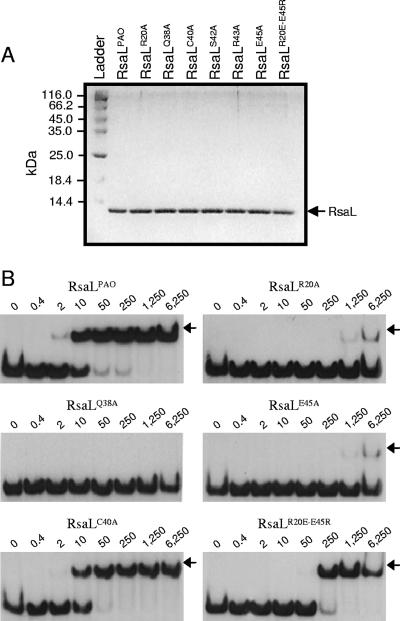
FIG. 3.
In vitro validation of the RsaLPAO model. (A) Sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis showing that purified RsaLPAO and its mutated derivatives (indicated above each lane) are very pure and that their concentrations are equilibrated. Two microliters of each protein was loaded on the gel. Ladder, PageRuler protein ladder (Fermentas); the molecular mass of each band is indicated on the left. (B) EMSA carried out with a DNA probe encompassing the RsaLPAO-binding site on PlasI and either RsaLPAO or its mutated derivatives (indicated above each gel). The EMSAs were carried out simultaneously, starting from the same mixture containing the DNA probe, with identical polyacrylamide gels run in parallel. RsaLS42A and RsaLR43A showed an EMSA pattern (not shown) identical to that of RsaLQ38A. The RsaL-DNA complexes are indicated by arrows. The protein concentration (nM) for each sample is indicated above its lane.