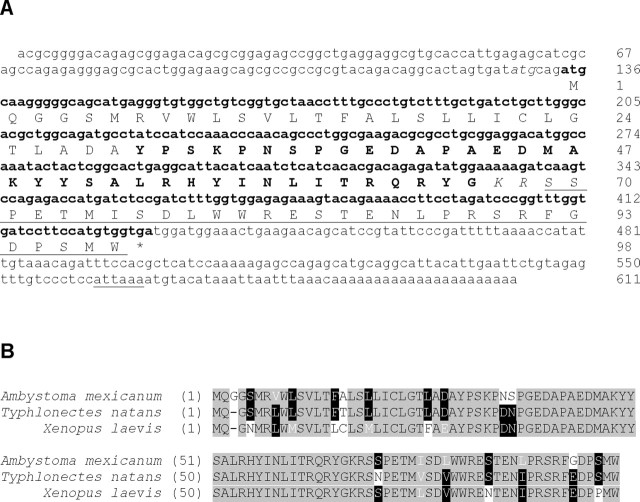
Figure 3.
Sequence of the NPY-encoding gene and propeptide sequence from axolotl. A, Nucleotide (lower case text) and amino acid (upper case text) sequences. The putative open reading frame is shown in bold text and the polyadenylation signal is underlined. Note an alternative atg codon (italics) positioned three nucleotides upstream of the putative open reading frame. Although both consensus start codons accommodate a signal peptide (Signal P 3.0; http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/SignalP/) that is subsequently cleaved between positions 29 (A) and 30 (Y), the second cleavage site results in a pre-pro-NPY that is more representative of other amphibian pre-pro-NPYs. Within the propeptide, note the mature NPY sequence (bold text), the dibasic (KR) cleavage site (italics) and the C-terminal extension (CPON) of NPY (underlined). The termination codon is marked by an asterisk. B, Amino acid alignments of axolotl NPY-encoding gene with the two amphibian NPY-encoding genes showing highest similarity. Black text on gray denotes identical residues, white text on black represents partially conserved residues, and similar residues appear as white text on gray.