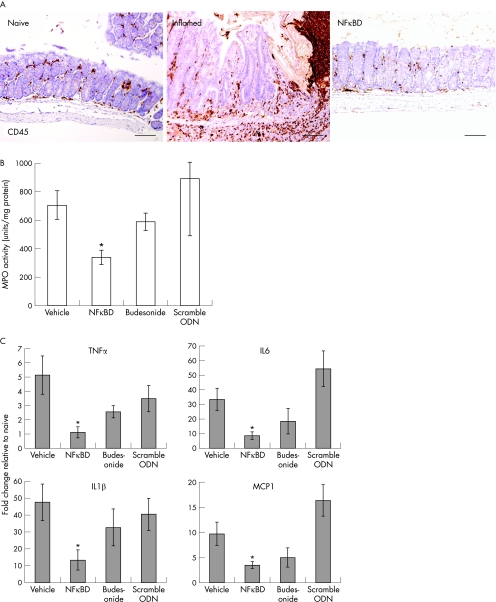
Figure 4 Nuclear factor‐κB decoy (NFκBD) reduces key inflammatory mediators in colon tissue. (A) Colons from trinitrobenzene sulphonic acid (TNBS)‐induced mice were evaluated for inflammatory infiltrate levels by immunohistochemical analysis using the pan‐leucocyte CD45 marker. Bars represent 100 μm. (B) Neutrophil infiltration was assessed by measuring myeloperoxidase (MPO) levels in the TNBS‐induced colons. Results are expressed as units of MPO activity/mg protein in colons (5–8 animals/group). (C) Ubiquitin‐normalised mRNA levels of tumour necrosis factor (TNF)α, IL6, IL1β and MCP‐1 from colon tissue in the TNBS model were determined by real‐time polymerase chain reaction analysis. Data are plotted as mean (SEM; n = 5–8 mice/group) from two independent experiments. *Significant difference relative to vehicle control group (p<0.05). ODN, phosphorothioated NFκBD oligonucleotide.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.