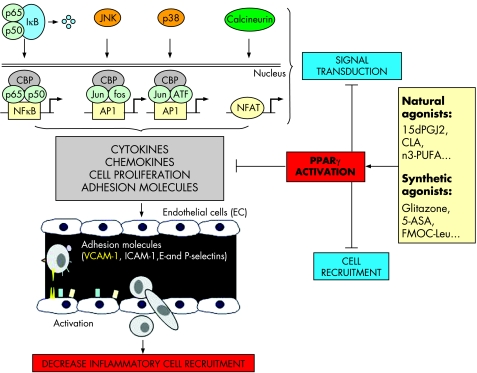
Figure 2 Interferences of peroxisome proliferator activated receptor γ (PPARγ) with inflammatory signalling pathways. PPARγ inhibits nuclear factor κB (NFκB) signalling pathway through interactions with NFκB, the inhibitory protein called IκB, and CBP, a coactivator of p65. The MAPK pathway is also regulated by PPARγ, which reduces JNK and p38 activation and inhibits the transcription factors c‐jun, c‐fos, and nuclear factor of activated T cell (NFAT). Regulation of these main signalling pathways results in inhibition of cytokine and chemokine production, cell proliferation, and adhesion molecule expression (mainly VCAM‐1), which decrease inflammatory cell recruitment in inflamed tissues. 15dPGJ2, 15‐deoxy‐Δ12,14‐prostaglandin J2; PUFAs, polyunsaturated fatty acids; 5‐ASA, 5‐aminosalicylic acid.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.