FIG. 2.
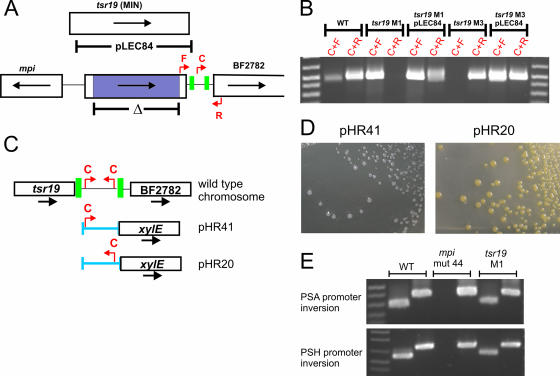
Tsr19 is necessary for inversion of the downstream promoter region. A. Open reading frame map of the mpi-tsr19 region showing the region that was deleted in the tsr19 mutant (purple) and the extent of DNA used to complement this mutant (pLEC84). The red arrows show the primers used to assay for inversion. Inverted repeats are shown as green boxes. B. Ethidium bromide-stained agarose gel of the inversion event from the wild type (WT), tsr19 mutants, and complemented mutants. Primers are those shown in panel A. C. Genetic regions (blue) cloned upstream of xylE in relation to the orientation of primer C, which undergoes inversion in wild-type bacteria and therefore is present in each orientation from a population of wild type bacteria. pHR20 and pHR41 contain identical DNA cloned in opposite orientations upstream of xylE. D. Analysis of functional promoter activity from B. fragilis 9343 containing pHR20 or pHR41 in trans. The transconjugants were sprayed with catechol, which is the substrate for XylE and convert the colonies to yellow if a functional promoter has been cloned. E. Ethidium bromide-stained agarose gels showing the inversion of the PSA and PSH promoter regions from the wild type, mpi deletion mutant 44, and Δtsr19 M3.