Fig. 3.
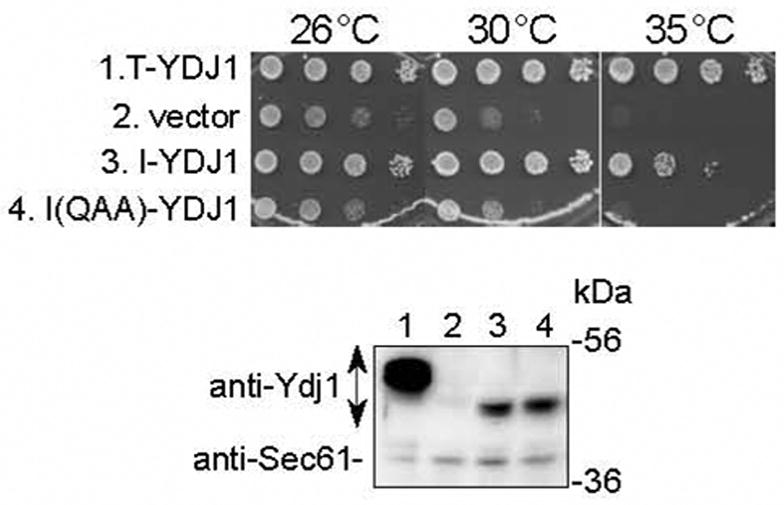
The HopI1 J domain can substitute functionally for the J domain of Ydj1 and rescues the slow growth phenotype of the ydj1 yeast mutant.
Ten-fold serial dilutions of ydj1 yeast containing the indicated constructs were grown for 4 days at 26, 30 and 35°C (upper panel). Ydj1 with its J domain replaced by the HopI1 J domain (I-YDJ1, JJ204) complemented the ydj1 null mutation. The HPD/QAA mutant of the HopI1 J domain (I(QAA)-YDJ1, JJ206) did not complement the yeast mutant phenotype. The SV40 T-antigen::Ydj1 chimera (T-YDJ1) and empty vector TEF414 were used as positive and negative controls, respectively. Ydj1 chimeras were expressed in yeast, as shown by SDS-PAGE and Western blot analysis with anti-Ydj1 antibody (lower panel): (1) T-YDJ1; (2) vector TEF414; (3) I-YDJ1, JJ204; (4) I(QAA)-YDJ1, JJ206. Detection of Sec61 (lower band) served as a loading control.
