Fig. 5.
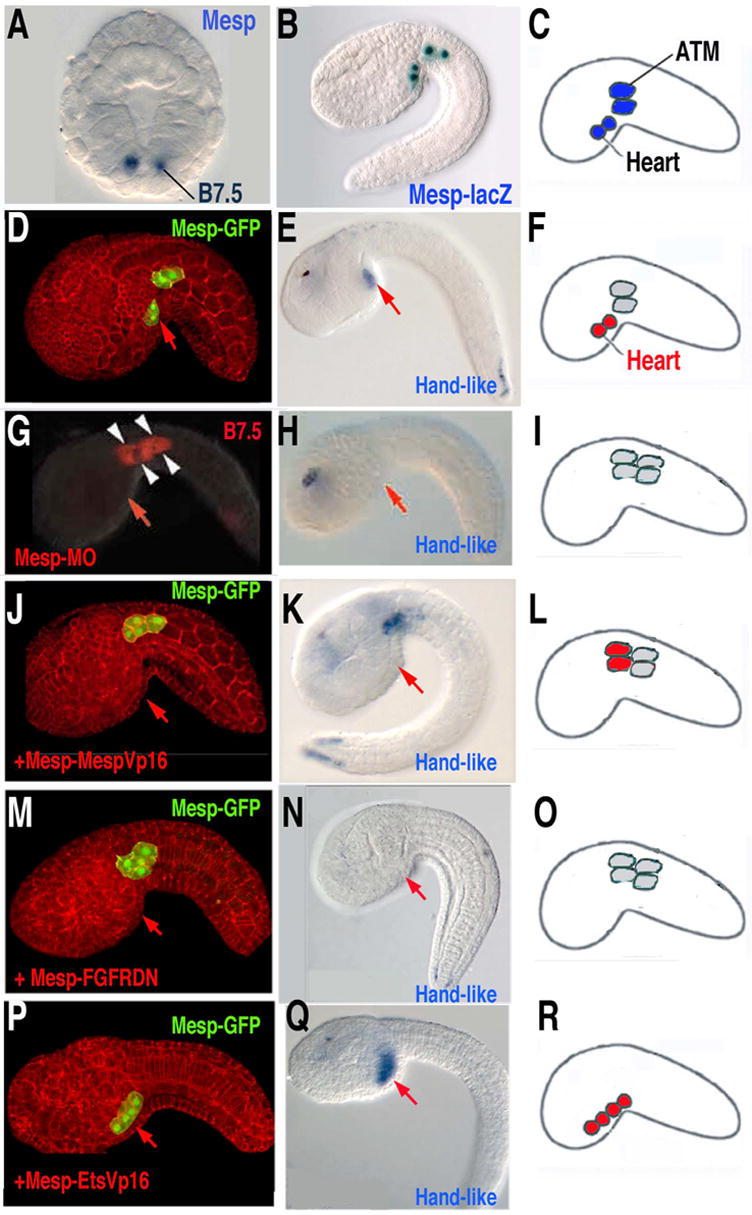
(A) Mesp expression in the B7.5 cells, gastrula stage, anterior is up. (B) X-gal staining of transgenic Mesp-lacZ embryos shows normal position of B7.5 lineage cells, as diagrammed in (C). (D–F) Control embryos show heart cell migration (D) and specification (Hand-like gene expression)(E), as diagrammed in (F). (G–I) Knockdown of Mesp (through injection of anti-sense morpholinos) blocks heart cell migration (G) and specification (Hand-like gene expression) (H), as diagrammed in (I). (J–L) Targeted expression of constitutively active MespVP16 in the B7.5 lineage cells blocks heart cell migration (J) but not specification (Handlike expression)(K), as diagrammed in (L). (M–O) Targeted expression of a dominant negative FGF receptor in the B7.5 lineage cells blocks heart cell migration (M) and specification (Handlike expression)(N), as diagrammed in (O). (P–R) Targeted expression of constitutively active EtsVp16 in the B7.5 lineage cells causes all B7.5 lineage cells to migrate (P) and express heart lineage genes (Hand-like expression)(Q), as diagrammed in (R). (Portions of this figure are modified from [24], [31] and [30].)
