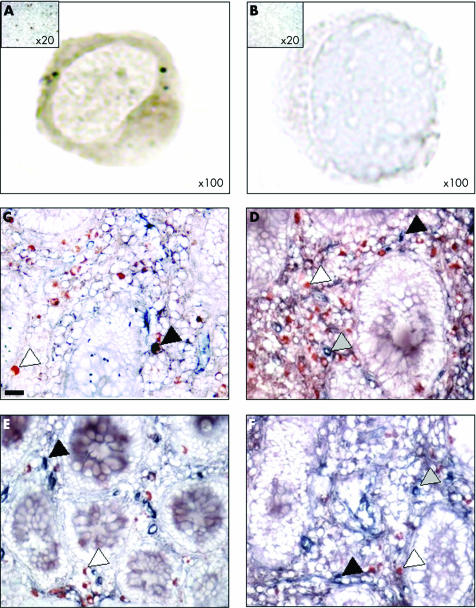
Figure 3 Mu opioid receptor (MOR) immunoreactive cells in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) and mucosal CD4+ and CD8+ T cells of patients with inflammatory bowel disease. (A, B) MOR immunostaining in PBMC of one representative Crohn's disease (CD) patient and the corresponding negative control (magnification ×100). The control, consisting of normal rabbit immunoglobulins, was negative. Insert: low magnification ×20 of MOR immunostaining of a CD patient and control. (C–F) Double immunostaining for MOR (red) and CD4 (blue) (C, D) or MOR (red) and CD8 (blue) (E, F) (original magnification ×400) in biopsies taken from one patient with CD in non‐inflamed (C, E) and inflamed (D, F) areas. Whereas only a few CD4+ and CD8+ cells stained positively with the antibody directed against MOR in the non‐inflamed mucosa, an increased number of CD4+ T cells (blue), MOR+ (red), and CD4+/MOR+ cells were observed in the inflamed mucosa of the CD patient. Scale bar represents 5 μm.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.