Figure 2. Inhibition of Cdk7 prevents Cdk2 activation and delays G1/S progression.
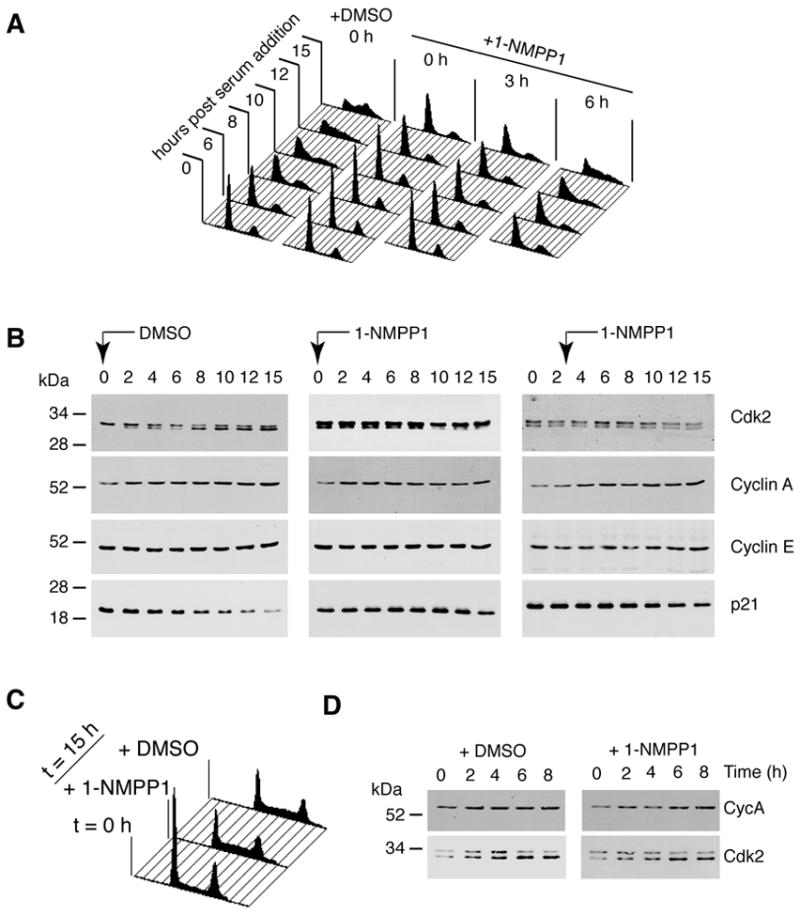
(A) Cells were arrested by serum starvation, then released into serum-containing medium with DMSO or 10 μM 1-NMPP1 added at the indicated times. We monitored DNA content at indicated times by flow cytometry. (B) Levels of Cdk2, cyclin A (Cyc A), cyclin E (Cyc E) and p21 were measured in immunoblots of whole-cell extracts at indicated times after release in DMSO-treated cells, or cells treated with 1-NMPP1 0 and 3 h after release. The higher-mobility isoform of Cdk2 is phosphorylated on Thr160 of the T-loop. Its apparent absence at time 0 in the DMSO-treated cells is anomalous; the other two samples taken at time 0 are more representative (see also Figure 3). (C) Wild-type HCT116 cells were synchronized by serum starvation for 48 h, released into fresh medium containing DMSO or 1-NMPP1 as indicated and collected for flow cytometry to measure DNA content at 15 h. (D) Extracts from DMSO- or 1-NMPP1-treated, wild-type HCT116 cells, collected at indicated times after release from serum starvation, were immunoblotted with antibodies to cyclin A and Cdk2, as indicated.
