Figure 6.
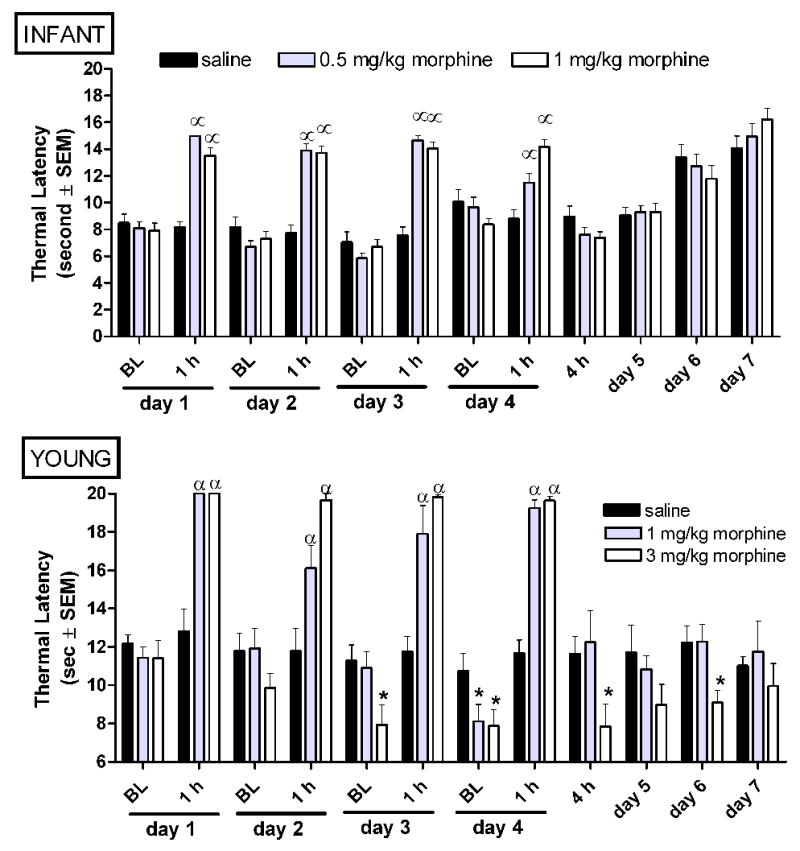
Intermittent morphine age-dependently alters thermal nociception in infant and young rats. Morphine was administered bid from experimental day 1–3, and once on experimental day 4. Baseline thermal latencies were collected in the morning immediately prior to the first dose of morphine, and at 1 and 4 hours post-morphine as indicated. Tolerance to the analgesic effect of morphine does not develop at either age. A progressive decrease in baseline thermal latencies across subsequent days of morphine exposure and withdrawal-associated thermal hypersensitivity are only observed in young rats. Data is average ± SEM (n=10−11/group in P7 rats, n=5−6/group in P21 rats). αp<0.05 compared to time matched saline injected. *p<0.05 compared to time matched saline exposed animals.
