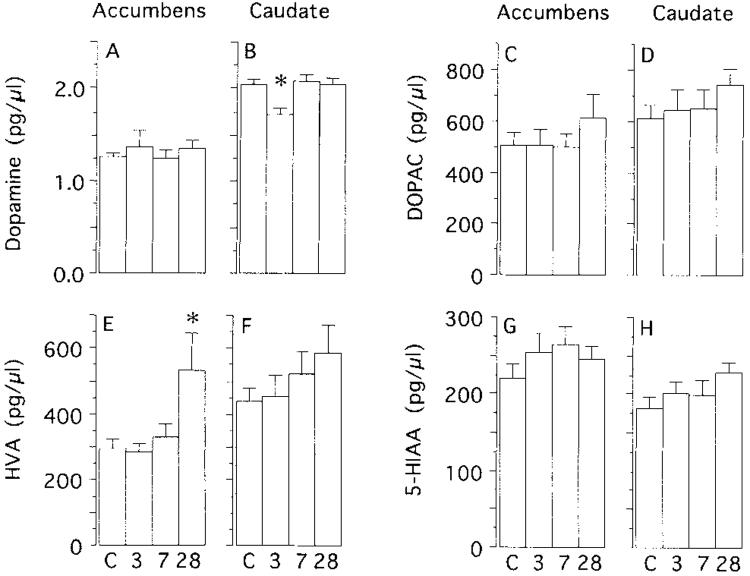
Fig. 3.
The mean (+S.E.M.) basal concentrations of DA (A,B), dihydroxyphenylacetic acid (DOPAC; C,D), homovanillic acid (HVA; E,F), and 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid (5-HIAA; G,H) in the nucleus accumbens (accumbens) and dorsolateral caudate nucleus (caudate) of control animals (C) and animals tested after 3, 7, or 28 days of withdrawal. The data were analyzed by one-way ANOVAs, and if significant, followed by Fisher’s PLSD tests. There was no effect of amphetamine withdrawal on the basal concentration of DA in the accumbens (F = 0.62), DOPAC in the accumbens (F = 0.52), DOPAC in the caudate (F = 0.861, HVA in the caudate (F = 1.29), 5-HIAA in the accumbens (F = 0.92), or 5-HIAA in the caudate (F = 1.79). There was a significant effect of amphetamine withdrawal on DA in the caudate (F = 4.62, P < 0.01) and HVA in the accumbens (F = 4.16, P = 0.012). The asterisk in panel B indicates that there was a significant (P < 0.05) decrease in basal DA in animals tested after 3 days of withdrawal relative to all other groups (which did not differ from one another). The asterisk in panel E indicates there was a significant (P < 0.05) increase in basal HVA in animals tested after 28 days of withdrawal, relative to all other groups (which did not differ from one another). Group Ns: accumbens control, N = 18-20; caudate control, N = 15-17; accumbens 3 day, N = 8-11; 7 day, N = 9-10; 28 day, N = 4-7; caudate 3 day, N = 6-7; 7 day, N = 8; 28 day, N = 9. Group Ns vary because both DA and metabolite data were not available for every animal.