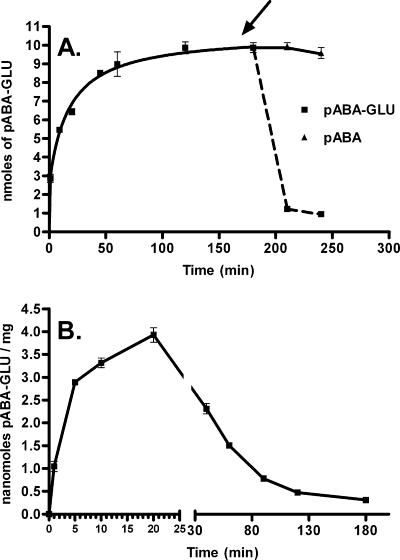
FIG. 5.
Transport and retention of radioactive p-aminobenzoyl-glutamate. (A) Effect of the addition of unlabeled p-aminobenzoyl-glutamate or p-aminobenzoate on cells (MG1655 transformed with pJMG128) that have accumulated radioactive p-aminobenzoyl-glutamate. Assays were performed as described in Materials and Methods. Briefly, cells were grown overnight, washed, and resuspended in minimal medium. After preincubation, the transport assay (final volume, 6 ml) was initiated by the addition of [3H]p-aminobenzoyl-glutamate to a final concentration of 50 μM. Duplicate samples (0.4 ml) were taken at the times shown. After the 180-min sample was taken, the mixture was divided in two equal portions and a nonradioactive sample of p-aminobenzoyl-glutamate (final concentration, 10 mM) or p-aminobenzoate (final concentration, 2 mM) was added. Duplicate samples were then taken of each mixture at 210 and 240 min. Samples were filtered, immediately washed with ice-cold minimal medium, and counted. Data were analyzed with GraphPad Prism 4; error bars represent standard errors. (B) Transport and retention of [3H]p-aminobenzoyl-glutamate by MG1655 transformed with both pJMG128 and pLJAB. Assays were performed as described in Materials and Methods. After preincubation, the transport assay (final volume, 6 ml) was initiated by the addition of [3H]p-aminobenzoyl-glutamate to a final concentration of 50 μM. Duplicate samples (0.1 ml) were taken at the times shown. Samples were filtered, immediately washed with ice-cold minimal medium, and counted. Data were analyzed with GraphPad Prism 4; error bars represent standard errors.