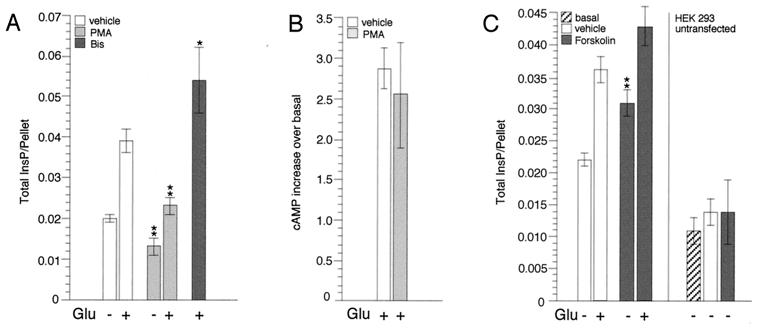
Figure 1.
PKC and PKA regulate mGluR1α signaling. (A) Effect of PMA and bisindolylmaleimide I (Bis) on mGluR1α-dependent InsP accumulation. For each experiment, HEK 293 cells were transfected with 10 μg of mGluR1α and 10 μg of carrier DNA and seeded into six wells of a 24-well cluster. Stimulation was carried out in Hanks' saline solution (containing divalents and glucose) after clearing glutamate from the media with glutamic-pyruvic transaminase/pyruvate (9). The cells were treated with either Me2SO (vehicle) or test reagents and then stimulated with Glu. Results represent means ± SEM of duplicate or triplicate determinations obtained from at least two independent experiments (*, P ≤ 0.05; **, P ≤ 0.01; two-tailed t test). (B) Effect of PMA on mGluR1α-dependent cAMP accumulation. HEK 293 cells were transfected with 5 μg of mGluR1α along with 5 μg of Gs and 10 μg of carrier DNA and seeded into four wells of a 24-well cluster. The cells were preincubated with either Me2SO or PMA for 30 min and then stimulated with Glu for 20 min in the continued presence of the test reagents. Results represent means ± SEM of duplicate determinations obtained from three independent experiments. (C) Effect of forskolin on mGluR1α-dependent InsP accumulation. Cell transfection and treatment were conducted as described in A; in control experiments, 4 × 105 untransfected cells were plated for each well. Results represent means ± SEM of triplicate determinations obtained from three independent experiments; for untransfected cells, results shown are means ± SD of triplicate determinations, representative of two independent experiments.