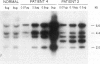
Abstract
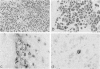
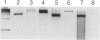
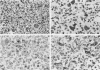
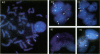
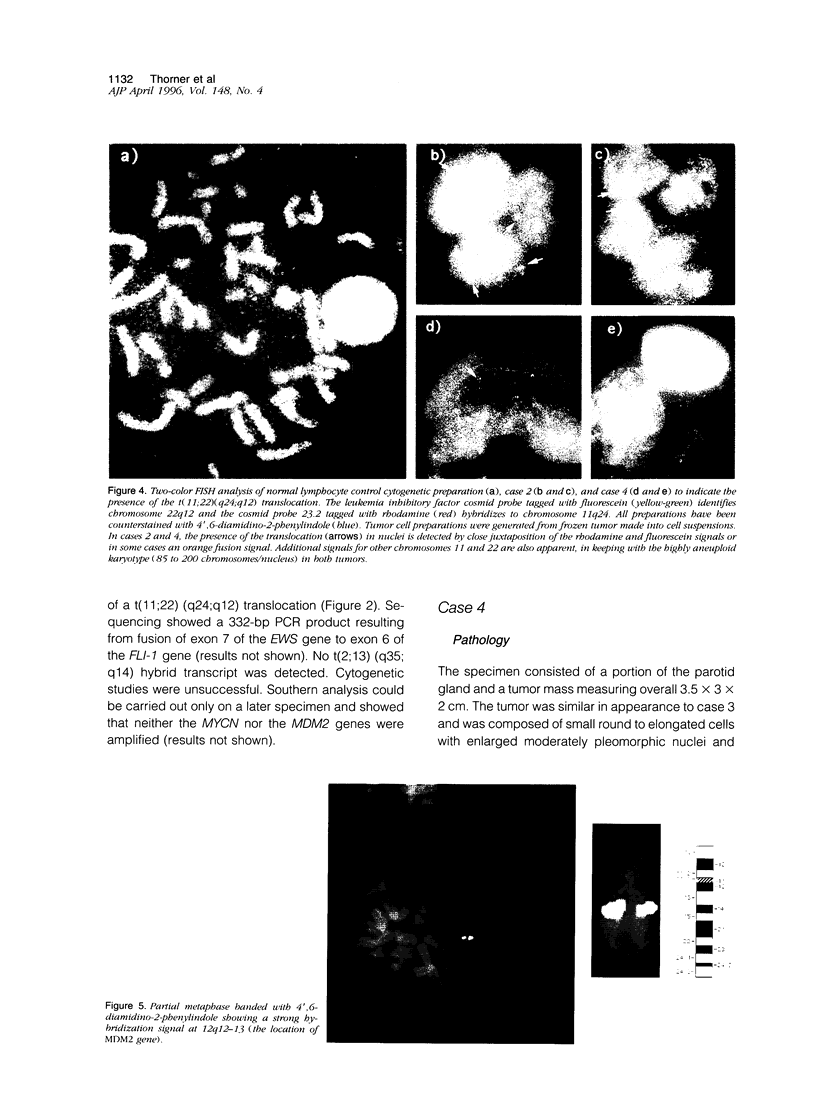
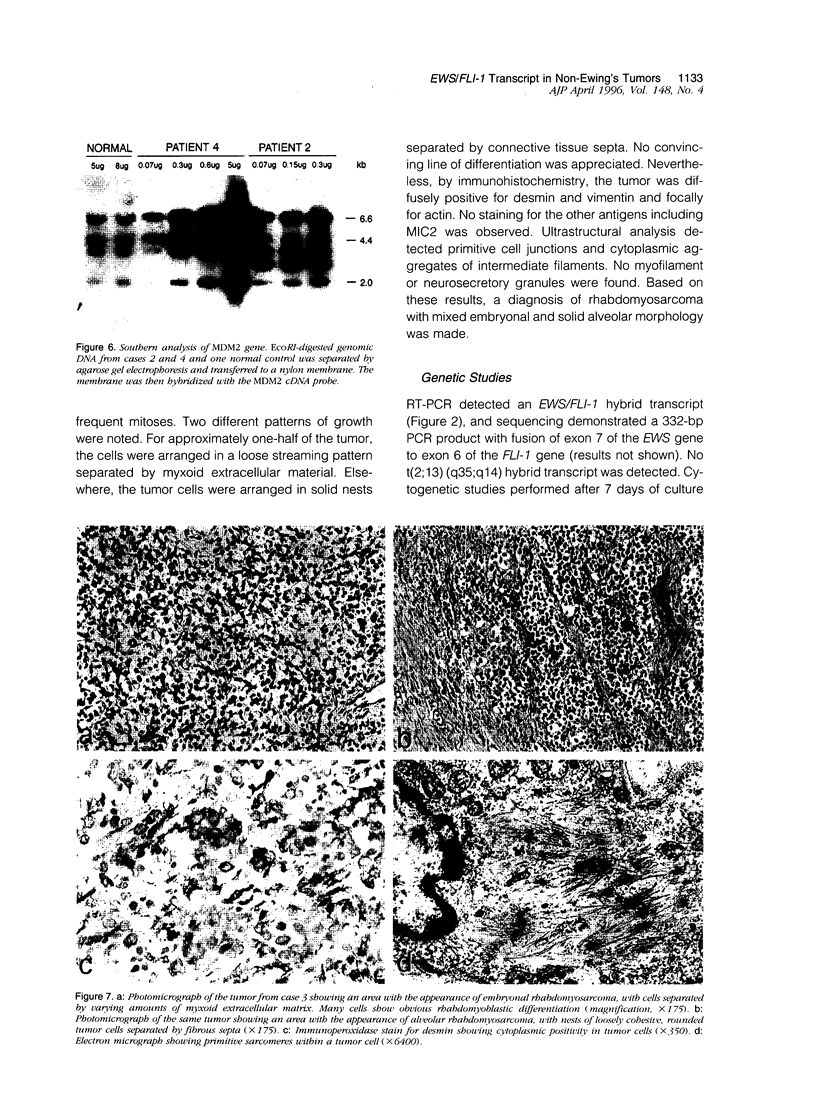
The presence of t(11;22)(q24;q12) is often considered diagnostic of Ewing sarcoma and peripheral primitive neuroectodermal tumor. We report four cases, all of which possessed this translocation as detected by reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction and confirmed by sequencing with or without fluorescent in situ hybridization, but none of which were Ewing sarcoma or peripheral primitive neuroectodermal tumor by histological criteria. Two were polyphenotypic tumors and two were mixed embryonal and alveolar rhabdomyosarcomas. Only one case was positive for MIC2 by immunohistochemistry and only in a rare cell. Two cases (one polyphenotypic tumor and one rhabdomyosarcoma) had double minute chromosomes with > 100 copies of the MDM2 gene. The presence of the t(11;22)(q24;ql2) translocation should probably not be considered diagnostic of Ewing sarcoma and peripheral primitive neuroectodermal tumor in the absence of supporting histological evidence. The presence of this translocation in Ewing sarcoma and peripheral primitive neuroectodermal tumor has been taken as evidence that these two tumors are related. Extending this relationship to include some polyphenotypic tumors and some rhabdomyosarcomas may not be justified unless additional evidence is gathered. Pathologists and oncologists will need to decide whether treatment regimens for tumors are better based on phenotype rather than genotype when these two profiles are seemingly in conflict.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ambros I. M., Ambros P. F., Strehl S., Kovar H., Gadner H., Salzer-Kuntschik M. MIC2 is a specific marker for Ewing's sarcoma and peripheral primitive neuroectodermal tumors. Evidence for a common histogenesis of Ewing's sarcoma and peripheral primitive neuroectodermal tumors from MIC2 expression and specific chromosome aberration. Cancer. 1991 Apr 1;67(7):1886–1893. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19910401)67:7<1886::aid-cncr2820670712>3.0.co;2-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arheden K., Rønne M., Mandahl N., Heim S., Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B., Mitelman F. In situ hybridization localizes the human putative oncogene GLI to chromosome subbands 12q13.3-14.1. Hum Genet. 1989 Apr;82(1):1–2. doi: 10.1007/BF00288260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barr F. G., Chatten J., D'Cruz C. M., Wilson A. E., Nauta L. E., Nycum L. M., Biegel J. A., Womer R. B. Molecular assays for chromosomal translocations in the diagnosis of pediatric soft tissue sarcomas. JAMA. 1995 Feb 15;273(7):553–557. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biegel J. A., Conard K., Brooks J. J. Translocation (11;22)(p13;q12): primary change in intra-abdominal desmoplastic small round cell tumor. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 1993 Jun;7(2):119–121. doi: 10.1002/gcc.2870070210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. J., D'Cruz C. M., Lovell M. A., Biegel J. A., Barr F. G. Fusion of PAX7 to FKHR by the variant t(1;13)(p36;q14) translocation in alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma. Cancer Res. 1994 Jun 1;54(11):2869–2872. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dehner L. P. Neuroepithelioma (primitive neuroectodermal tumor) and Ewing's sarcoma. At least a partial consensus. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1994 Jun;118(6):606–607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dehner L. P. Primitive neuroectodermal tumor and Ewing's sarcoma. Am J Surg Pathol. 1993 Jan;17(1):1–13. doi: 10.1097/00000478-199301000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delattre O., Zucman J., Melot T., Garau X. S., Zucker J. M., Lenoir G. M., Ambros P. F., Sheer D., Turc-Carel C., Triche T. J. The Ewing family of tumors--a subgroup of small-round-cell tumors defined by specific chimeric transcripts. N Engl J Med. 1994 Aug 4;331(5):294–299. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199408043310503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delattre O., Zucman J., Plougastel B., Desmaze C., Melot T., Peter M., Kovar H., Joubert I., de Jong P., Rouleau G. Gene fusion with an ETS DNA-binding domain caused by chromosome translocation in human tumours. Nature. 1992 Sep 10;359(6391):162–165. doi: 10.1038/359162a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglass E. C., Valentine M., Etcubanas E., Parham D., Webber B. L., Houghton P. J., Houghton J. A., Green A. A. A specific chromosomal abnormality in rhabdomyosarcoma. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1987;45(3-4):148–155. doi: 10.1159/000132446. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downing J. R., Khandekar A., Shurtleff S. A., Head D. R., Parham D. M., Webber B. L., Pappo A. S., Hulshof M. G., Conn W. P., Shapiro D. N. Multiplex RT-PCR assay for the differential diagnosis of alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma and Ewing's sarcoma. Am J Pathol. 1995 Mar;146(3):626–634. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driman D., Thorner P. S., Greenberg M. L., Chilton-MacNeill S., Squire J. MYCN gene amplification in rhabdomyosarcoma. Cancer. 1994 Apr 15;73(8):2231–2237. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19940415)73:8<2231::aid-cncr2820730832>3.0.co;2-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galili N., Davis R. J., Fredericks W. J., Mukhopadhyay S., Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Emanuel B. S., Rovera G., Barr F. G. Fusion of a fork head domain gene to PAX3 in the solid tumour alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma. Nat Genet. 1993 Nov;5(3):230–235. doi: 10.1038/ng1193-230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerald W. L., Miller H. K., Battifora H., Miettinen M., Silva E. G., Rosai J. Intra-abdominal desmoplastic small round-cell tumor. Report of 19 cases of a distinctive type of high-grade polyphenotypic malignancy affecting young individuals. Am J Surg Pathol. 1991 Jun;15(6):499–513. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kallioniemi A., Kallioniemi O. P., Sudar D., Rutovitz D., Gray J. W., Waldman F., Pinkel D. Comparative genomic hybridization for molecular cytogenetic analysis of solid tumors. Science. 1992 Oct 30;258(5083):818–821. doi: 10.1126/science.1359641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karcioglu Z., Someren A., Mathes S. J. Ectomesenchymoma. A malignant tumor of migratory neural crest (ectomesenchyme) remnants showing ganglionic, schwannian, melanocytic and rhabdomyoblastic differentiation. Cancer. 1977 Jun;39(6):2486–2496. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197706)39:6<2486::aid-cncr2820390627>3.0.co;2-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khatib Z. A., Matsushime H., Valentine M., Shapiro D. N., Sherr C. J., Look A. T. Coamplification of the CDK4 gene with MDM2 and GLI in human sarcomas. Cancer Res. 1993 Nov 15;53(22):5535–5541. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohl N. E., Gee C. E., Alt F. W. Activated expression of the N-myc gene in human neuroblastomas and related tumors. Science. 1984 Dec 14;226(4680):1335–1337. doi: 10.1126/science.6505694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohl N. E., Kanda N., Schreck R. R., Bruns G., Latt S. A., Gilbert F., Alt F. W. Transposition and amplification of oncogene-related sequences in human neuroblastomas. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):359–367. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90169-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovar H., Auinger A., Jug G., Aryee D., Zoubek A., Salzer-Kuntschik M., Gadner H. Narrow spectrum of infrequent p53 mutations and absence of MDM2 amplification in Ewing tumours. Oncogene. 1993 Oct;8(10):2683–2690. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ladanyi M., Gerald W. Fusion of the EWS and WT1 genes in the desmoplastic small round cell tumor. Cancer Res. 1994 Jun 1;54(11):2837–2840. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ladanyi M., Lewis R., Garin-Chesa P., Rettig W. J., Huvos A. G., Healey J. H., Jhanwar S. C. EWS rearrangement in Ewing's sarcoma and peripheral neuroectodermal tumor. Molecular detection and correlation with cytogenetic analysis and MIC2 expression. Diagn Mol Pathol. 1993 Sep;2(3):141–146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ladanyi M., Lewis R., Jhanwar S. C., Gerald W., Huvos A. G., Healey J. H. MDM2 and CDK4 gene amplification in Ewing's sarcoma. J Pathol. 1995 Feb;175(2):211–217. doi: 10.1002/path.1711750209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichter P., Tang C. J., Call K., Hermanson G., Evans G. A., Housman D., Ward D. C. High-resolution mapping of human chromosome 11 by in situ hybridization with cosmid clones. Science. 1990 Jan 5;247(4938):64–69. doi: 10.1126/science.2294592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May W. A., Lessnick S. L., Braun B. S., Klemsz M., Lewis B. C., Lunsford L. B., Hromas R., Denny C. T. The Ewing's sarcoma EWS/FLI-1 fusion gene encodes a more potent transcriptional activator and is a more powerful transforming gene than FLI-1. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Dec;13(12):7393–7398. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.12.7393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meltzer P. S., Jankowski S. A., Dal Cin P., Sandberg A. A., Paz I. B., Coccia M. A. Identification and cloning of a novel amplified DNA sequence in human malignant fibrous histiocytoma derived from a region of chromosome 12 frequently rearranged in soft tissue tumors. Cell Growth Differ. 1991 Oct;2(10):495–501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliner J. D., Kinzler K. W., Meltzer P. S., George D. L., Vogelstein B. Amplification of a gene encoding a p53-associated protein in human sarcomas. Nature. 1992 Jul 2;358(6381):80–83. doi: 10.1038/358080a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröck E., Thiel G., Lozanova T., du Manoir S., Meffert M. C., Jauch A., Speicher M. R., Nürnberg P., Vogel S., Jänisch W. Comparative genomic hybridization of human malignant gliomas reveals multiple amplification sites and nonrandom chromosomal gains and losses. Am J Pathol. 1994 Jun;144(6):1203–1218. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwab M., Alitalo K., Klempnauer K. H., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M., Gilbert F., Brodeur G., Goldstein M., Trent J. Amplified DNA with limited homology to myc cellular oncogene is shared by human neuroblastoma cell lines and a neuroblastoma tumour. Nature. 1983 Sep 15;305(5931):245–248. doi: 10.1038/305245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scrable H., Witte D., Shimada H., Seemayer T., Sheng W. W., Soukup S., Koufos A., Houghton P., Lampkin B., Cavenee W. Molecular differential pathology of rhabdomyosarcoma. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 1989 Sep;1(1):23–35. doi: 10.1002/gcc.2870010106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selleri L., Hermanson G. G., Eubanks J. H., Lewis K. A., Evans G. A. Molecular localization of the t(11;22)(q24;q12) translocation of Ewing sarcoma by chromosomal in situ suppression hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 1;88(3):887–891. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.3.887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorensen P. H., Liu X. F., Delattre O., Rowland J. M., Biggs C. A., Thomas G., Triche T. J. Reverse transcriptase PCR amplification of EWS/FLI-1 fusion transcripts as a diagnostic test for peripheral primitive neuroectodermal tumors of childhood. Diagn Mol Pathol. 1993 Sep;2(3):147–157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorensen P. H., Shimada H., Liu X. F., Lim J. F., Thomas G., Triche T. J. Biphenotypic sarcomas with myogenic and neural differentiation express the Ewing's sarcoma EWS/FLI1 fusion gene. Cancer Res. 1995 Mar 15;55(6):1385–1392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson C. F., Bridge J. A., Sandberg A. A. Cytogenetic and pathologic aspects of Ewing's sarcoma and neuroectodermal tumors. Hum Pathol. 1992 Nov;23(11):1270–1277. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(92)90295-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turc-Carel C., Aurias A., Mugneret F., Lizard S., Sidaner I., Volk C., Thiery J. P., Olschwang S., Philip I., Berger M. P. Chromosomes in Ewing's sarcoma. I. An evaluation of 85 cases of remarkable consistency of t(11;22)(q24;q12). Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1988 Jun;32(2):229–238. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(88)90285-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waber P. G., Chen J., Nisen P. D. Infrequency of MDM2 gene amplification in pediatric solid tumors and lack of association with p53 mutations in adult squamous cell carcinomas. Cancer Res. 1993 Dec 15;53(24):6028–6030. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whang-Peng J., Knutsen T., Theil K., Horowitz M. E., Triche T. Cytogenetic studies in subgroups of rhabdomyosarcoma. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 1992 Nov;5(4):299–310. doi: 10.1002/gcc.2870050405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeger H., Mor O., Pawlin G., Kaplinsky C., Shiloh Y. Importance of phenotypic and molecular characterization for identification of a neuroepithelioma tumor cell line, NUB-20. Cancer Res. 1990 May 1;50(9):2794–2802. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeoh G., Russell P., Wills E. J., Fleming S. Intra-abdominal desmoplastic small round cell tumor. Pathology. 1993 Apr;25(2):197–202. doi: 10.3109/00313029309084800. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucman J., Delattre O., Desmaze C., Plougastel B., Joubert I., Melot T., Peter M., De Jong P., Rouleau G., Aurias A. Cloning and characterization of the Ewing's sarcoma and peripheral neuroepithelioma t(11;22) translocation breakpoints. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 1992 Nov;5(4):271–277. doi: 10.1002/gcc.2870050402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucman J., Melot T., Desmaze C., Ghysdael J., Plougastel B., Peter M., Zucker J. M., Triche T. J., Sheer D., Turc-Carel C. Combinatorial generation of variable fusion proteins in the Ewing family of tumours. EMBO J. 1993 Dec;12(12):4481–4487. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06137.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]