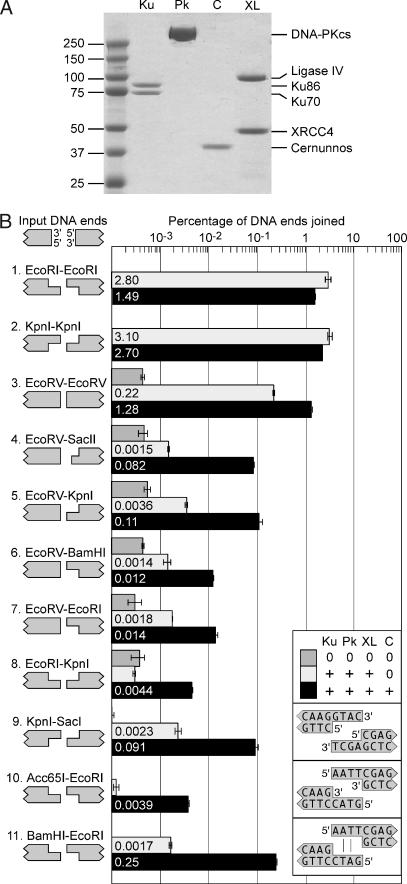
Fig. 1.
Cernunnos stimulates the joining of mismatched DNA ends. (A) Purification of NHEJ proteins. Coomassie staining after SDS/PAGE shows our purified preparations of Ku, DNA-PKcs (Pk), Cernunnos (C), and XL. (B) Cernunnos stimulates the joining of noncohesive ends by Ku, DNA-PKcs, and XL. Linear DNA substrates were incubated with no protein (dark gray bars), Ku, DNA-PKcs and XL (light gray bars), or Ku, DNA-PKcs, XL, and Cernunnos (black bars). The orientation of DNA is depicted in the upper left corner. We tested compatible ends (rows 1–3) with cohesive 5′ overhangs (EcoRI–EcoRI), cohesive 3′ overhangs (KpnI–KpnI), or blunt ends (EcoRV–EcoRV). We also tested eight combinations of mismatched ends (rows 4–11). Note that SacII creates a 2-nt 3′ overhang. All other 3′ and 5′ overhangs were 4 nt. We measured joining efficiency by quantitative PCR and expressed efficiency as the percentage of input DNA ends joined (18). Because of large differences among experiments, we plotted joining efficiency on a logarithmic scale. Concentrations of Ku, DNA-PKcs, XL, and Cernunnos were 5, 5, 0.5, and 2.5 nM, respectively, here and elsewhere unless otherwise noted. (Insets) The overhangs from the KpnI–SacI, Acc65I–EcoRI, and EcoRI–BamHI ends.