Figure 1. Generation of Cdk7as/as HCT116 cells.
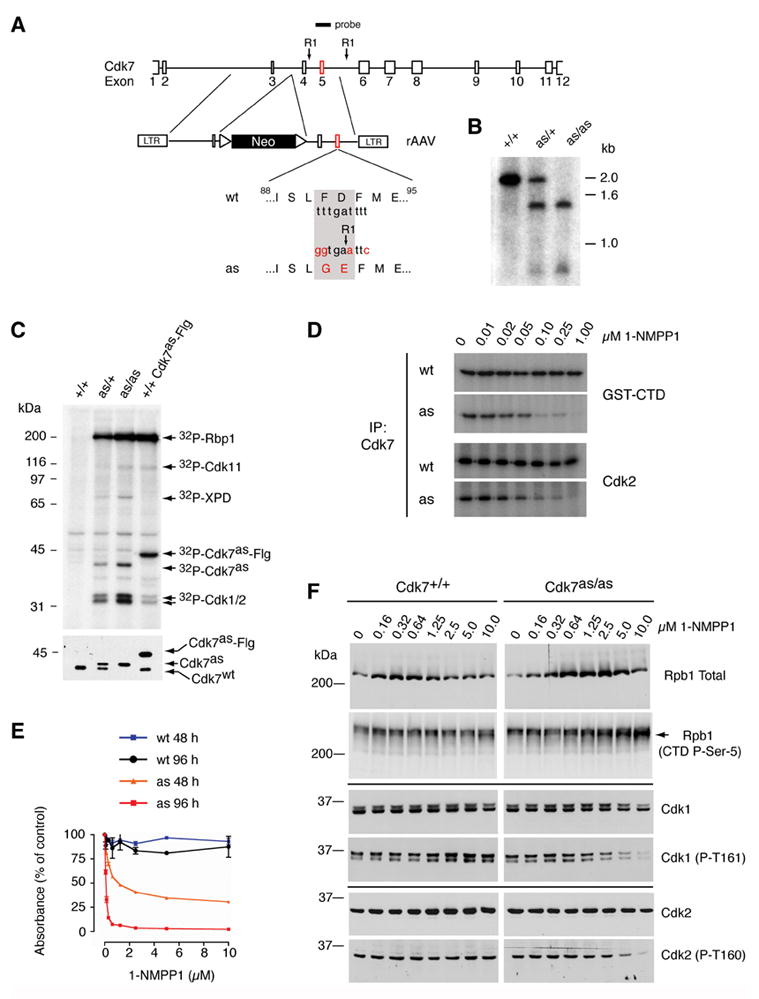
(A) The rAAV targeting vector, containing sequences from the Cdk7 locus flanking a neomycin resistance (neor) marker bounded by loxP sites. Exon 5 contained the F91G/D92E mutation and a novel EcoRI site for purposes of genotyping. The diagram indicates positions of Cdk7-derived sequences in the targeting vector and of the labeled hybridization probe, relative to EcoRI sites (RI) in the fourth and fifth introns. (B) Southern blot hybridization to EcoRI-digested genomic DNA detects single bands of ~2.0 and ~1.4 kb in the wild-type (+/+) and homozygous mutant (as/as) DNA, respectively, and an equal mixture of the two in heterozygotes (as/+). (C) Labeling with [γ-32P]N6-(benzyl)-ATP in whole-cell extracts of indicated genotypes (top). Identities of proteins labeled by both endogenous Cdk7as and recombinant, Flag-tagged Cdk7as (Cdk7as-Flg) in wild-type extract (last lane)—Rpb1 (the largest subunit of Pol II), Cdk1, -2 and -11—were inferred from similarity to the published pattern (Larochelle et al., 2006). The ~80 kDa polypeptide labeled by endogenous Cdk7as was identified by immunoprecipitation with anti-XPD antibodies. Immunoblot of kinase reaction mixtures (bottom) detects Cdk7wt and slower-migrating Cdk7as in the expected ratios; the two were expressed equally in heterozygous cells prior to excision of the neor gene (not shown), obviating the need for marker excision in homozygous Cdk7as/as cells. (D) Inhibition of Cdk7 immunoprecipitated from Cdk7as/as (AS) but not Cdk7+/+ (WT) cells by 1-NMPP1. The inhibitor was added at the indicated concentrations to GST-CTD or Cdk2 kinase assays, which contained 200 μM unlabeled ATP. (E) The dose-response of wild-type (wt) and Cdk7as/as (as) cells to 1-NMPP1 measured at 48 and 96 h of treatment by cell viability (MTT) assay. Error bars denote standard error of the mean in triplicate samples from a single representative experiment. (F) Dose-dependent effects of Cdk7 inhibition on phosphorylation of Cdk1, Cdk2 and Pol II in vivo. Asynchronous populations of Cdk7+/+ and Cdk7as/as HCT116 cells were incubated 14 h with the indicated concentrations of 1-NMPP1. Extracts were prepared and analyzed by immunoblotting with antibodies to: the amino-terminus of the Pol II subunit Rpb1 (Rpb1 Total); the Rpb1 CTD phosphorylated at the Ser5 position (CTD P-Ser-5); total Cdk1; Cdk1 phosphorylated on the T-loop (Cdk1 (P-T161)); total Cdk2 ; and Cdk2 phosphorylated on the T-loop (Cdk2 (P-T160)). Arrow at right indicates position of phosphorylated Rpb1 isoform that accumulates in Cdk7as/as cells treated with 1-NMPP1, which has a faster mobility than the slowest-migrating form (see also Supplemental Figure 1).
