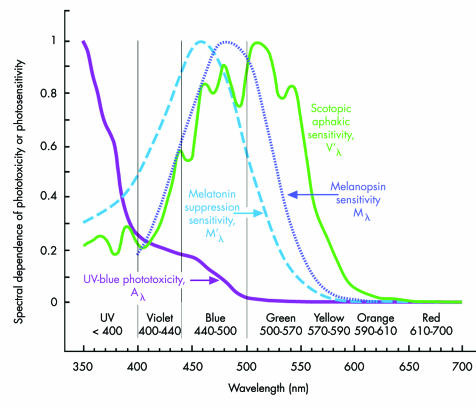
Figure 1 Acute aphakic UV‐blue phototoxicity (Aλ),10,12,73 aphakic scotopic luminous efficiency (V'λ),46 melanopsin spectral sensitivity (Mλ, peak sensitivity, 479–483 nm),68,69,70,71,188 and melatonin suppression sensitivity (M'λ, peak sensitivity, 459–464 nm).66,67,72 Original rather than smoothed aphakic scotopic luminous efficiency (V'λ) data are shown.46 The potential hazardousness of acute UV‐blue type phototoxicity increases with decreasing wavelength. Acute blue‐green retinal phototoxicity has an action spectrum similar to aphakic scotopic sensitivity because rhodopsin mediates both processes.43,44 Melatonin suppression and melanopsin sensitivity are more heavily dependent on blue light than rod (rhodopsin) mediated visual functions.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.