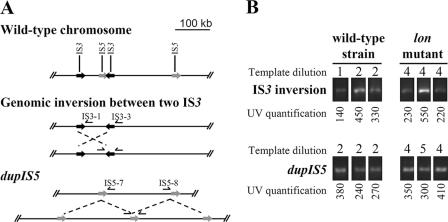
FIG. 3.
Genome instability of wild type versus that of lon mutant. (A) Schematic representation of the genomic inversion and tandem amplification detected. ISs are presented as black (IS3) or dark gray (IS5) arrows along the E. coli chromosome. The PCR primers used to detect the inversion and the duplication are shown on their hybridization sites along the chromosome. (B) Detection of genetic inversions and duplications in a wild-type strain and a lon mutant. DNA from three independent growths of AG100 (wild type) or M113R (lon3::IS186) in LB broth was extracted and quantified by determination of the A260. Comparative PCR of 35 cycles was done with 150 ng (dilution 1), 50 ng (dilution 2), 5.5 ng (dilution 4), or 1.9 ng (dilution 5) of template DNA. The amplified bands were quantified (see Materials and Methods).