Figure 2. CKI ε phosphorylates SIPA1L1, promotes its degradation, and alleviates SIPA1L1-mediated Rap1 inhibition.
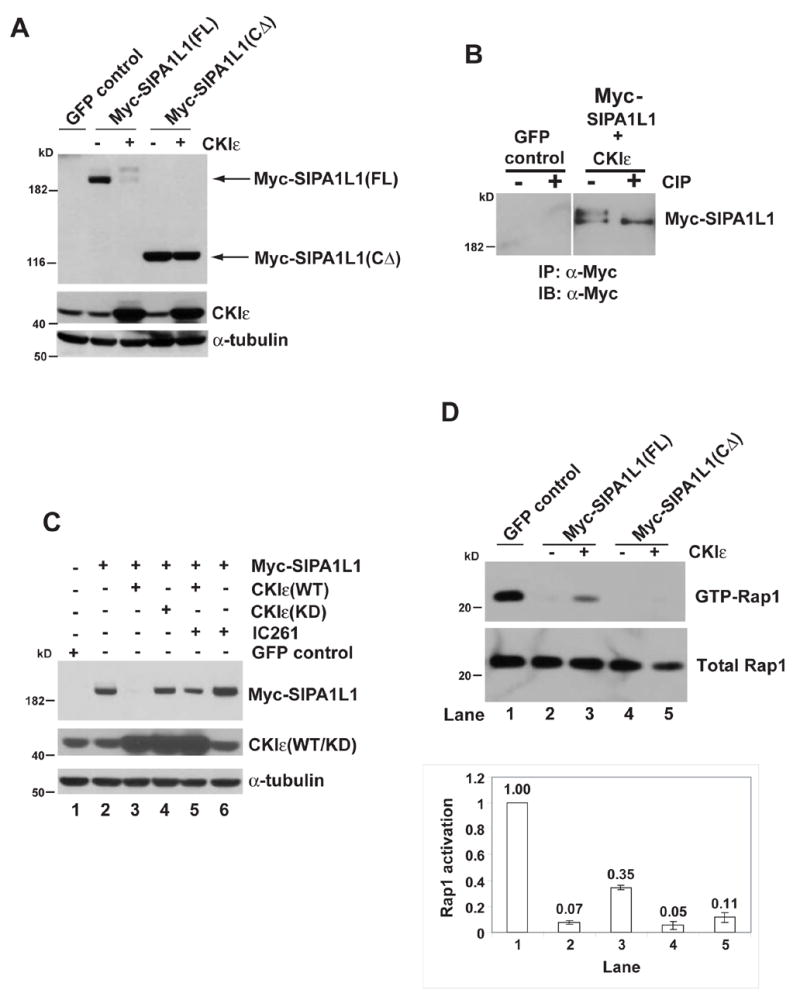
(A) CKIε expression causes an electrophoretic mobility shift of SIPA1L1(FL) but not SIPA1L1(CΔ). IB, Immunoblot of whole cell lysates from HEK 293 cells expressing the indicated proteins. CKIε and α-tubulin abundance are shown in the middle and bottom panels.
(B) SIPA1L1 is phosphorylated by CKIε. Myc-SIPA1L1 plus CKIε or GFP (as the negative control for IP) were expressed in HEK 293 cells. Myc-SIPA1L1 was precipitated and treated with or without CIP.
(C) CKIε stimulates SIPA1L1 degradation. Lanes 1–5, Myc-SIPA1L1 was co-expressed with CKIε(WT) or CKIε(KD) as indicated. Lane 5 and lane 6, cells expressing Myc-SIPA1L1 were treated with IC261 (50 μM) for 5 hr. IC261 treatment increased SIPA1L1 abundance (compare lane 5 to lane3 and lane 6 to lane 2). Expression of CKIε(WT/KD) and endogenous α-tubulin abundance are shown in middle and lower panels.
(D) CKIε rescues SIPA1L1-mediated Rap1 inhibition. Myc-SIPA1L1(FL) or Myc-SIPA1L1(CΔ) was co-expressed with or without CKIε in the CHO cells, followed by GST-RalGDS pull-down assay. The abundance of GTP-Rap1 and total Rap1 was quantified by ImageQuant. The ratio of GTP-Rap1 to total Rap1 is shown in the lower panel.
