Abstract
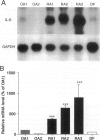
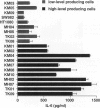
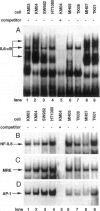
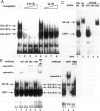
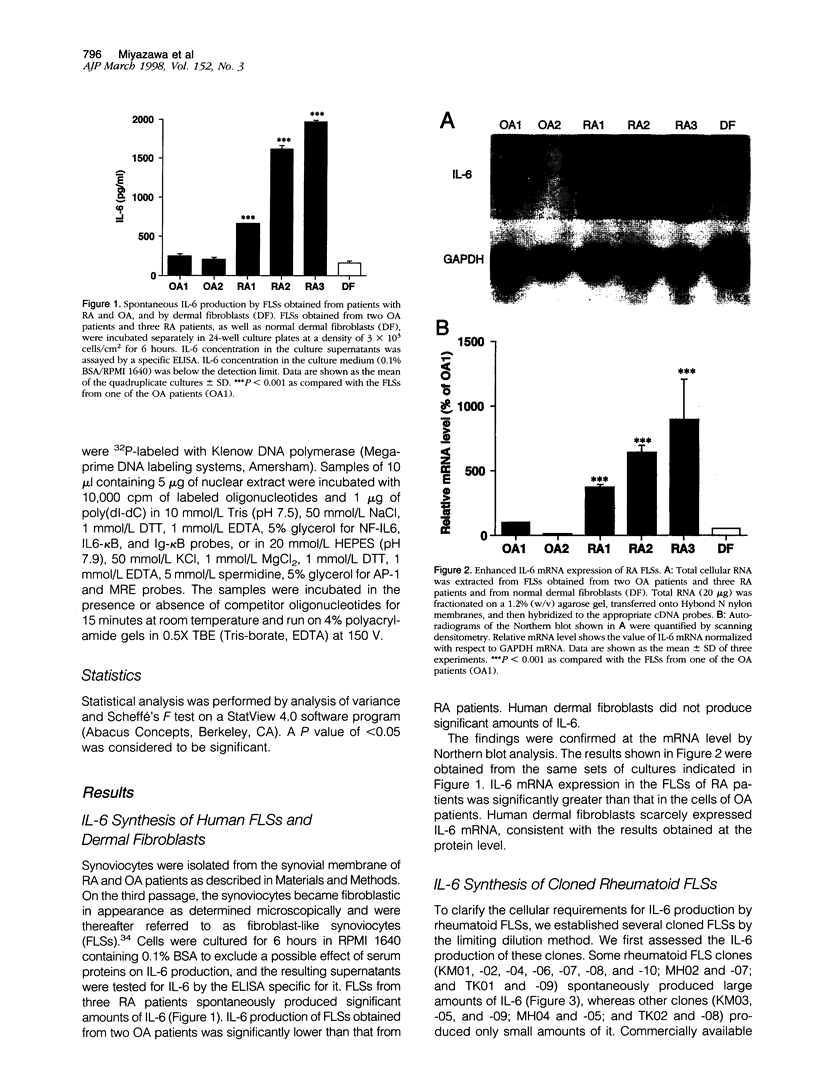
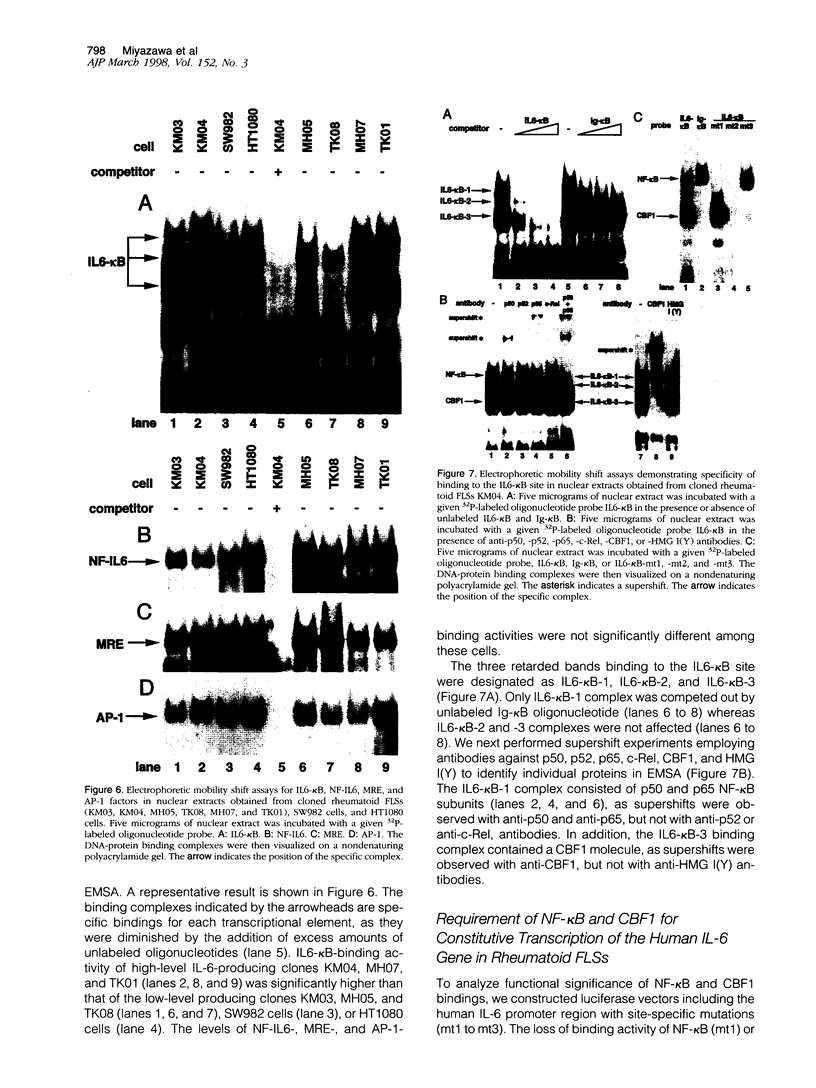
The involvement of IL-6 in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) has been recently demonstrated. In the present study, we investigated the cellular and molecular mechanisms involved in the spontaneous IL-6 production by the fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLSs) obtained from patients with RA. Cloned FLSs were established from the bulk cultures of FLSs by the limiting dilution method. Some FLS clones spontaneously produced large amounts of IL-6, whereas others produced low amounts of it. Neither anti-human TNF-alpha nor IL-1 antibody affected spontaneous IL-6 production of these FLS clones, suggesting that IL-6 production of the FLSs was endogenously up-regulated. A luciferase reporter plasmid containing the human IL-6 promoter region was significantly transcribed when transfected into the IL-6 high-producing clones, indicating that the rheumatoid FLSs retained constitutive transcriptional activity of the IL-6 gene. Electrophoretic mobility shift assays revealed that the binding activity of p50 and p65 NF-kappaB subunits and CBF1 was significantly enhanced in the IL-6 high-producing clones compared with that of IL-6 low-producing clones and cultured sarcoma cells, suggesting that spontaneous activation of NF-kappaB and CBF1 may lead to the constitutive transcription of the IL-6 gene by rheumatoid FLSs.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akira S., Taga T., Kishimoto T. Interleukin-6 in biology and medicine. Adv Immunol. 1993;54:1–78. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60532-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altman R., Asch E., Bloch D., Bole G., Borenstein D., Brandt K., Christy W., Cooke T. D., Greenwald R., Hochberg M. Development of criteria for the classification and reporting of osteoarthritis. Classification of osteoarthritis of the knee. Diagnostic and Therapeutic Criteria Committee of the American Rheumatism Association. Arthritis Rheum. 1986 Aug;29(8):1039–1049. doi: 10.1002/art.1780290816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arend W. P., Dayer J. M. Inhibition of the production and effects of interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor alpha in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1995 Feb;38(2):151–160. doi: 10.1002/art.1780380202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnett F. C., Edworthy S. M., Bloch D. A., McShane D. J., Fries J. F., Cooper N. S., Healey L. A., Kaplan S. R., Liang M. H., Luthra H. S. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Mar;31(3):315–324. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballard D. W., Dixon E. P., Peffer N. J., Bogerd H., Doerre S., Stein B., Greene W. C. The 65-kDa subunit of human NF-kappa B functions as a potent transcriptional activator and a target for v-Rel-mediated repression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 1;89(5):1875–1879. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.5.1875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan F. M., Zachariae C. O., Chantry D., Larsen C. G., Turner M., Maini R. N., Matsushima K., Feldmann M. Detection of interleukin 8 biological activity in synovial fluids from patients with rheumatoid arthritis and production of interleukin 8 mRNA by isolated synovial cells. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Sep;20(9):2141–2144. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brozik M., Rosztóczy I., Merétey K., Bálint G., Gaál M., Balogh Z., Bart M., Mituszova M., Velics V., Falus A. Interleukin 6 levels in synovial fluids of patients with different arthritides: correlation with local IgM rheumatoid factor and systemic acute phase protein production. J Rheumatol. 1992 Jan;19(1):63–68. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bucala R., Ritchlin C., Winchester R., Cerami A. Constitutive production of inflammatory and mitogenic cytokines by rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts. J Exp Med. 1991 Mar 1;173(3):569–574. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.3.569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchan G., Barrett K., Fujita T., Taniguchi T., Maini R., Feldmann M. Detection of activated T cell products in the rheumatoid joint using cDNA probes to Interleukin-2 (IL-2) IL-2 receptor and IFN-gamma. Clin Exp Immunol. 1988 Feb;71(2):295–301. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchan G., Barrett K., Turner M., Chantry D., Maini R. N., Feldmann M. Interleukin-1 and tumour necrosis factor mRNA expression in rheumatoid arthritis: prolonged production of IL-1 alpha. Clin Exp Immunol. 1988 Sep;73(3):449–455. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Content J., De Wit L., Poupart P., Opdenakker G., Van Damme J., Billiau A. Induction of a 26-kDa-protein mRNA in human cells treated with an interleukin-1-related, leukocyte-derived factor. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Oct 15;152(2):253–257. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09191.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayer J. M., de Rochemonteix B., Burrus B., Demczuk S., Dinarello C. A. Human recombinant interleukin 1 stimulates collagenase and prostaglandin E2 production by human synovial cells. J Clin Invest. 1986 Feb;77(2):645–648. doi: 10.1172/JCI112350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dendorfer U., Oettgen P., Libermann T. A. Multiple regulatory elements in the interleukin-6 gene mediate induction by prostaglandins, cyclic AMP, and lipopolysaccharide. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jul;14(7):4443–4454. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.7.4443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldmann M., Brennan F. M., Maini R. N. Role of cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis. Annu Rev Immunol. 1996;14:397–440. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.14.1.397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firestein G. S., Alvaro-Gracia J. M., Maki R., Alvaro-Garcia J. M. Quantitative analysis of cytokine gene expression in rheumatoid arthritis. J Immunol. 1990 May 1;144(9):3347–3353. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firestein G. S. Invasive fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis. Passive responders or transformed aggressors? Arthritis Rheum. 1996 Nov;39(11):1781–1790. doi: 10.1002/art.1780391103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauldie J., Northemann W., Fey G. H. IL-6 functions as an exocrine hormone in inflammation. Hepatocytes undergoing acute phase responses require exogenous IL-6. J Immunol. 1990 May 15;144(10):3804–3808. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauldie J., Richards C., Harnish D., Lansdorp P., Baumann H. Interferon beta 2/B-cell stimulatory factor type 2 shares identity with monocyte-derived hepatocyte-stimulating factor and regulates the major acute phase protein response in liver cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7251–7255. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goto M., Sasano M., Yamanaka H., Miyasaka N., Kamatani N., Inoue K., Nishioka K., Miyamoto T. Spontaneous production of an interleukin 1-like factor by cloned rheumatoid synovial cells in long-term culture. J Clin Invest. 1987 Sep;80(3):786–796. doi: 10.1172/JCI113135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerne P. A., Zuraw B. L., Vaughan J. H., Carson D. A., Lotz M. Synovium as a source of interleukin 6 in vitro. Contribution to local and systemic manifestations of arthritis. J Clin Invest. 1989 Feb;83(2):585–592. doi: 10.1172/JCI113921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handel M. L., McMorrow L. B., Gravallese E. M. Nuclear factor-kappa B in rheumatoid synovium. Localization of p50 and p65. Arthritis Rheum. 1995 Dec;38(12):1762–1770. doi: 10.1002/art.1780381209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. D., Jr Rheumatoid arthritis. Pathophysiology and implications for therapy. N Engl J Med. 1990 May 3;322(18):1277–1289. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199005033221805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henkel T., Ling P. D., Hayward S. D., Peterson M. G. Mediation of Epstein-Barr virus EBNA2 transactivation by recombination signal-binding protein J kappa. Science. 1994 Jul 1;265(5168):92–95. doi: 10.1126/science.8016657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano T., Matsuda T., Turner M., Miyasaka N., Buchan G., Tang B., Sato K., Shimizu M., Maini R., Feldmann M. Excessive production of interleukin 6/B cell stimulatory factor-2 in rheumatoid arthritis. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Nov;18(11):1797–1801. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830181122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano T., Taga T., Nakano N., Yasukawa K., Kashiwamura S., Shimizu K., Nakajima K., Pyun K. H., Kishimoto T. Purification to homogeneity and characterization of human B-cell differentiation factor (BCDF or BSFp-2). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(16):5490–5494. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.16.5490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houssiau F. A., Devogelaer J. P., Van Damme J., de Deuxchaisnes C. N., Van Snick J. Interleukin-6 in synovial fluid and serum of patients with rheumatoid arthritis and other inflammatory arthritides. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Jun;31(6):784–788. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isshiki H., Akira S., Tanabe O., Nakajima T., Shimamoto T., Hirano T., Kishimoto T. Constitutive and interleukin-1 (IL-1)-inducible factors interact with the IL-1-responsive element in the IL-6 gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2757–2764. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kannabiran C., Zeng X., Vales L. D. The mammalian transcriptional repressor RBP (CBF1) regulates interleukin-6 gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1997 Jan;17(1):1–9. doi: 10.1128/mcb.17.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto T., Akira S., Narazaki M., Taga T. Interleukin-6 family of cytokines and gp130. Blood. 1995 Aug 15;86(4):1243–1254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lafyatis R., Remmers E. F., Roberts A. B., Yocum D. E., Sporn M. B., Wilder R. L. Anchorage-independent growth of synoviocytes from arthritic and normal joints. Stimulation by exogenous platelet-derived growth factor and inhibition by transforming growth factor-beta and retinoids. J Clin Invest. 1989 Apr;83(4):1267–1276. doi: 10.1172/JCI114011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leary A. G., Ikebuchi K., Hirai Y., Wong G. G., Yang Y. C., Clark S. C., Ogawa M. Synergism between interleukin-6 and interleukin-3 in supporting proliferation of human hematopoietic stem cells: comparison with interleukin-1 alpha. Blood. 1988 Jun;71(6):1759–1763. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling P. D., Rawlins D. R., Hayward S. D. The Epstein-Barr virus immortalizing protein EBNA-2 is targeted to DNA by a cellular enhancer-binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Oct 15;90(20):9237–9241. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.20.9237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotz M., Jirik F., Kabouridis P., Tsoukas C., Hirano T., Kishimoto T., Carson D. A. B cell stimulating factor 2/interleukin 6 is a costimulant for human thymocytes and T lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1988 Mar 1;167(3):1253–1258. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.3.1253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu F. M., Lux S. E. Constitutively active human Notch1 binds to the transcription factor CBF1 and stimulates transcription through a promoter containing a CBF1-responsive element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 May 28;93(11):5663–5667. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.11.5663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maini R. N., Elliott M. J., Brennan F. M., Williams R. O., Chu C. Q., Paleolog E., Charles P. J., Taylor P. C., Feldmann M. Monoclonal anti-TNF alpha antibody as a probe of pathogenesis and therapy of rheumatoid disease. Immunol Rev. 1995 Apr;144:195–223. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1995.tb00070.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marok R., Winyard P. G., Coumbe A., Kus M. L., Gaffney K., Blades S., Mapp P. I., Morris C. J., Blake D. R., Kaltschmidt C. Activation of the transcription factor nuclear factor-kappaB in human inflamed synovial tissue. Arthritis Rheum. 1996 Apr;39(4):583–591. doi: 10.1002/art.1780390407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsunami N., Hamaguchi Y., Yamamoto Y., Kuze K., Kangawa K., Matsuo H., Kawaichi M., Honjo T. A protein binding to the J kappa recombination sequence of immunoglobulin genes contains a sequence related to the integrase motif. Nature. 1989 Dec 21;342(6252):934–937. doi: 10.1038/342934a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medvedev A. E., Espevik T., Ranges G., Sundan A. Distinct roles of the two tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptors in modulating TNF and lymphotoxin alpha effects. J Biol Chem. 1996 Apr 19;271(16):9778–9784. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.16.9778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mihara M., Moriya Y., Kishimoto T., Ohsugi Y. Interleukin-6 (IL-6) induces the proliferation of synovial fibroblastic cells in the presence of soluble IL-6 receptor. Br J Rheumatol. 1995 Apr;34(4):321–325. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/34.4.321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori N., Shirakawa F., Shimizu H., Murakami S., Oda S., Yamamoto K., Eto S. Transcriptional regulation of the human interleukin-6 gene promoter in human T-cell leukemia virus type I-infected T-cell lines: evidence for the involvement of NF-kappa B. Blood. 1994 Nov 1;84(9):2904–2911. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mourad W., Mehindate K., Schall T. J., McColl S. R. Engagement of major histocompatibility complex class II molecules by superantigen induces inflammatory cytokine gene expression in human rheumatoid fibroblast-like synoviocytes. J Exp Med. 1992 Feb 1;175(2):613–616. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.2.613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murayama T., Tsuchiya N., Jisaki F., Ozaki M., Sakamuro D., Hirai K., Shimizu S., Ito K., Matsushima K., Furukawa T. Elevated cytokine levels in synovial fluid of rheumatoid arthritis correlates with the presence of cytomegalovirus genome. Autoimmunity. 1994;17(4):333–337. doi: 10.3109/08916939409010674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panayi G. S., Lanchbury J. S., Kingsley G. H. The importance of the T cell in initiating and maintaining the chronic synovitis of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1992 Jul;35(7):729–735. doi: 10.1002/art.1780350702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qu Z., Garcia C. H., O'Rourke L. M., Planck S. R., Kohli M., Rosenbaum J. T. Local proliferation of fibroblast-like synoviocytes contributes to synovial hyperplasia. Results of proliferating cell nuclear antigen/cyclin, c-myc, and nucleolar organizer region staining. Arthritis Rheum. 1994 Feb;37(2):212–220. doi: 10.1002/art.1780370210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray A., Prefontaine K. E. Physical association and functional antagonism between the p65 subunit of transcription factor NF-kappa B and the glucocorticoid receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jan 18;91(2):752–756. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.2.752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray A., Sassone-Corsi P., Sehgal P. B. A multiple cytokine- and second messenger-responsive element in the enhancer of the human interleukin-6 gene: similarities with c-fos gene regulation. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;9(12):5537–5547. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.12.5537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray A., Zhang D. H., Siegel M. D., Ray P. Regulation of interleukin-6 gene expression by steroids. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1995 Jul 21;762:79–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1995.tb32316.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruben S. M., Narayanan R., Klement J. F., Chen C. H., Rosen C. A. Functional characterization of the NF-kappa B p65 transcriptional activator and an alternatively spliced derivative. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;12(2):444–454. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.2.444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schall T. J., Bacon K., Toy K. J., Goeddel D. V. Selective attraction of monocytes and T lymphocytes of the memory phenotype by cytokine RANTES. Nature. 1990 Oct 18;347(6294):669–671. doi: 10.1038/347669a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz M. L., Baeuerle P. A. The p65 subunit is responsible for the strong transcription activating potential of NF-kappa B. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(12):3805–3817. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04950.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber E., Matthias P., Müller M. M., Schaffner W. Rapid detection of octamer binding proteins with 'mini-extracts', prepared from a small number of cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Aug 11;17(15):6419–6419. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.15.6419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sengupta T. K., Chen A., Zhong Z., Darnell J. E., Jr, Ivashkiv L. B. Activation of monocyte effector genes and STAT family transcription factors by inflammatory synovial fluid is independent of interferon gamma. J Exp Med. 1995 Mar 1;181(3):1015–1025. doi: 10.1084/jem.181.3.1015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu H., Mitomo K., Watanabe T., Okamoto S., Yamamoto K. Involvement of a NF-kappa B-like transcription factor in the activation of the interleukin-6 gene by inflammatory lymphokines. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;10(2):561–568. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.2.561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland G. R., Baker E., Callen D. F., Hyland V. J., Wong G., Clark S., Jones S. S., Eglinton L. K., Shannon M. F., Lopez A. F. Interleukin 4 is at 5q31 and interleukin 6 is at 7p15. Hum Genet. 1988 Aug;79(4):335–337. doi: 10.1007/BF00282171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanabe O., Akira S., Kamiya T., Wong G. G., Hirano T., Kishimoto T. Genomic structure of the murine IL-6 gene. High degree conservation of potential regulatory sequences between mouse and human. J Immunol. 1988 Dec 1;141(11):3875–3881. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tso J. Y., Sun X. H., Kao T. H., Reece K. S., Wu R. Isolation and characterization of rat and human glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase cDNAs: genomic complexity and molecular evolution of the gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Apr 11;13(7):2485–2502. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.7.2485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Damme J., Cayphas S., Opdenakker G., Billiau A., Van Snick J. Interleukin 1 and poly(rI).poly(rC) induce production of a hybridoma growth factor by human fibroblasts. Eur J Immunol. 1987 Jan;17(1):1–7. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830170102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walther Z., May L. T., Sehgal P. B. Transcriptional regulation of the interferon-beta 2/B cell differentiation factor BSF-2/hepatocyte-stimulating factor gene in human fibroblasts by other cytokines. J Immunol. 1988 Feb 1;140(3):974–977. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wendling D., Racadot E., Wijdenes J. Treatment of severe rheumatoid arthritis by anti-interleukin 6 monoclonal antibody. J Rheumatol. 1993 Feb;20(2):259–262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasukawa K., Hirano T., Watanabe Y., Muratani K., Matsuda T., Nakai S., Kishimoto T. Structure and expression of human B cell stimulatory factor-2 (BSF-2/IL-6) gene. EMBO J. 1987 Oct;6(10):2939–2945. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02598.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y. H., Lin J. X., Vilcek J. Interleukin-6 induction by tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-1 in human fibroblasts involves activation of a nuclear factor binding to a kappa B-like sequence. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;10(7):3818–3823. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.7.3818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Leeuwen M. A., Westra J., Limburg P. C., van Riel P. L., van Rijswijk M. H. Interleukin-6 in relation to other proinflammatory cytokines, chemotactic activity and neutrophil activation in rheumatoid synovial fluid. Ann Rheum Dis. 1995 Jan;54(1):33–38. doi: 10.1136/ard.54.1.33. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]