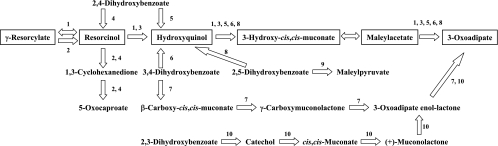
FIG. 4.
Various dihydroxybenzoate catabolic pathways in microorganisms. 1, γ-resorcylate pathway of Rhizobium sp. strain MTP-10005; 2, γ-resorcylate pathway of Clostridium sp. KN 245 (21); 3, resorcinol pathway of Corynebacterium glutamicum (17), Pseudomonas putida (9), and Trichosporon cutaneum (14); 4, 2,4-dihydroxybenzoate pathway of Clostridium sp. KN 245 (21); 5, 2,4-dihydroxybenzoate pathway of Pseudomonas sp. BN9 (34) and Sphingomonas sp. strain RW1 (5); 6, 3,4-dihydroxybenzoate pathway of Trichosporon cutaneum (2); 7, 3,4-dihydroxybenzoate 3,4-cleavage pathway of Agrobacterium sp. (27, 28), Bradyrhizobium sp. (27), Rhizobium sp. (27), Roseobacter sp. (8), and Streptomyces sp. strain 2065 (19); 8, 2,5-dihydroxybenzoate pathway of Trichosporon cutaneum (2); 9, 2,5-dihydroxybenzoate 1,2-cleavage pathway of Pseudomonas acidovorans (16) and Pseudomonas testosteroni (16); 10, 2,3-dihydroxybenzoate pathway of Aspergillus niger (20) and Trichosporon cutaneum (2, 3).