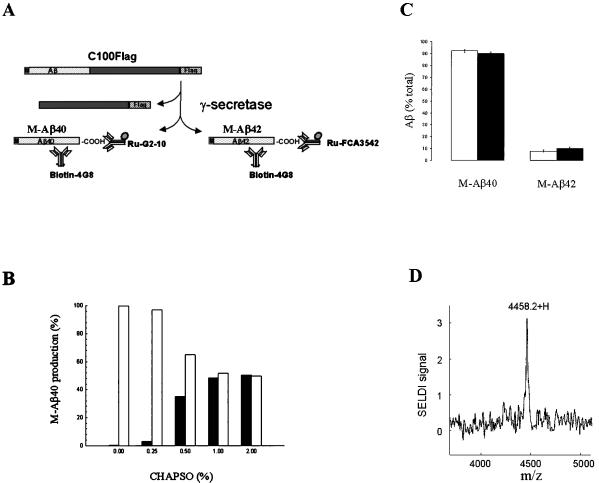
Figure 1.
In vitro γ-secretase assay. (A) Schematic representation of the fusion protein substrate, C100Flag, consisting sequentially of an N-terminal Met (M), APP597–695 (the Aβ domain is shown), and the Flag tag (Flag) sequence, and its processing by γ-secretase. The Aβ40- and Aβ42-related products (M-Aβ40 and M-Aβ42, respectively) are detected by ECL using biotinylated 4G8 antibody and the ruthenylated G2–10 or FCA3542 antibodies, respectively. (B) Solubilization of γ-secretase activity by extraction of cellular membranes with CHAPSO detergent. HeLa cell membranes were treated with the indicated CHAPSO concentration, and the samples were centrifuged. The supernatant solutions (filled bars) and resuspended pellets (open bars) were diluted in assay buffer to yield a uniform CHAPSO concentration (0.25%), incubated with C100Flag, and assayed for M-Aβ40 production by ECL. The γ-secretase activities are expressed as % of the total activity (supernatant solution plus pellet) at each detergent concentration. The data are the mean values of two independent experiments. (C) Generation of the Aβ40- and Aβ42-related products from C100Flag by HeLa cell membranes or solubilized γ-secretase. Intact membranes (500 μg/ml) (open bars) or solubilized γ-secretase (125 μg/ml) (filled bars) was incubated in the presence of C100Flag (1.7 μM) and CHAPSO (0.25%) at 37°C for 90 min. The reactions were quenched with RIPA and boiled. The resulting mixtures were centrifuged and the supernatant solutions were assayed for M-Aβ40 and M-Aβ42 by ECL. Standard curves using Aβ40 and Aβ42 were generated to measure production of the corresponding peptides. The data show the M-Aβ40 and M-Aβ42 levels as a % of total M-Aβ40 and M-Aβ42 (mean ± SD, n = 3). The total amount of the Aβ-related species was 556 fmol and 310 fmol for the intact membranes and solubilized γ-secretase, respectively. (D) Mass spectrometric confirmation of the identity of the Aβ40-related product (M-Aβ40) in the in vitro γ-secretase assay using solubilized γ-secretase and C100Flag. SELDI, surface-enhanced laser desorption/ionization.