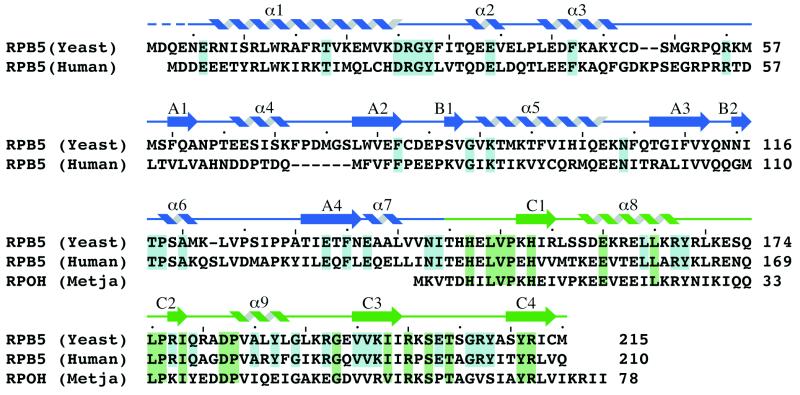
Figure 1.
Amino acid sequence alignment of the eukaryotic S. cerevisiae and human RPB5 subunits with the archaeal M. jannaschii RpoH subunit. Highlighted in blue are the amino acid residues that are strictly conserved in the six available eukaryotic sequences whereas the residues that are conserved in 15 of 17 homologues of the C-terminal domain, including both eukaryotic and archaeal sequences, are shown in green. The position of secondary structure elements determined by using the algorithm of Kabsch and Sander (40) is indicated above the sequence. The secondary structure elements are colored in blue when belonging to the N-terminal domain and in green when belonging to the C-terminal domain. A dashed line indicates residues omitted from the final model.