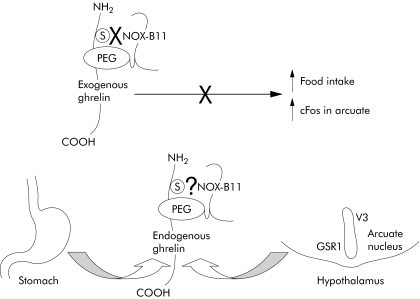
Figure 1 NOX‐B11 is a PEGylated ghrelin Spiegelmer that binds to the serine on the amino terminus of ghrelin. In the paper by Kobelt and colleagues,1 NOX‐B11 prevented both exogenous ghrelin induced increased food intake in the first hour and, in separate experiments, ghrelin evoked activation of neurones in the arcuate nucleus (presumably those that express the receptor growth hormone secretagogue receptor 1 (GSR1)). Endogenous ghrelin is released from the stomach and it is not known whether NOX‐B11 interferes with the activity of the circulating peptide to prevent its site of action in the hypothalamus. NOX‐B11 would not be expected to cross the blood‐brain barrier and inhibit the local release of ghrelin in the arcuate nucleus where it presumably acts nearby. Thus although these pharmacodynamic effects of NOX‐B11 in vivo are encouraging, the extent to which NOX‐B11 can modify disease states in which endogenous levels of ghrelin are elevated is not clear.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.