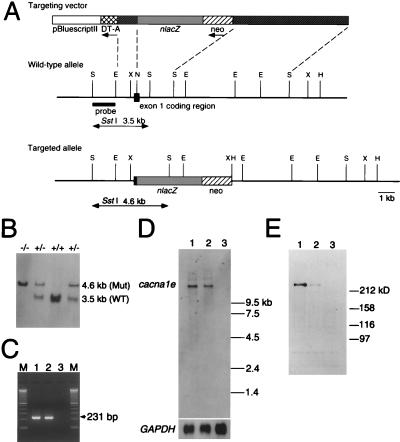
Figure 1.
Generation of α1E-deficient mice. (A) Simplified restriction map around exon 1 of cacna1e gene and structure of the targeting vector. Coding region of exon 1 is boxed. neo, PGK-neo cassette; DT-A, diphtheria toxin-A fragment gene; E, EcoRI; N, NotI; S, SstI; X, XbaI. (B) Southern blot analysis of tail DNA. DNA was digested with SstI, and the blot was hybridized with a probe shown in A. The 3.5-kb band is derived from the wild-type allele (WT) and the 4.6-kb band from the targeted allele (Mut). +/+, wild-type; +/−, heterozygote; −/−, homozygous mutant. (C) RT-PCR analysis. cDNA derived from brain total RNA was used as a template. A fragment of 231 bp is diagnostic of cacna1e expression. M, 100 bp ladder (GIBCO/BRL). (D) Northern blot analysis. Poly(A)+ RNA (2.5 μg) from mouse brains was loaded in each lane. The blot was probed with a cacna1e cDNA fragment (about 1 kb) corresponding to cytoplasmic loop between the repeat II and III of α1E. GAPDH probe was used for loading control (35). (E) Immunoblot analysis. Brain membrane proteins (100 μg/lane) were probed with a rabbit polyclonal anti-α1E antibody. This antibody detects a single band with molecular mass of ca. 250 kDa. Lane 1, wild-type; lane 2, heterozygote; lane 3, homozygous mutant in C, D, and E.