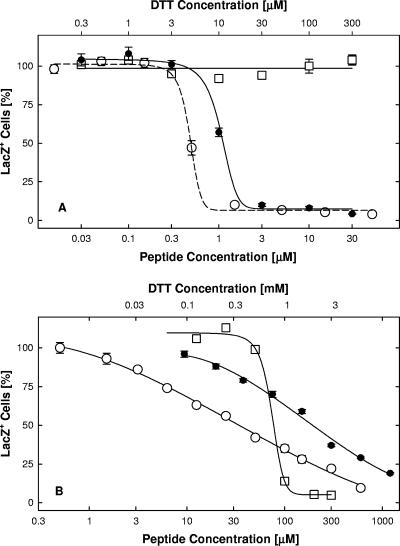
FIG. 11.
Effects of TAT-Cd0 dimerization on induction of cellular resistance to infection and on virus inactivation in solution. Panel A: induction of cell resistance. Vero cell cultures were exposed for 1 h at 37°C to TAT-Cd0 monomers in the presence of DTT (•; EC50, 1.1 μM), TAT-C0 dimers in the absence of DTT (○; EC50, 0.4 μM), or DTT alone (□). Cultures were then infected in the absence of peptide and DTT and scored for infectivity by measuring β-galactosidase activity in lysates 6 h later. DTT was added to freshly prepared peptide solutions in 10-fold molar excess. Panel B: inactivation of virions in solution. Virions in serum-free medium were exposed for 1 h at 37°C to TAT-Cd0 dimers (○; EC50, 34 μM) or monomers (•; EC50, 200 μM) or to DTT (□; EC50, 90 μM). Free peptide and DTT were removed by pelleting the virus, and infectivity was assayed by measuring β-galactosidase activity in lysates. Exposure to monomer was under strictly anaerobic conditions (argon atmosphere) in the absence of DTT. The data points represent the means of triplicate determinations with standard errors of the means.