Figure 7.
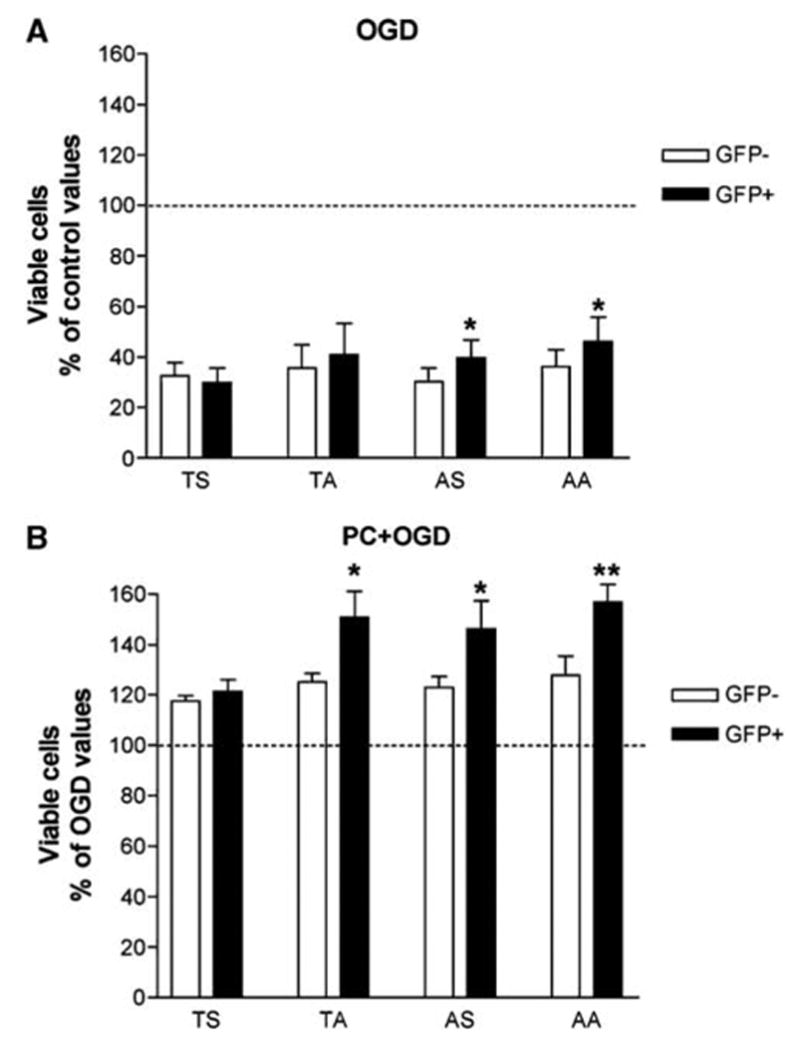
Effect of transfection of inactive Akt mutants and preconditioning on oxygen and glucose deprivation (OGD)-induced apoptosis in PC12 cells. Results represent means + s.e.m. (n = 6) of the percentage of total of viable PC12 cells (% of control or OGD values) obtained by fluorescence-activated cell sorter (FACS) analysis using propidium iodide (PI) and Hoechst 33342 labeling. Four different transfections, with either the wild-type Akt (TS) or Akt mutants were analyzed. In the mutants, an alanine was substituted for Ser473 (TA) or Thr308 (AS) or for both residues (AA). The wild-type (TS) and the mutated Akt constructs (TA, AS, and AA) were fused to the N-terminus of green fluorescent protein (GFP) and transiently transfected in PC12 cells. Fluorescence-activated cell sorter analysis allowed the separation of transfected (GFP + ) and nontransfected cells (GFP−). (A) Oxygen and glucose deprivation-induced decrease in viable cells was significantly counteracted by transfection with AS and AA (*P < 0.05 compared with GFP− cells; bifactorial repeated measures analysis of varainve (ANOVA)). (B) Preconditioning counteraction of OGD-induced decrease in viable cells was significantly potentiated by transfection with TA, AS, and AA (*P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01, compared with nontransfected GFP− cells; bifactorial repeated measures analysis of variance).
