomic DNA was extracted from the resultant pools and was subjected to PCR analysis using an oligonucleotide complementary to sequences in the indicator cassette (437NEOs) and another present just upstream of the poly(A) addition site in the vectors (Cep237as). Fluorescent Primer Extension (FluPE) then was conducted on the resultant PCR products using the Cy5 primer (black horizontal arrow). The arrows at bottom indicate the expected sizes of the Cy5 primer, the expected signal from the reporter construct (elongation of five nucleotides), and the expected signal from the driver construct (elongation of seven nucleotides). Retrotransposition events generated by template choice would be five nucleotides in size, whereas those formed via template switching would be seven nucleotides in size. The signals present in each pool (1–12) were five nucleotides in length, consistent with a template-choice mechanism for ORF1mneoI pseudogene formation. Traces t1, t2, and t3 represent positive control FluPE reactions performed on genomic DNA from cells transfected with an RC-L1 containing both the 2-bp insertion and the retrotransposition indicator cassette (pJM101/L1RP SDM). All experiments were repeated at least three times with the same results. The X-axis represents the running time of the reaction (minutes).