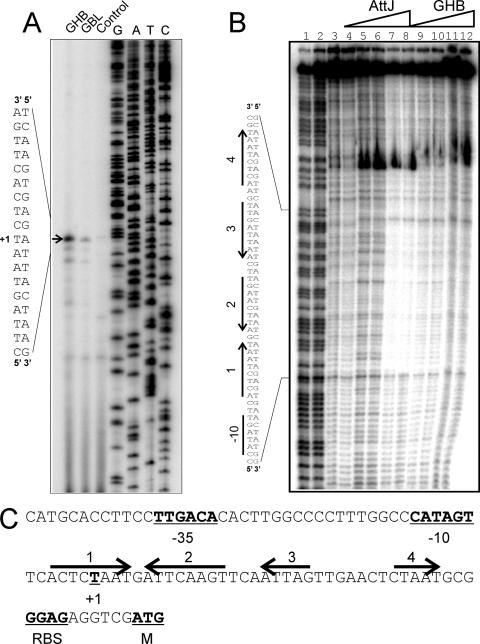
FIG. 1.
Primer extension and DNase I footprinting assays of the attK promoter. (A) Primer extension assays. Lanes 1 and 2 identify mRNA from cultures incubated with GHB or GBL, respectively, added at a final concentration of 10 mM to strain NTL4. Primer extension assays were performed by using a protocol described previously (3). RNA was prepared by using RNeasy minikits (QIAGEN) from exponential-phase cultures of NTL4 after 2 h of growth in the presence of 100 μM GBL or GHB. The arrow indicates the position of the transcription start. (B) Footprinting assays using purified His6-AttJ and the radiolabeled attK promoter DNA. Lanes 1 and 2 represent G+C ladders; lanes 3 and 4 represent free DNA; in lanes 5 and 6, His-AttJ was added at 1 μM; in lanes 7 and 8, His-AttJ was added at 3 μM; in lanes 9 and 10, His-AttJ was added at 3 μM and GHB (sodium salt) was added at 10 mM; and in lanes 11 and 12, His-AttJ was added at 3 μM and GHB was added at 30 mM. Sequences protected by AttJ are indicated on the left. DNase I footprinting assays were carried out using a 217-nucleotide PCR product digested with EcoRI and SacII and end labeled at the EcoRI site using [α-32P]dATP and Klenow DNA polymerase. AttJ was added to the DNA fragment and allowed to bind for 30 min in a 50-μl volume. DNase I (0.25 U) was then added to the samples, and the reactions were terminated after 30 s by the addition of 0.25 M EDTA and 5 mg of yeast tRNA/ml. DNA was precipitated using ethanol and size fractionated using 6% polyacrylamide denaturing gels in 1× Tris-borate-EDTA buffer. (C) Sequence analysis of the attKLM promoter. The −35 and −10 RNA polymerase binding site motifs, the transcriptional start, and the predicted ribosome-binding site and translational start of the attK gene are underlined and in boldface. The four arrows represent DNA sequences with a limited dyad symmetry that overlap the region that is protected by His-AttJ in footprinting assays. All gels were analyzed by using a Storm B840 PhosphorImager (Molecular Dynamics).