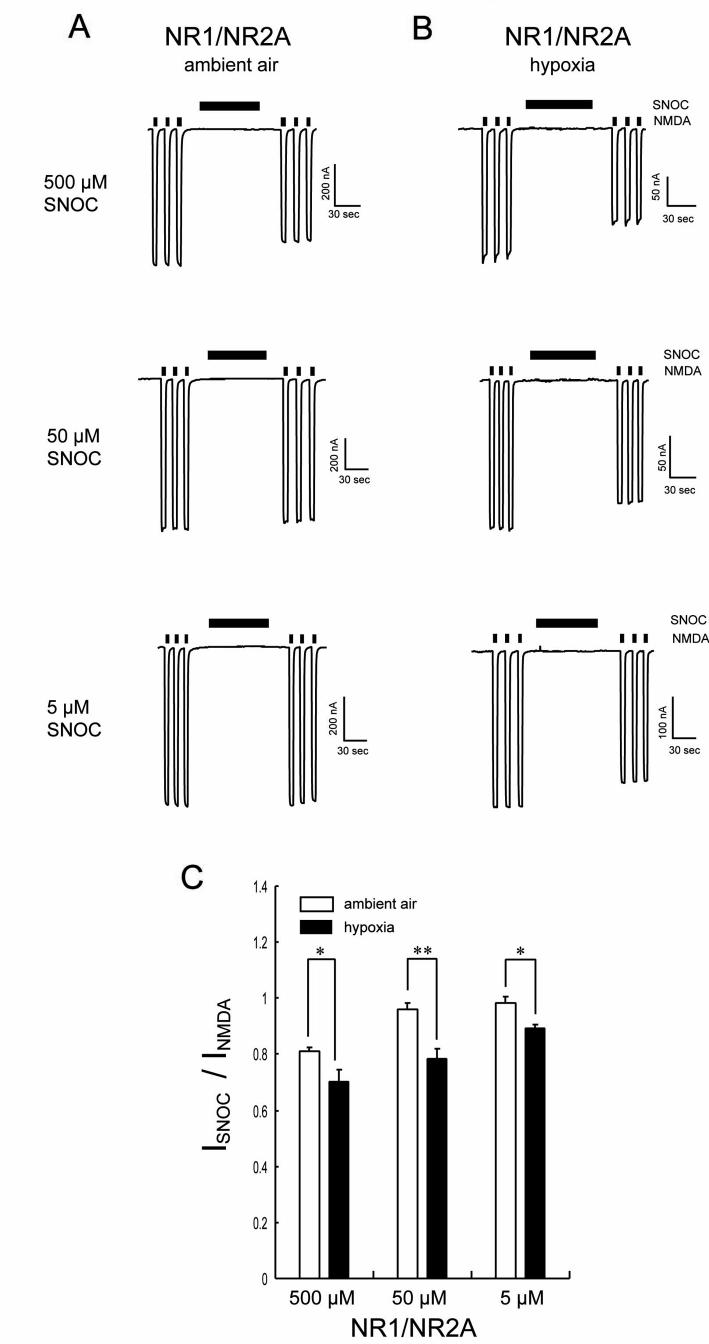
Figure 4.
Hypoxia Shifts the Sensitivity of NMDA Receptor Inhibition Towards Lower Concentrations of NO
(A) Inhibition of NMDA responses by SNOC (5-500 μM) under ambient conditions. (B) Inhibition of NMDA responses by SNOC (5-500 μM) under hypoxic conditions. At each concentration of SNOC, hypoxic conditions augmented inhibition of NMDA-evoked currents greater than ambient air conditions. Remarkably, at lower concentrations of SNOC, inhibition of NMDA-evoked current was evident only under hypoxic conditions. (C) Potentiation of NMDA-evoked currents expressed as normalized responses to NMDA before SNOC application. Values are mean ± SEM (n = 7 in each case). SNOC inhibition of NMDA currents was significantly greater under hypoxic compared to ambient conditions (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01; Mann-Whitney U test).