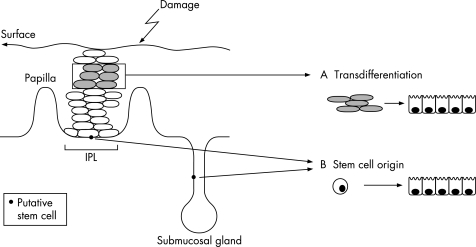
Figure 2 Possible cells of origin for Barrett's metaplasia. If the metaplastic process occurs by altered differentiation of a mature squamous oesophageal epithelial cell (shaded cells in grey in the mucosal layer) without requiring proliferation, it is called transdifferentiation. Alternatively, the cell of origin may be an undifferentiated cell with the capacity to form multiple‐cell lineages: a so‐called “stem cell”. These stem cells may be of tissue or bone marrow origin. The tissue‐derived stem cells may be located in the basal compartment of the interpapillary layer or in the submucosal gland duct. In either case, the trigger for columnar differentiation seems to depend on surface epithelial damage from luminal factors.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.