Abstract
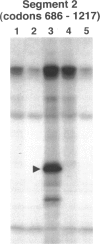
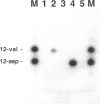
Juvenile polyps are regarded as hamartomatous polyps and occur in sporadic and familial syndromic settings. There is increased risk of gastrointestinal neoplasia in patients with juvenile polyposis syndrome, but the molecular mechanisms are not known. We therefore studied 78 colorectal juvenile polyposis from 12 patients with juvenile polyps syndrome and 34 sporadic juvenile polyps for epithelial dysplasia and genetic changes associated with colorectal neoplasia. Dysplasia occurred in 31% of syndromic juvenile polyps but not in sporadic juvenile polyps (P < 0.0001). Topographic control of proliferation and expression of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21(WAFI/CIP1) seen in native colorectal epithelium was lost in 79% of dysplastic juvenile polyps and in 8% of nondysplastic juvenile polyps (P < 0.000001). Somatic mutations in the adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) gene were demonstrated in 50% of dysplastic juvenile polyps (3 of 6) but not in any of 16 juvenile polyps without dysplasia (P = 0.01). Both sporadic and syndromic juvenile polyps had K-ras mutations (14%) and there was no relationship to dysplasia. p53 gene product overexpression identified by immunohistochemical staining occurred rarely in dysplastic juvenile polyps (2 of 24, 8%). Our results indicate that the multiple genetic alterations involved in usual colorectal neoplasia also play a role in neoplastic transformation of juvenile polyps, predominantly in juvenile polyposis syndrome.
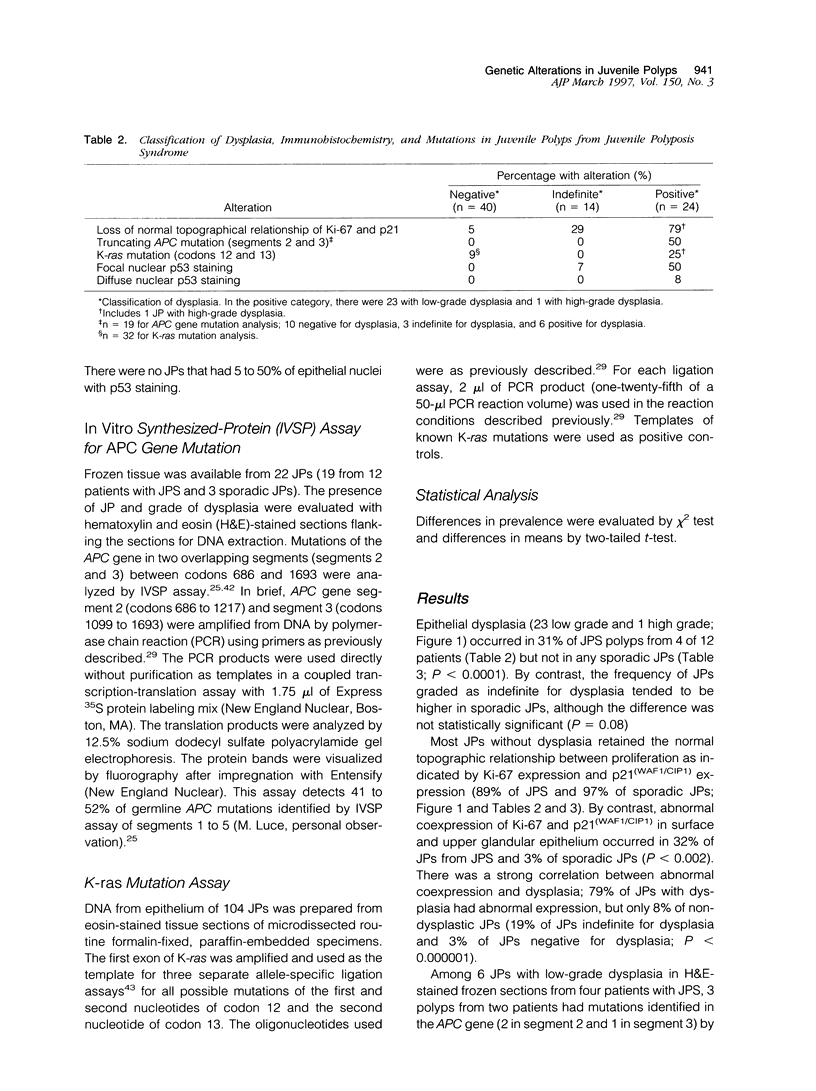
Full text
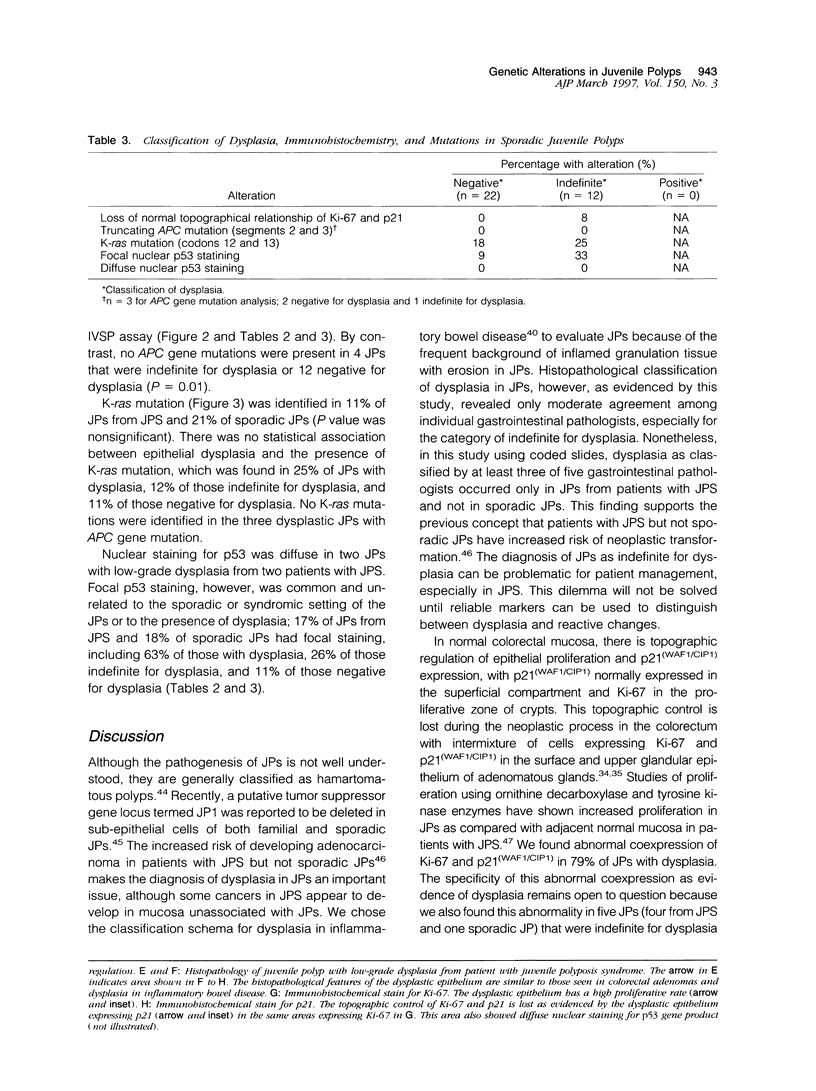
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- APPLEMAN R. M., JACKMAN R. J. Regional enteritis: proctoscopic clues in diagnosis. Dis Colon Rectum. 1962 Sep-Oct;5:361–363. doi: 10.1007/BF02616588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baas I. O., Mulder J. W., Offerhaus G. J., Vogelstein B., Hamilton S. R. An evaluation of six antibodies for immunohistochemistry of mutant p53 gene product in archival colorectal neoplasms. J Pathol. 1994 Jan;172(1):5–12. doi: 10.1002/path.1711720104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bankfalvi A., Navabi H., Bier B., Böcker W., Jasani B., Schmid K. W. Wet autoclave pretreatment for antigen retrieval in diagnostic immunohistochemistry. J Pathol. 1994 Nov;174(3):223–228. doi: 10.1002/path.1711740312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell S. M., Kelly S. A., Hoyle J. A., Lewis F. A., Taylor G. R., Thompson H., Dixon M. F., Quirke P. c-Ki-ras gene mutations in dysplasia and carcinomas complicating ulcerative colitis. Br J Cancer. 1991 Jul;64(1):174–178. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1991.264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentley E., Chandrasoma P., Radin R., Cohen H. Generalized juvenile polyposis with carcinoma. Am J Gastroenterol. 1989 Nov;84(11):1456–1459. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bos J. L., Fearon E. R., Hamilton S. R., Verlaan-de Vries M., van Boom J. H., van der Eb A. J., Vogelstein B. Prevalence of ras gene mutations in human colorectal cancers. 1987 May 28-Jun 3Nature. 327(6120):293–297. doi: 10.1038/327293a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burmer G. C., Levine D. S., Kulander B. G., Haggitt R. C., Rubin C. E., Rabinovitch P. S. c-Ki-ras mutations in chronic ulcerative colitis and sporadic colon carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 1990 Aug;99(2):416–420. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(90)91024-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burmer G. C., Rabinovitch P. S., Haggitt R. C., Crispin D. A., Brentnall T. A., Kolli V. R., Stevens A. C., Rubin C. E. Neoplastic progression in ulcerative colitis: histology, DNA content, and loss of a p53 allele. Gastroenterology. 1992 Nov;103(5):1602–1610. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(92)91184-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campo E., de la Calle-Martin O., Miquel R., Palacin A., Romero M., Fabregat V., Vives J., Cardesa A., Yague J. Loss of heterozygosity of p53 gene and p53 protein expression in human colorectal carcinomas. Cancer Res. 1991 Aug 15;51(16):4436–4442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaubert P., Benhattar J., Saraga E., Costa J. K-ras mutations and p53 alterations in neoplastic and nonneoplastic lesions associated with longstanding ulcerative colitis. Am J Pathol. 1994 Apr;144(4):767–775. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coburn M. C., Pricolo V. E., DeLuca F. G., Bland K. I. Malignant potential in intestinal juvenile polyposis syndromes. Ann Surg Oncol. 1995 Sep;2(5):386–391. doi: 10.1007/BF02306370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham J., Lust J. A., Schaid D. J., Bren G. D., Carpenter H. A., Rizza E., Kovach J. S., Thibodeau S. N. Expression of p53 and 17p allelic loss in colorectal carcinoma. Cancer Res. 1992 Apr 1;52(7):1974–1980. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dajani Y. F., Kamal M. F. Colorectal juvenile polyps: an epidemiological and histopathological study of 144 cases in Jordanians. Histopathology. 1984 Sep;8(5):765–779. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1984.tb02393.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delattre O., Olschwang S., Law D. J., Melot T., Remvikos Y., Salmon R. J., Sastre X., Validire P., Feinberg A. P., Thomas G. Multiple genetic alterations in distal and proximal colorectal cancer. Lancet. 1989 Aug 12;2(8659):353–356. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)90537-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elitsur Y., Koh S. J., Moshier J. A., Dosescu J., Tureaud J., Majumdar A. P. Ornithine decarboxylase and tyrosine kinase activity in juvenile polyps of childhood. Pediatr Res. 1995 Oct;38(4):574–578. doi: 10.1203/00006450-199510000-00017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fearon E. R., Vogelstein B. A genetic model for colorectal tumorigenesis. Cell. 1990 Jun 1;61(5):759–767. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90186-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores-Rozas H., Kelman Z., Dean F. B., Pan Z. Q., Harper J. W., Elledge S. J., O'Donnell M., Hurwitz J. Cdk-interacting protein 1 directly binds with proliferating cell nuclear antigen and inhibits DNA replication catalyzed by the DNA polymerase delta holoenzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Aug 30;91(18):8655–8659. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.18.8655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forrester K., Almoguera C., Han K., Grizzle W. E., Perucho M. Detection of high incidence of K-ras oncogenes during human colon tumorigenesis. 1987 May 28-Jun 3Nature. 327(6120):298–303. doi: 10.1038/327298a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman C. J., Fechner R. E. A solitary juvenile polyp with hyperplastic and adenomatous glands. Dig Dis Sci. 1982 Oct;27(10):946–948. doi: 10.1007/BF01316581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giardiello F. M., Hamilton S. R., Kern S. E., Offerhaus G. J., Green P. A., Celano P., Krush A. J., Booker S. V. Colorectal neoplasia in juvenile polyposis or juvenile polyps. Arch Dis Child. 1991 Aug;66(8):971–975. doi: 10.1136/adc.66.8.971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman Z. D., Yardley J. H., Milligan F. D. Pathogenesis of colonic polyps in multiple juvenile polyposis: report of a case associated with gastric polyps and carcinoma of the rectum. Cancer. 1979 May;43(5):1906–1913. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197905)43:5<1906::aid-cncr2820430548>3.0.co;2-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwald B. D., Harpaz N., Yin J., Huang Y., Tong Y., Brown V. L., McDaniel T., Newkirk C., Resau J. H., Meltzer S. J. Loss of heterozygosity affecting the p53, Rb, and mcc/apc tumor suppressor gene loci in dysplastic and cancerous ulcerative colitis. Cancer Res. 1992 Feb 1;52(3):741–745. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grigioni W. F., Alampi G., Martinelli G., Piccaluga A. Atypical juvenile polyposis. Histopathology. 1981 Jul;5(4):361–376. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1981.tb01798.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grotsky H. W., Rickert R. R., Smith W. D., Newsome J. F. Familial juvenile polyposis coli. A clinical and pathologic study of a large kindred. Gastroenterology. 1982 Mar;82(3):494–501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harpaz N., Peck A. L., Yin J., Fiel I., Hontanosas M., Tong T. R., Laurin J. N., Abraham J. M., Greenwald B. D., Meltzer S. J. p53 protein expression in ulcerative colitis-associated colorectal dysplasia and carcinoma. Hum Pathol. 1994 Oct;25(10):1069–1074. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(94)90067-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heiss K. F., Schaffner D., Ricketts R. R., Winn K. Malignant risk in juvenile polyposis coli: increasing documentation in the pediatric age group. J Pediatr Surg. 1993 Sep;28(9):1188–1193. doi: 10.1016/0022-3468(93)90162-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ilyas M., Tomlinson I. P. Genetic pathways in colorectal cancer. Histopathology. 1996 May;28(5):389–399. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2559.1996.339381.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
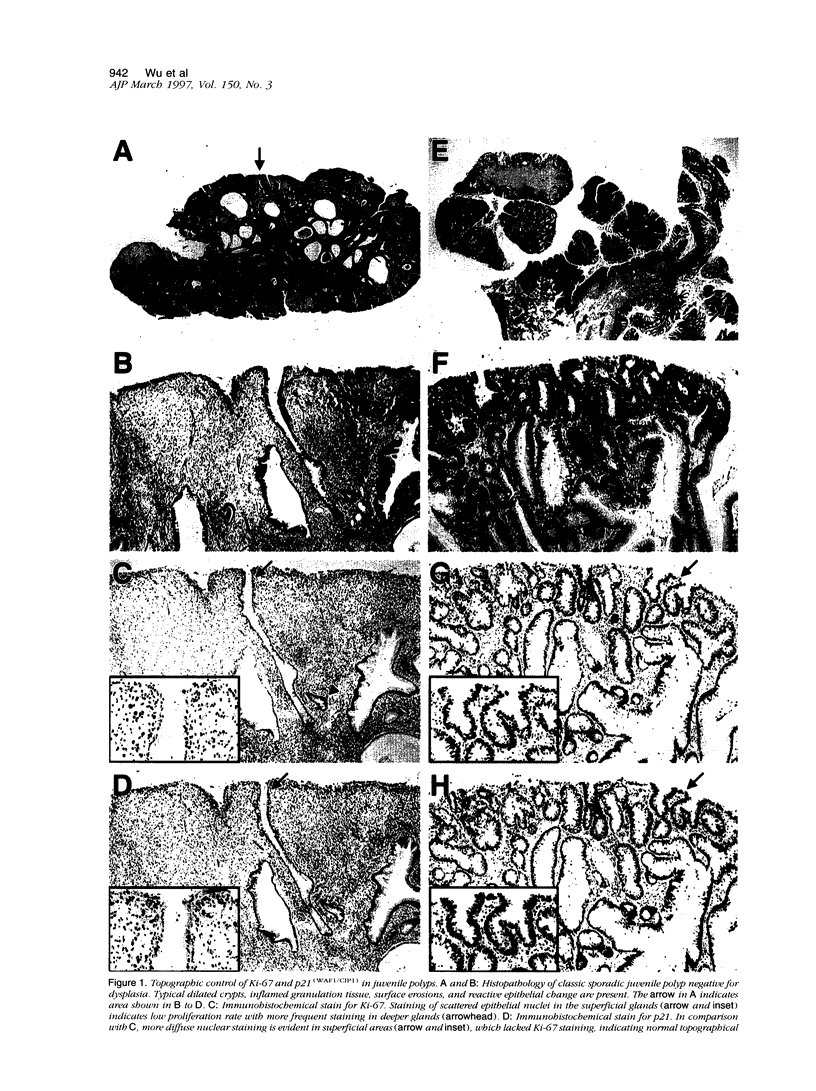
- Jass J. R., Williams C. B., Bussey H. J., Morson B. C. Juvenile polyposis--a precancerous condition. Histopathology. 1988 Dec;13(6):619–630. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1988.tb02093.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jen J., Powell S. M., Papadopoulos N., Smith K. J., Hamilton S. R., Vogelstein B., Kinzler K. W. Molecular determinants of dysplasia in colorectal lesions. Cancer Res. 1994 Nov 1;54(21):5523–5526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
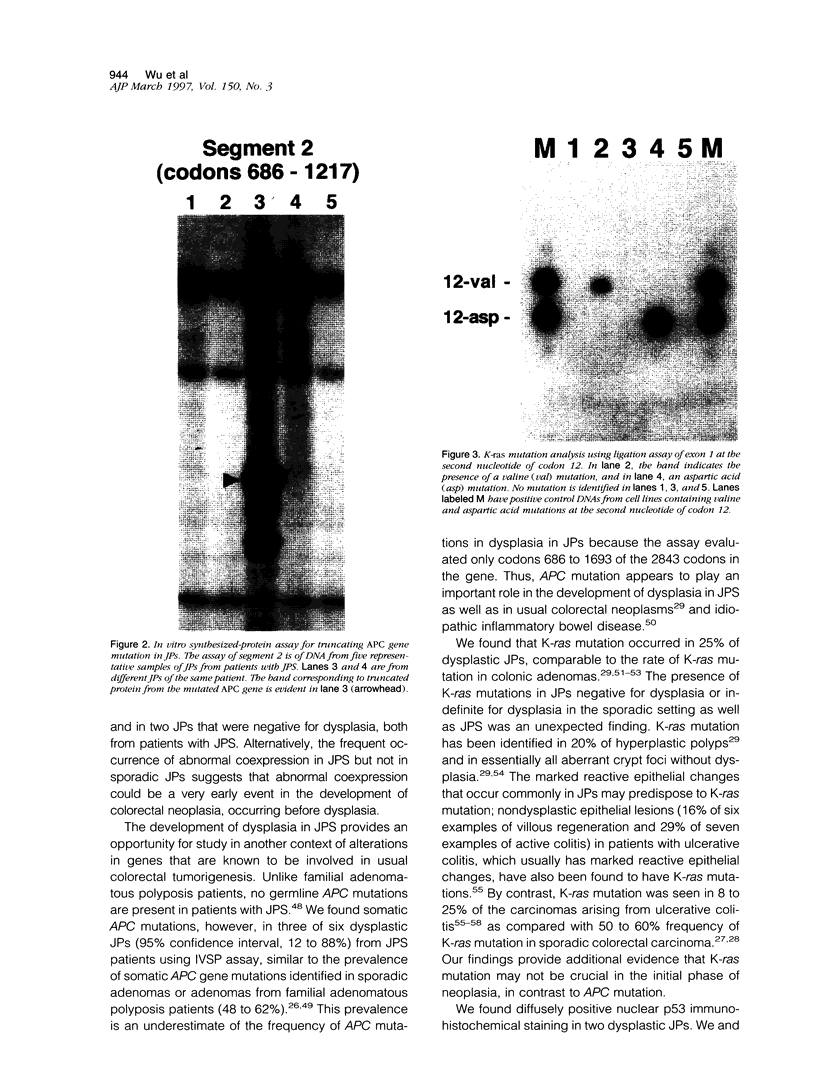
- Jones M. A., Hebert J. C., Trainer T. D. Juvenile polyp with intramucosal carcinoma. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1987 Feb;111(2):200–201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Järvinen H., Franssila K. O. Familial juvenile polyposis coli; increased risk of colorectal cancer. Gut. 1984 Jul;25(7):792–800. doi: 10.1136/gut.25.7.792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern S. E., Redston M., Seymour A. B., Caldas C., Powell S. M., Kornacki S., Kinzler K. W. Molecular genetic profiles of colitis-associated neoplasms. Gastroenterology. 1994 Aug;107(2):420–428. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(94)90167-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landegren U., Kaiser R., Sanders J., Hood L. A ligase-mediated gene detection technique. Science. 1988 Aug 26;241(4869):1077–1080. doi: 10.1126/science.3413476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leggett B. A., Thomas L. R., Knight N., Healey S., Chenevix-Trench G., Searle J. Exclusion of APC and MCC as the gene defect in one family with familial juvenile polyposis. Gastroenterology. 1993 Nov;105(5):1313–1316. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(93)90134-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li R., Waga S., Hannon G. J., Beach D., Stillman B. Differential effects by the p21 CDK inhibitor on PCNA-dependent DNA replication and repair. Nature. 1994 Oct 6;371(6497):534–537. doi: 10.1038/371534a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipper S., Kahn L. B., Sandler R. S., Varma V. Multiple juvenile polyposis. A study of the pathogenesis of juvenile polyps and their relationship to colonic adenomas. Hum Pathol. 1981 Sep;12(9):804–813. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(81)80083-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCCOLL I., BUSXEY H. J., VEALE A. M., MORSON B. C. JUVENILE POLYPOSIS COLI. Proc R Soc Med. 1964 Oct;57:896–897. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLellan E. A., Owen R. A., Stepniewska K. A., Sheffield J. P., Lemoine N. R. High frequency of K-ras mutations in sporadic colorectal adenomas. Gut. 1993 Mar;34(3):392–396. doi: 10.1136/gut.34.3.392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meltzer S. J., Mane S. M., Wood P. K., Resau J. H., Newkirk C., Terzakis J. A., Korelitz B. I., Weinstein W. M., Needleman S. W. Activation of c-Ki-ras in human gastrointestinal dysplasias determined by direct sequencing of polymerase chain reaction products. Cancer Res. 1990 Jun 15;50(12):3627–3630. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills S. E., Fechner R. E. Unusual adenomatous polyps in juvenile polyposis coli. Am J Surg Pathol. 1982 Mar;6(2):177–183. doi: 10.1097/00000478-198203000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyaki M., Konishi M., Kikuchi-Yanoshita R., Enomoto M., Igari T., Tanaka K., Muraoka M., Takahashi H., Amada Y., Fukayama M. Characteristics of somatic mutation of the adenomatous polyposis coli gene in colorectal tumors. Cancer Res. 1994 Jun 1;54(11):3011–3020. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nugent K. P., Talbot I. C., Hodgson S. V., Phillips R. K. Solitary juvenile polyps: not a marker for subsequent malignancy. Gastroenterology. 1993 Sep;105(3):698–700. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(93)90885-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Riordain D. S., O'Dwyer P. J., Cullen A. F., McDermott E. W., Murphy J. J. Familial juvenile polyposis coli and colorectal cancer. Cancer. 1991 Aug 15;68(4):889–892. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19910815)68:4<889::aid-cncr2820680435>3.0.co;2-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polyak K., Hamilton S. R., Vogelstein B., Kinzler K. W. Early alteration of cell-cycle-regulated gene expression in colorectal neoplasia. Am J Pathol. 1996 Aug;149(2):381–387. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell S. M., Petersen G. M., Krush A. J., Booker S., Jen J., Giardiello F. M., Hamilton S. R., Vogelstein B., Kinzler K. W. Molecular diagnosis of familial adenomatous polyposis. N Engl J Med. 1993 Dec 30;329(27):1982–1987. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199312303292702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell S. M., Zilz N., Beazer-Barclay Y., Bryan T. M., Hamilton S. R., Thibodeau S. N., Vogelstein B., Kinzler K. W. APC mutations occur early during colorectal tumorigenesis. Nature. 1992 Sep 17;359(6392):235–237. doi: 10.1038/359235a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed K., Vose P. C. Diffuse juvenile polyposis of the colon: a premalignant condition? Dis Colon Rectum. 1981 Apr;24(3):205–210. doi: 10.1007/BF02962337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
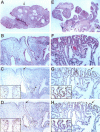
- Riddell R. H., Goldman H., Ransohoff D. F., Appelman H. D., Fenoglio C. M., Haggitt R. C., Ahren C., Correa P., Hamilton S. R., Morson B. C. Dysplasia in inflammatory bowel disease: standardized classification with provisional clinical applications. Hum Pathol. 1983 Nov;14(11):931–968. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(83)80175-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues N. R., Rowan A., Smith M. E., Kerr I. B., Bodmer W. F., Gannon J. V., Lane D. P. p53 mutations in colorectal cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7555–7559. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozen P., Baratz M. Familial juvenile colonic polyposis with associated colon cancer. Cancer. 1982 Apr 1;49(7):1500–1503. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19820401)49:7<1500::aid-cncr2820490732>3.0.co;2-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandler R. S., Lipper S. Multiple adenomas in juvenile polyposis. Am J Gastroenterol. 1981 May;75(5):361–366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sassatelli R., Bertoni G., Serra L., Bedogni G., Ponz de Leon M. Generalized juvenile polyposis with mixed pattern and gastric cancer. Gastroenterology. 1993 Mar;104(3):910–915. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(93)91031-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott N., Bell S. M., Sagar P., Blair G. E., Dixon M. F., Quirke P. p53 expression and K-ras mutation in colorectal adenomas. Gut. 1993 May;34(5):621–624. doi: 10.1136/gut.34.5.621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. J., Stern H. S., Penner M., Hay K., Mitri A., Bapat B. V., Gallinger S. Somatic APC and K-ras codon 12 mutations in aberrant crypt foci from human colons. Cancer Res. 1994 Nov 1;54(21):5527–5530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subramony C., Scott-Conner C. E., Skelton D., Hall T. J. Familial juvenile polyposis. Study of a kindred: evolution of polyps and relationship to gastrointestinal carcinoma. Am J Clin Pathol. 1994 Jul;102(1):91–97. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/102.1.91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogelstein B., Fearon E. R., Hamilton S. R., Kern S. E., Preisinger A. C., Leppert M., Nakamura Y., White R., Smits A. M., Bos J. L. Genetic alterations during colorectal-tumor development. N Engl J Med. 1988 Sep 1;319(9):525–532. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198809013190901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamagata S., Muto T., Uchida Y., Masaki T., Sawada T., Tsuno N., Hirooka T. Lower incidence of K-ras codon 12 mutation in flat colorectal adenomas than in polypoid adenomas. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1994 Feb;85(2):147–151. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.1994.tb02075.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin J., Harpaz N., Tong Y., Huang Y., Laurin J., Greenwald B. D., Hontanosas M., Newkirk C., Meltzer S. J. p53 point mutations in dysplastic and cancerous ulcerative colitis lesions. Gastroenterology. 1993 Jun;104(6):1633–1639. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(93)90639-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Deiry W. S., Tokino T., Velculescu V. E., Levy D. B., Parsons R., Trent J. M., Lin D., Mercer W. E., Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B. WAF1, a potential mediator of p53 tumor suppression. Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):817–825. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90500-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Deiry W. S., Tokino T., Waldman T., Oliner J. D., Velculescu V. E., Burrell M., Hill D. E., Healy E., Rees J. L., Hamilton S. R. Topological control of p21WAF1/CIP1 expression in normal and neoplastic tissues. Cancer Res. 1995 Jul 1;55(13):2910–2919. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]