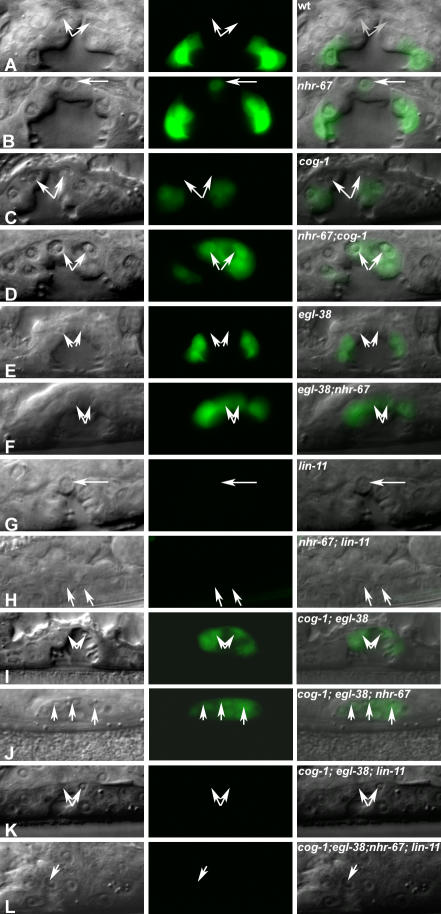
Figure 5. Regulation of egl-17 Expression in the 1° Vulval Cells.
(A–L) Nomarski (left), fluorescence (center), and overlaid (right). Display animals from Table 1. Arrows indicate the position of the visible vulF cells during the mid L4 stage. All animals displayed carry the ayIs4 transgene in their background. (A) In wild-type animals egl-17 expression is absent in the vulE and vulF cells.
(B) nhr-67 RNAi typically results in ectopic egl-17 expression in one out of four vulF cells. In contrast, egl-17 remains off in the vulE cells.
(C) In cog-1(sy275) mutants, egl-17 is misexpressed in vulE cells and is absent in vulF cells.
(D) cog-1(sy275); nhr-67 RNAi doubles show a markedly stronger derepression phenotype in both 1° vulE and vulF lineages.
(E) In egl-38(n578) mutants, egl-17 expression is invariably off in both vulE and vulF cells.
(F) egl-38(n578); nhr-67 RNAi doubles show robust expression of egl-17 in both vulE and vulF cells.
(G) In lin-11(n389) animals, egl-17 expression is absent.
(H) In lin-11(n389); nhr-67 RNAi doubles, the ectopic egl-17 expression in vulF is eliminated.
(I) cog-1(sy275); egl-38(n578) mutants misexpress egl-17 in vulE and vulF cells.
(J) The cog-1 (sy275); egl-38(n578); nhr-67 RNAi triple shows complete egl-17 derepression in all the vulE and vulF descendants.
(K) In cog-1(sy275); egl-38(n578); lin-11(n389) mutants, egl-17 is completely absent.
(L) In cog-1(sy275); egl-38(n578); lin-11(n389); nhr-67 RNAi quadruples, egl-17 expression in the vulva is abolished.