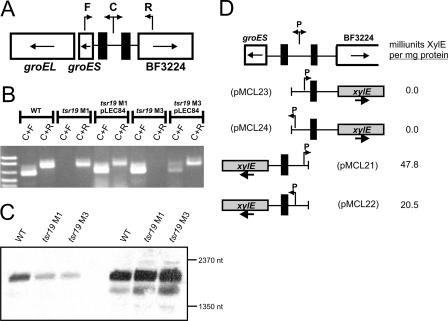
FIG. 4.
Tsr19 is necessary for inversion of a distant chromosomal region. A. Schematic showing the genetic regions flanking the Tsr19-like inverted repeats (filled boxes). The direction of transcription of each gene is shown with arrows inside the boxes, and primers used to demonstrate inversion of DNA between the IRs are indicated as F, C, and R. B. Ethidium bromide-stained agarose gel of the resulting PCR products from the wild type (WT), tsr19 mutants, and complemented mutants, using the F, C, and R primers shown in panel A. C. Northern blot analysis of wild type and tsr19 mutants grown to early log phase (optical density at 600 nm = 0.3) (first three lanes) and mid-log phase (optical density at 600 nm = 0.8) (last three lanes), using 30 μg of RNA per well probed with an internal portion of groEL. D. Analysis of the transcription of groES and BF3224 by the adjacent Tsr19-regulated invertible promoter, using xylE transcriptional fusion clones. pMCL23 and pMCL24 detect transcription into BF3224 when the invertible promoter is cloned in either the ON or OFF orientation, respectively. pMCL21 and pMCL22 detect transcription into groES when the invertible promoter is cloned in either the OFF or ON orientation, respectively. The resulting milliunits of XylE activity per milligram of protein are reported for each of these constructs when in trans in B. fragilis 9343.