Figure 4. Epitope-specific IFN-γ-producing CD8+ T cell in the CNS of WT or mutant virus-infected mice.
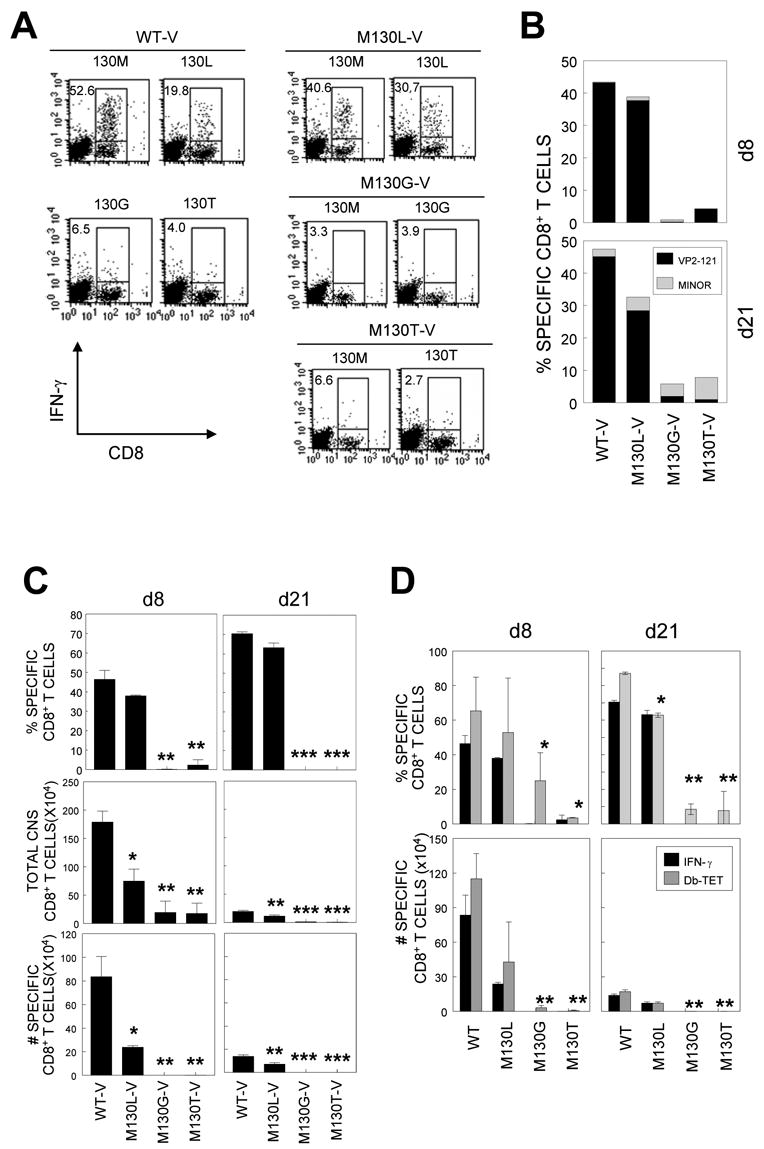
A, CNS-infiltrating cells were stimulated with indicated peptides at 2 μM for 6 h. Cells were stained for both CD8 and intracellular IFN-γ followed by flow cytometric analysis. The percentage of IFN-γ+CD8+ T cells is shown in the upper left quadrant of each plot. Data are representative of 3 independent experiments. B, CNS-infiltrating cells from mice at 8 d and 21 d post infection were stimulated with the predominant (VP2121–130) or a mixture of minor epitope peptides (VP2165–173 and VP3110–120) for 6 h and the percentage of IFN-γ+CD8+ T cells was determined. C, Proportion of epitope-specific CD8+ T cells (Top panel), total number of CNS-infiltrating MNC (middle panel), and the number of epitope-specific CD8+ T cells in the CNS (bottom panel) is shown. Values given are the mean of percentage or numbers of at least two independent experiments (mean ± SD). D, Comparison of Db-VP2121–130 tetramer-positive and VP2121–130-specific IFN-γ-positive CNS-infiltrating CD8+ T cells. CNS-infiltration of specific CD8+ T cells in mice infected with M130G-V and M130T-V was significantly lower compared to that in mice infected with WT-V or M130L-V. *, p<0.05; **, p<0.01.
