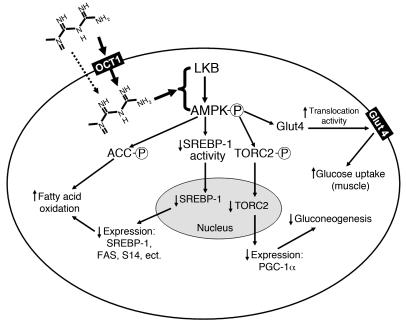
Figure 9. Mechanism of metformin action in cells.
By controlling the intracellular concentrations, OCT1 is a direct determinant of metformin pharmacological effects in the liver (bold arrow). Passive diffusion and other transporters may account for small portion of hepatic uptake of metformin (dashed arrow). Other transporters may control metformin uptake into other tissues, such as skeletal muscle. Factors such as genetic variation in transporter genes may alter transporter activity and thus metformin response. LKB, alias of serine-threonine kinase 11 (STK11); PGC-1α, peroxisome proliferator activated receptor γ coactivator 1 α; TORC2, target of rapamycin complex 2.