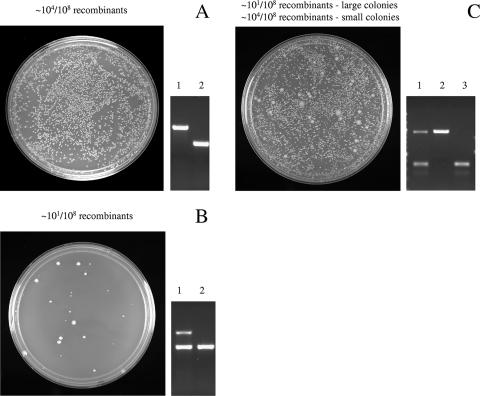
FIG. 3.
Three patterns of gene knockouts observed during analysis of gene essentiality by recombineering. A. Nonessential gene pattern characterized by a standard high recombination frequency on LB plates (left panel) and single configuration of a replaced gene as analyzed by agarose gel electrophoresis (right panel). The agarose gel shows a gene replaced with an antibiotic resistance cassette (lane 1) versus the original wild-type gene (lane 2). B. Essential gene pattern characterized by a low recombination frequency of colonies and duplicated configuration of the disrupted gene (lane 1) versus its wild-type allele (lane 2) by gel analysis. The duplication includes the gene replaced with an antibiotic resistance cassette (lane 1, upper band) and the wild-type gene (lane 1, lower band). C. Growth-impaired pattern characterized by a mixed pattern of two colony sizes with different recombination frequencies. The large colonies appear first with a low recombination frequency and a duplicated configuration (lane 1) of the essential gene. The small colonies have a high recombination frequency and a single configuration of the replaced gene (lane 2) versus its wild-type allele (lane 3).