Abstract
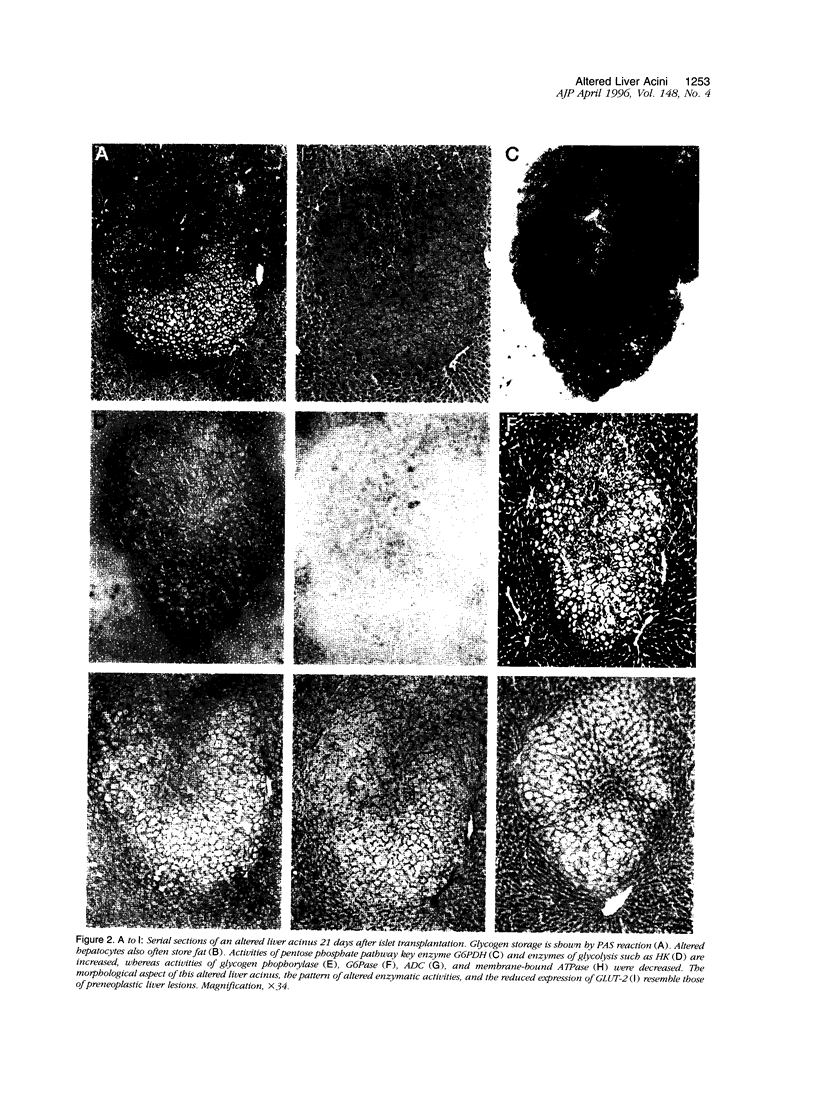
As demonstrated previously, liver acini draining the blood from intraportally transplanted pancreatic islets in streptozotocin-diabetic rats are altered in various respects. The hepatocytes in these acini store glycogen and/or fat, and they show an increase in proliferation as well as in apoptotic activity. Thus, they are phenotypically similar to carcinogen-induced preneoplastic liver foci (glycogen-storing foci and sometimes also mixed cell foci). By means of catalytic enzyme histochemistry or immunohistochemistry, we investigated the activity of key enzymes of alternative pathways of carbohydrate metabolism and some additional marker enzymes (well known from studies on preneoplastic hepatic foci) in the altered liver acini surrounding the islet isografts. In addition, the expression of glucose transporter proteins 1 and 2 (GLUT-1 and GLUT-2) were investigated immunohistochemically. The activities of hexokinase, pyruvate kinase, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase were increased, whereas the activities of glycogen phosphorylase, adenylate cyclase, glucose-6-phosphatase, and membrane-bound adenosine triphosphatase were decreased in the altered liver acini. The expression of GLUT-2 was also decreased. GLUT-1 and glutathione S-transferase placental form were not expressed, and the activities of glycogen synthase and gamma-glutamyl-transferase remained unchanged. All changes of the enzyme activities were in line with the well known effects of insulin and resembled alterations characteristic of preneoplastic liver foci observed in different models of hepatocarcinogenesis. It remains to be clarified in long-term experiments whether or not these foci represent preneoplastic lesions and may proceed to neoplasia.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baba M., Yamamoto R., Iishi H., Tatsuta M., Wada A. Role of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase on enhanced proliferation of pre-neoplastic and neoplastic cells in rat liver induced by N-nitrosomorpholine. Int J Cancer. 1989 May 15;43(5):892–895. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910430526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bannasch P., Benner U., Enzmann H., Hacker H. J. Tigroid cell foci and neoplastic nodules in the liver of rats treated with a single dose of aflatoxin B1. Carcinogenesis. 1985 Nov;6(11):1641–1648. doi: 10.1093/carcin/6.11.1641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bannasch P., Hacker H. J., Klimek F., Mayer D. Hepatocellular glycogenosis and related pattern of enzymatic changes during hepatocarcinogenesis. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1984;22:97–121. doi: 10.1016/0065-2571(84)90010-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bannasch P., Mayer D., Hacker H. J. Hepatocellular glycogenosis and hepatocarcinogenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 May 6;605(2):217–245. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(80)90005-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benner U., Hacker H. J., Bannasch P. Electron microscopical demonstration of glucose-6-phosphatase in native cryostat sections fixed with glutaraldehyde through semipermeable membranes. Histochemistry. 1979;65(1):41–47. doi: 10.1007/BF00496684. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bucher M. L., Swaffield M. N. Regulation of hepatic regeneration in rats by synergistic action of insulin and glucagon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1157–1160. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burrows C. J., Jones A. W. Hepatic subcapsular steatosis in a patient with insulin dependent diabetes receiving dialysis. J Clin Pathol. 1994 Mar;47(3):274–275. doi: 10.1136/jcp.47.3.274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Columbano A., Ledda-Columbano G. M., Rao P. M., Rajalakshmi S., Sarma D. S. Occurrence of cell death (apoptosis) in preneoplastic and neoplastic liver cells. A sequential study. Am J Pathol. 1984 Sep;116(3):441–446. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cossel L., Wohlrab F., Blech W., Hahn H. J. Morphological findings in the liver of diabetic rats after intraportal transplantation of neonatal isologous pancreatic islets. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1990;59(2):65–77. doi: 10.1007/BF02899389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dombrowski F., Lehringer-Polzin M., Pfeifer U. Hyperproliferative liver acini after intraportal islet transplantation in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Lab Invest. 1994 Nov;71(5):688–699. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enzmann H., Bannasch P. Potential significance of phenotypic heterogeneity of focal lesions at different stages in hepatocarcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis. 1987 Nov;8(11):1607–1612. doi: 10.1093/carcin/8.11.1607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francavilla A., Starzl T. E., Porter K., Foglieni C. S., Michalopoulos G. K., Carrieri G., Trejo J., Azzarone A., Barone M., Zeng Q. H. Screening for candidate hepatic growth factors by selective portal infusion after canine Eck's fistula. Hepatology. 1991 Oct;14(4 Pt 1):665–670. doi: 10.1016/0270-9139(91)90055-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith R. C., Scharp D. W., Hartman B. K., Ballinger W. F., Lacy P. E. A morphologic study of intrahepatic portal-vein islet isografts. Diabetes. 1977 Mar;26(3):201–214. doi: 10.2337/diab.26.3.201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grobholz R., Hacker H. J., Thorens B., Bannasch P. Reduction in the expression of glucose transporter protein GLUT 2 in preneoplastic and neoplastic hepatic lesions and reexpression of GLUT 1 in late stages of hepatocarcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 1993 Sep 15;53(18):4204–4211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grotting J. C., Rosai J., Matas A. J., Frenzel E. M., Payne W. D., Sutherland D. E., Najarian J. S. The fate of intraportally transplanted islets in diabetic rats. A morphologic and immunohistochemical study. Am J Pathol. 1978 Sep;92(3):653–670. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hacker H. J., Grobholz R., Klimek F. Enzyme histochemistry and biochemical microanalysis of preneoplastic lesions. Prog Histochem Cytochem. 1991;23(1-4):61–72. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6336(11)80169-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hacker H. J. Histochemische Darstellung der Glykogenphosphorylase (E.C. 2.4.11) mit Hilfe semipermeabler Membranen. Histochemistry. 1978 Dec 13;58(4):289–296. doi: 10.1007/BF00495385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hacker H. J., Moore M. A., Mayer D., Bannasch P. Correlative histochemistry of some enzymes of carbohydrate metabolism in preneoplastic and neoplastic lesions in the rat liver. Carcinogenesis. 1982;3(11):1265–1272. doi: 10.1093/carcin/3.11.1265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han K., Lehringer-Polzin M., Zhou H., Pfeifer U. Cellular autophagy in proximal tubules of early diabetic rats following insulin treatment and islet transplantation. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1992;61(6):367–373. doi: 10.1007/BF02890440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanigan M. H., Pitot H. C. Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase--its role in hepatocarcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis. 1985 Feb;6(2):165–172. doi: 10.1093/carcin/6.2.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson B. Quantitative cytochemical measurement of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase activity. Histochemistry. 1976 Aug 25;48(3):191–204. doi: 10.1007/BF00497455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp C. B., Knight M. J., Scharp D. W., Ballinger W. F., Lacy P. E. Effect of transplantation site on the results of pancreatic islet isografts in diabetic rats. Diabetologia. 1973 Dec;9(6):486–491. doi: 10.1007/BF00461694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klimek F., Bannasch P. Isoenzyme shift from glucokinase to hexokinase is not an early but a late event in hepatocarcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis. 1993 Sep;14(9):1857–1861. doi: 10.1093/carcin/14.9.1857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klimek F., Mayer D., Bannasch P. Biochemical microanalysis of glycogen content and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase activity in focal lesions of the rat liver induced by N-nitrosomorpholine. Carcinogenesis. 1984 Feb;5(2):265–268. doi: 10.1093/carcin/5.2.265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klimek F., Moore M. A., Schneider E., Bannasch P. Histochemical and microbiochemical demonstration of reduced pyruvate kinase activity in thioacetamide-induced neoplastic nodules of rat liver. Histochemistry. 1988;90(1):37–42. doi: 10.1007/BF00495704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledda-Columbano G. M., Columbano A., Dessì S., Coni P., Chiodino C., Pani P. Enhancement of cholesterol synthesis and pentose phosphate pathway activity in proliferating hepatocyte nodules. Carcinogenesis. 1985 Sep;6(9):1371–1373. doi: 10.1093/carcin/6.9.1371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manchester J., Kong X., Lowry O. H., Lawrence J. C., Jr Ras signaling in the activation of glucose transport by insulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 May 24;91(11):4644–4648. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.11.4644. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer D., Hacker H. J., Bannasch P. Re-evaluation of the specificity of adenylyl (beta,gamma-methylene)diphosphonate as a substrate for adenylate cyclase. Histochem J. 1991 Feb;23(2):100–106. doi: 10.1007/BF01047114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meijer A. E., de Vries G. P. Semipermeable membranes for improving the histochemical demonstration of enzyme activities in tissue sections. IV. Glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase and 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase (decarboxylating). Histochemistry. 1974;40(4):349–359. doi: 10.1007/BF00495042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore M. A., Nakamura T., Shirai T., Ichihara A., Ito N. Immunohistochemical demonstration of increased glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase in preneoplastic and neoplastic lesions induced by propylnitrosamines in F344 rats and Syrian hamsters. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1986 Feb;77(2):131–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeifer U. Inhibition by insulin of the formation of autophagic vacuoles in rat liver. A morphometric approach to the kinetics of intracellular degradation by autophagy. J Cell Biol. 1978 Jul;78(1):152–167. doi: 10.1083/jcb.78.1.152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeifer U. Methods in laboratory investigation. Application of test substances to the surface of rat liver in situ: opposite effects of insulin and isoproterenol on cellular autophagy. Lab Invest. 1984 Mar;50(3):348–354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pipeleers-Marichal M. A., Pipeleers D. G., Cutler J., Lacy P. E., Kipnis D. M. Metabolic and morphologic studies in intraportal-islet-transplanted rats. Diabetes. 1976 Nov;25(11):1041–1051. doi: 10.2337/diab.25.11.1041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabes H. M., Bücher T., Hartmann A., Linke I., Dünnwald M. Clonal growth of carcinogen-induced enzyme-deficient preneoplastic cell populations in mouse liver. Cancer Res. 1982 Aug;42(8):3220–3227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed G. B., Grisham J. W. Insulin and hydrocortisone effects on viability and glycogen stores of postnatal rat liver organ culture. Lab Invest. 1975 Sep;33(3):298–304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricordi C., Flye M. W., Lacy P. E. Renal subcapsular transplantation of clusters of hepatocytes in conjunction with pancreatic islets. Transplantation. 1988 Jun;45(6):1148–1151. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198806000-00034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato K., Kitahara A., Satoh K., Ishikawa T., Tatematsu M., Ito N. The placental form of glutathione S-transferase as a new marker protein for preneoplasia in rat chemical hepatocarcinogenesis. Gan. 1984 Mar;75(3):199–202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulte-Hermann R., Timmermann-Trosiener I., Barthel G., Bursch W. DNA synthesis, apoptosis, and phenotypic expression as determinants of growth of altered foci in rat liver during phenobarbital promotion. Cancer Res. 1990 Aug 15;50(16):5127–5135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starzl T. E., Porter K. A., Kashiwagi N. Portal hepatotrophic factors, diabetes mellitus and acute liver atrophy, hypertrophy and regeneration. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1975 Dec;141(6):843–858. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starzl T. E., Watanabe K., Porter K. A., Putnam C. W. Effects of insulin, glucagon, and insuling/glucagon infusions on liver morphology and cell division after complete portacaval shunt in dogs. Lancet. 1976 Apr 17;1(7964):821–825. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)90477-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toshkov I., Chisari F. V., Bannasch P. Hepatic preneoplasia in hepatitis B virus transgenic mice. Hepatology. 1994 Nov;20(5):1162–1172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuji S., Ogawa K., Takasaka H., Sonoda T., Mori M. Clonal origin of gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase-positive hepatic lesions induced by initiation-promotion in ornithine carbamoyltransferase mosaic mice. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1988 Feb;79(2):148–151. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.1988.tb01569.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wanless I. R., Bargman J. M., Oreopoulos D. G., Vas S. I. Subcapsular steatonecrosis in response to peritoneal insulin delivery: a clue to the pathogenesis of steatonecrosis in obesity. Mod Pathol. 1989 Mar;2(2):69–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber E., Bannasch P. Dose and time dependence of the cellular phenotype in rat hepatic preneoplasia and neoplasia induced in stop experiments by oral exposure to N-nitrosomorpholine. Carcinogenesis. 1994 Jun;15(6):1227–1234. doi: 10.1093/carcin/15.6.1227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber E., Moore M. A., Bannasch P. Enzyme histochemical and morphological phenotype of amphophilic foci and amphophilic/tigroid cell adenomas in rat liver after combined treatment with dehydroepiandrosterone and N-nitrosomorpholine. Carcinogenesis. 1988 Jun;9(6):1049–1054. doi: 10.1093/carcin/9.6.1049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg W. C., Iannaccone P. M. Clonality of preneoplastic liver lesions: histological analysis in chimeric rats. J Cell Sci. 1988 Mar;89(Pt 3):423–431. doi: 10.1242/jcs.89.3.423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zerban H., Radig S., Kopp-Schneider A., Bannasch P. Cell proliferation and cell death (apoptosis) in hepatic preneoplasia and neoplasia are closely related to phenotypic cellular diversity and instability. Carcinogenesis. 1994 Nov;15(11):2467–2473. doi: 10.1093/carcin/15.11.2467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]