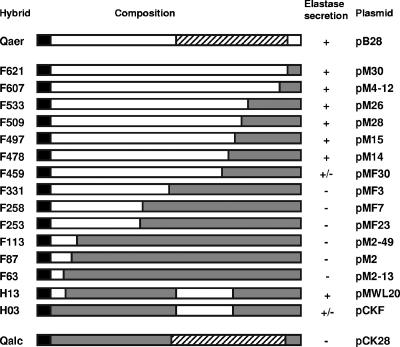
FIG. 1.
Schematic diagrams of the different (chimeric) XcpQ proteins. Open bars, XcpQaer; shaded bars, XcpQalc; solid bars, signal sequences; cross-hatched bars, C-terminal domain that is conserved in the various members of the secretin family. The designations of the proteins are indicated on the left; in each case the number refers to the position of the amino acid residue at the fusion site (the numbering includes the signal sequence). The corresponding plasmids are indicated on the right. The functionality of XcpQ was based on the ability of the xcpQ mutant PAN1 supplemented with the different xcpQ genes to form haloes on elastin-containing plates after 24 h of growth. +, formation of haloes whose sizes were similar to the sizes of haloes formed by the wild-type strain; +/−, formation of smaller haloes; −, no halo formation.