Figure 6.
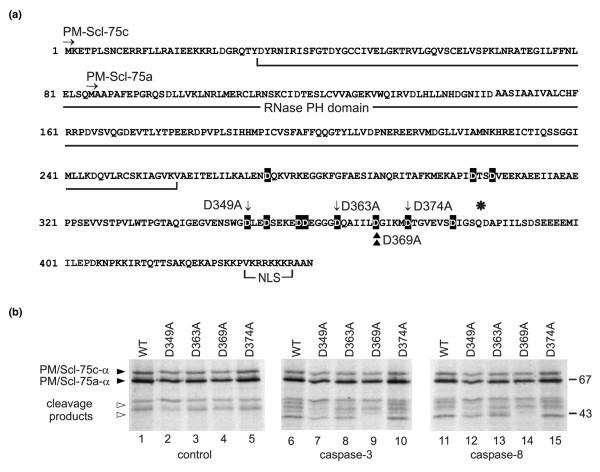
Mapping of the caspase cleavage site in PM/Scl-75. (a) Amino acid sequence of PM/Scl-75 (α variant). The RNase pleckstrin homology (PH) domain, the nuclear localization signal, the N termini of both published sequences, PM/Scl-75a [13] and PM/Scl-75c [14], and the position (asterisk) where the β splice variant contains a 17-amino-acid insertion are indicated. Note that the numbering of the amino acid positions corresponds to that of PM/Scl-75c-α. All aspartic acid residues that were replaced by alanines are highlighted in black. The mutants that were used in the experiment shown in (b) are marked by arrows (D349A, D363A and D374A) and the identified cleavage site by arrowheads (D369A). (b) Cleavage of PM/Scl-75 mutants by recombinant caspases. In vitro translated 35S-labeled PM/Scl-75c-α and mutants of the protein in which the aspartic acid residues at positions 347 (D347A), 363 (D363A), 368 (D369A) or 374 (D374A) were changed into alanine residues were incubated with purified murine recombinant caspase-3 or caspase-8 for 1.5 hours at 37°C. The resulting reaction products were analyzed by SDS-PAGE followed by autoradiography. In lanes 1 to 5 the proteins incubated in parallel in the absence of caspases were loaded (control). The positions of molecular mass markers are indicated in kDa at the right, and the positions of relevant polypeptides are shown at the left. Filled arrowheads indicate full-length PM/Scl-75c-α and open arrowheads indicate the PM/Scl-75 cleavage product. Note that in this experiment the pCR4-TOPO-PM/Scl-75c-α cDNA [14] was used for the transcription and translation of PM/Scl-75 in vitro. As a result of translation initiation at an internal start codon in the reticulocyte lysate, a relatively high level of a second polypeptide was produced, which was shown to represent a polypeptide initiated at Met85, thus corresponding to PM/Scl-75a-α. WT, wild type.
