Abstract
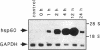
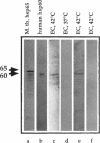
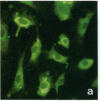
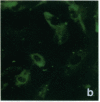
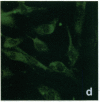
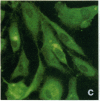
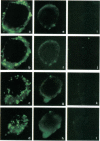
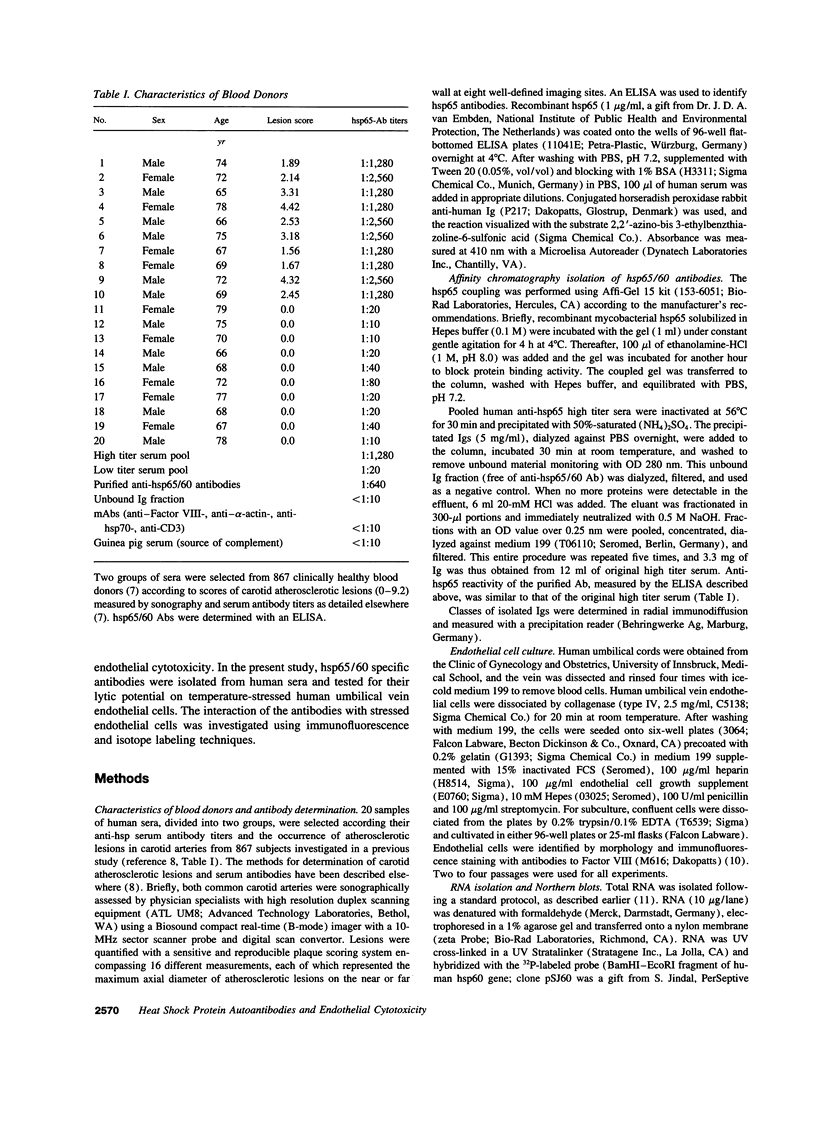
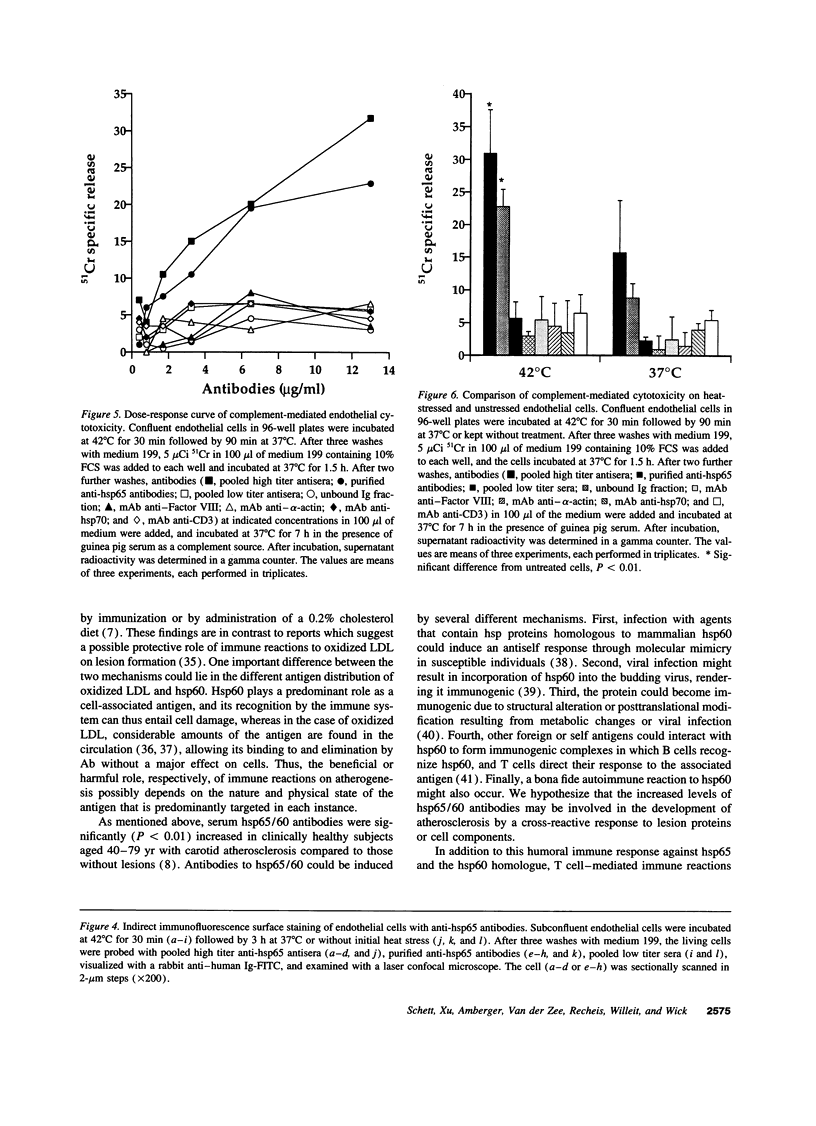
Stress or heat shock proteins (hsp) are a family of approximately two dozen proteins with a high degree of amino acid sequence homology between different species, ranging from prokaryotes to humans, and are representative of a generalized response to environmental and metabolic stressors. Our previous studies showed increased expression of human hsp60 on endothelial cells of arterial intima with atherosclerotic lesions, and elevated levels of serum antibodies (Ab) against hsp65/60 in subjects with carotid atherosclerosis. To investigate the possible involvement of anti-hsp65/60 Ab in endothelial injury, specific hsp-Ab were isolated from human high titer sera by affinity chromatography and probed on heat-shock human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Purified human anti-hsp65/60 Ab reacted specifically with mycobacterial hsp65, human hsp60, and a 60-kD protein band of heat-shocked endothelial cells. High levels of hsp60 mRNA expression in endothelial cells were found between 4 and 12 h after 30 min treatment at 42 degrees C. In immunofluorescence tests, positive staining of heat-stressed endothelial cells was observed not only in the cytoplasm but also on the cell surface. Furthermore, only heat-stressed, but not untreated, Cr-labeled endothelial cells were lysed by anti-hsp65/60 Ab in the presence of complement (complement-mediated cytotoxicity) or peripheral blood mononuclear cells (antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity). Control Abs, including human anti-hsp65/60 low titer antiserum, human Ig fraction deprived of hsp65/60 Ab, and mAbs to Factor VIII, alpha-actin, hsp70, and CD3 showed no cytotoxic effect. In conclusion, human serum anti-hsp65 antibodies act as autoantibodies reacting with hsp60 on stressed endothelial cells and are able to mediate endothelial cytotoxicity. Thus, a humoral immune reaction to hsp60 may play an important role in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen I. R. A heat shock protein, molecular mimicry and autoimmunity. Isr J Med Sci. 1990 Dec;26(12):673–676. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulie P. G., Van Snick J. Rheumatoid factor (RF) production during anamnestic immune responses in the mouse. III. Activation of RF precursor cells is induced by their interaction with immune complexes and carrier-specific helper T cells. J Exp Med. 1985 Jan 1;161(1):88–97. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.1.88. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies P. F., Remuzzi A., Gordon E. J., Dewey C. F., Jr, Gimbrone M. A., Jr Turbulent fluid shear stress induces vascular endothelial cell turnover in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(7):2114–2117. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.7.2114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Cesare S., Poccia F., Mastino A., Colizzi V. Surface expressed heat-shock proteins by stressed or human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-infected lymphoid cells represent the target for antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity. Immunology. 1992 Jun;76(2):341–343. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dugaiczyk A., Haron J. A., Stone E. M., Dennison O. E., Rothblum K. N., Schwartz R. J. Cloning and sequencing of a deoxyribonucleic acid copy of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase messenger ribonucleic acid isolated from chicken muscle. Biochemistry. 1983 Mar 29;22(7):1605–1613. doi: 10.1021/bi00276a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emeson E. E., Robertson A. L., Jr T lymphocytes in aortic and coronary intimas. Their potential role in atherogenesis. Am J Pathol. 1988 Feb;130(2):369–376. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. J., Norton P., Ivanyi J. Distribution in tissue sections of the human groEL stress-protein homologue. APMIS. 1990 May;98(5):437–441. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1990.tb01055.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fyfe A. I., Qiao J. H., Lusis A. J. Immune-deficient mice develop typical atherosclerotic fatty streaks when fed an atherogenic diet. J Clin Invest. 1994 Dec;94(6):2516–2520. doi: 10.1172/JCI117622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansson G. K., Holm J., Holm S., Fotev Z., Hedrich H. J., Fingerle J. T lymphocytes inhibit the vascular response to injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10530–10534. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansson G. K., Jonasson L., Lojsthed B., Stemme S., Kocher O., Gabbiani G. Localization of T lymphocytes and macrophages in fibrous and complicated human atherosclerotic plaques. Atherosclerosis. 1988 Aug;72(2-3):135–141. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(88)90074-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodis H. N., Kramsch D. M., Avogaro P., Bittolo-Bon G., Cazzolato G., Hwang J., Peterson H., Sevanian A. Biochemical and cytotoxic characteristics of an in vivo circulating oxidized low density lipoprotein (LDL-). J Lipid Res. 1994 Apr;35(4):669–677. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollander W., Colombo M. A., Kirkpatrick B., Paddock J. Soluble proteins in the human atherosclerotic plaque. With spectral reference to immunoglobulins, C3-complement component, alpha 1-antitrypsin and alpha 2-macroglobulin. Atherosclerosis. 1979 Dec;34(4):391–405. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(79)90064-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jindal S., Burke E., Bettencourt B., Khandekar S., Young R. A., Dwyer D. S. Human Hsp60: bacterial expression, purification, development of monoclonal antibodies and a sandwich ELISA for quantitation. Immunol Lett. 1994 Feb;39(2):127–135. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(94)90097-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. B., Coulson A. F., Duff G. W. Sequence homologies between hsp60 and autoantigens. Immunol Today. 1993 Mar;14(3):115–118. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(93)90210-C. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jürgens G., Chen Q., Esterbauer H., Mair S., Ledinski G., Dinges H. P. Immunostaining of human autopsy aortas with antibodies to modified apolipoprotein B and apoprotein(a). Arterioscler Thromb. 1993 Nov;13(11):1689–1699. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.13.11.1689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jürgens G., Xu Q. B., Huber L. A., Böck G., Howanietz H., Wick G., Traill K. N. Promotion of lymphocyte growth by high density lipoproteins (HDL). Physiological significance of the HDL binding site. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):8549–8556. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiessling R., Grönberg A., Ivanyi J., Söderström K., Ferm M., Kleinau S., Nilsson E., Klareskog L. Role of hsp60 during autoimmune and bacterial inflammation. Immunol Rev. 1991 Jun;121:91–111. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1991.tb00824.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleindienst R., Xu Q., Willeit J., Waldenberger F. R., Weimann S., Wick G. Immunology of atherosclerosis. Demonstration of heat shock protein 60 expression and T lymphocytes bearing alpha/beta or gamma/delta receptor in human atherosclerotic lesions. Am J Pathol. 1993 Jun;142(6):1927–1937. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Libby P., Hansson G. K. Involvement of the immune system in human atherogenesis: current knowledge and unanswered questions. Lab Invest. 1991 Jan;64(1):5–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marder V. J., Mannucci P. M., Firkin B. G., Hoyer L. W., Meyer D. Standard nomenclature for factor VIII and von Willebrand factor: a recommendation by the International Committee on Thrombosis and Haemostasis. Thromb Haemost. 1985 Dec 17;54(4):871–872. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto R. I. Cells in stress: transcriptional activation of heat shock genes. Science. 1993 Mar 5;259(5100):1409–1410. doi: 10.1126/science.8451637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muscari A., Bozzoli C., Gerratana C., Zaca' F., Rovinetti C., Zauli D., La Placa M., Puddu P. Association of serum IgA and C4 with severe atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis. 1988 Nov;74(1-2):179–186. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(88)90204-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palinski W., Miller E., Witztum J. L. Immunization of low density lipoprotein (LDL) receptor-deficient rabbits with homologous malondialdehyde-modified LDL reduces atherogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Jan 31;92(3):821–825. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.3.821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R. The pathogenesis of atherosclerosis: a perspective for the 1990s. Nature. 1993 Apr 29;362(6423):801–809. doi: 10.1038/362801a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salonen J. T., Ylä-Herttuala S., Yamamoto R., Butler S., Korpela H., Salonen R., Nyyssönen K., Palinski W., Witztum J. L. Autoantibody against oxidised LDL and progression of carotid atherosclerosis. Lancet. 1992 Apr 11;339(8798):883–887. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)90926-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schattner A., Rager-Zisman B. Virus-induced autoimmunity. Rev Infect Dis. 1990 Mar-Apr;12(2):204–222. doi: 10.1093/clinids/12.2.204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seifert P. S., Hansson G. K. Complement receptors and regulatory proteins in human atherosclerotic lesions. Arteriosclerosis. 1989 Nov-Dec;9(6):802–811. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.9.6.802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seifert P. S., Hugo F., Hansson G. K., Bhakdi S. Prelesional complement activation in experimental atherosclerosis. Terminal C5b-9 complement deposition coincides with cholesterol accumulation in the aortic intima of hypercholesterolemic rabbits. Lab Invest. 1989 Jun;60(6):747–754. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seifert P. S., Hugo F., Tranum-Jensen J., Zâhringer U., Muhly M., Bhakdi S. Isolation and characterization of a complement-activating lipid extracted from human atherosclerotic lesions. J Exp Med. 1990 Aug 1;172(2):547–557. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.2.547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seifert P. S., Kazatchkine M. D. The complement system in atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis. 1988 Oct;73(2-3):91–104. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(88)90030-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sgonc R., Boeck G., Dietrich H., Gruber J., Recheis H., Wick G. Simultaneous determination of cell surface antigens and apoptosis. Trends Genet. 1994 Feb;10(2):41–42. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(94)90140-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimano H., Yamada N., Ishibashi S., Mokuno H., Mori N., Gotoda T., Harada K., Akanuma Y., Murase T., Yazaki Y. Oxidation-labile subfraction of human plasma low density lipoprotein isolated by ion-exchange chromatography. J Lipid Res. 1991 May;32(5):763–773. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh B., Gupta R. S. Expression of human 60-kD heat shock protein (HSP60 or P1) in Escherichia coli and the development and characterization of corresponding monoclonal antibodies. DNA Cell Biol. 1992 Jul-Aug;11(6):489–496. doi: 10.1089/dna.1992.11.489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stemme S., Faber B., Holm J., Wiklund O., Witztum J. L., Hansson G. K. T lymphocytes from human atherosclerotic plaques recognize oxidized low density lipoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Apr 25;92(9):3893–3897. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.9.3893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udelsman R., Blake M. J., Stagg C. A., Li D. G., Putney D. J., Holbrook N. J. Vascular heat shock protein expression in response to stress. Endocrine and autonomic regulation of this age-dependent response. J Clin Invest. 1993 Feb;91(2):465–473. doi: 10.1172/JCI116224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlaicu R., Niculescu F., Rus H. G., Cristea A. Immunohistochemical localization of the terminal C5b-9 complement complex in human aortic fibrous plaque. Atherosclerosis. 1985 Nov;57(2-3):163–177. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(85)90030-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wand-Württenberger A., Schoel B., Ivanyi J., Kaufmann S. H. Surface expression by mononuclear phagocytes of an epitope shared with mycobacterial heat shock protein 60. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Apr;21(4):1089–1092. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wick G., Schett G., Amberger A., Kleindienst R., Xu Q. Is atherosclerosis an immunologically mediated disease? Immunol Today. 1995 Jan;16(1):27–33. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(95)80067-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu Q. B., Oberhuber G., Gruschwitz M., Wick G. Immunology of atherosclerosis: cellular composition and major histocompatibility complex class II antigen expression in aortic intima, fatty streaks, and atherosclerotic plaques in young and aged human specimens. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1990 Sep;56(3):344–359. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(90)90155-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu Q., Dietrich H., Steiner H. J., Gown A. M., Schoel B., Mikuz G., Kaufmann S. H., Wick G. Induction of arteriosclerosis in normocholesterolemic rabbits by immunization with heat shock protein 65. Arterioscler Thromb. 1992 Jul;12(7):789–799. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.12.7.789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu Q., Kleindienst R., Waitz W., Dietrich H., Wick G. Increased expression of heat shock protein 65 coincides with a population of infiltrating T lymphocytes in atherosclerotic lesions of rabbits specifically responding to heat shock protein 65. J Clin Invest. 1993 Jun;91(6):2693–2702. doi: 10.1172/JCI116508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu Q., Luef G., Weimann S., Gupta R. S., Wolf H., Wick G. Staining of endothelial cells and macrophages in atherosclerotic lesions with human heat-shock protein-reactive antisera. Arterioscler Thromb. 1993 Dec;13(12):1763–1769. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.13.12.1763. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu Q., Schett G., Seitz C. S., Hu Y., Gupta R. S., Wick G. Surface staining and cytotoxic activity of heat-shock protein 60 antibody in stressed aortic endothelial cells. Circ Res. 1994 Dec;75(6):1078–1085. doi: 10.1161/01.res.75.6.1078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu Q., Willeit J., Marosi M., Kleindienst R., Oberhollenzer F., Kiechl S., Stulnig T., Luef G., Wick G. Association of serum antibodies to heat-shock protein 65 with carotid atherosclerosis. Lancet. 1993 Jan 30;341(8840):255–259. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)92613-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ylä-Herttuala S., Palinski W., Butler S. W., Picard S., Steinberg D., Witztum J. L. Rabbit and human atherosclerotic lesions contain IgG that recognizes epitopes of oxidized LDL. Arterioscler Thromb. 1994 Jan;14(1):32–40. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.14.1.32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkernagel R. M., Cooper S., Chambers J., Lazzarini R. A., Hengartner H., Arnheiter H. Virus-induced autoantibody response to a transgenic viral antigen. Nature. 1990 May 3;345(6270):68–71. doi: 10.1038/345068a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]