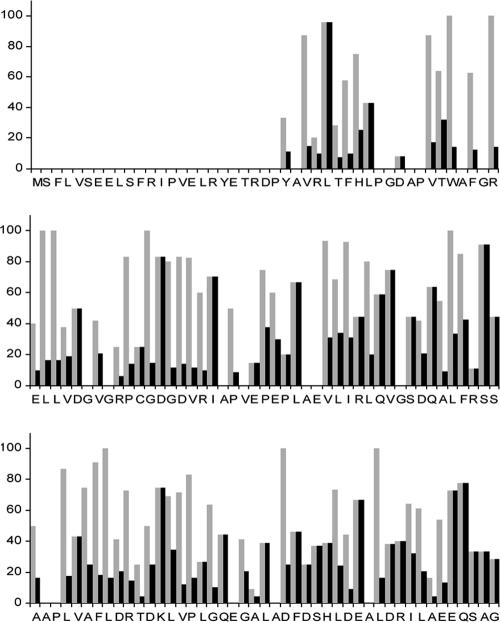
FIG. 4.
Graph showing the importance scores (gray bars) and specificity scores (black bars) in percentages on the y axis. The amino acid sequence of SsgA is shown along the x axis. The SsgA importance score represents the frequency at which a certain mutation occurs in a nonfunctional ssgA clone, where 100% would indicate that an amino acid is essential for SsgA function. By dividing the importance score by the conservation value, amino acids are identified as primarily important for the function of SsgA and less important for the other SALPs. A score of 100% would indicate that an amino acid is essential for SsgA function and unique for the SsgA protein. Data sets below the statistical threshold (specific residues mutated in fewer than four clones) were not included in the analysis.