Abstract
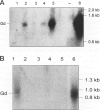
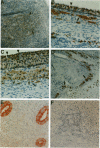
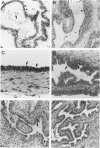
Glycodelin is a glycoprotein with potent immunosuppressive and contraceptive activities. It reacts with antibodies against placental protein 14, or progesterone-associated endometrial protein, and has a unique carbohydrate structure. Previous nomenclature is misleading, because glycodelin is neither synthesized in the placenta nor is it endometrium specific. No ovarian synthesis of glycodelin has been demonstrated. We present evidence for glycodelin synthesis in the human ovary and ovarian tumors. In follicular phase, immunoperoxidase staining of microwave-treated tissue sections employing affinity-purified polyclonal antibodies localized glycodelin to areas of stromal cell condensation in ovarian cortex, theca interna, and the granulosa. In luteal phase, cortical stroma was negative or only weakly positive, whereas glycodelin was present in theca interna of the corpus luteum and luteinized granulosa cells and also in corpus albicans and Leydig cells of the ovarian hilus. In situ hybridization gave negative results for glycodelin mRNA in normal ovary, whereas in ovarian tumors strong expression of both the glycodelin mRNA and the protein were found in benign and malignant serous cystadenomas, mucinous ovarian tumors being negative. We conclude that glycodelin is synthesized in human ovarian tumors, and its occurrence in normal human ovary may represent either synthesis or a site of glycodelin action.
Full text
PDF



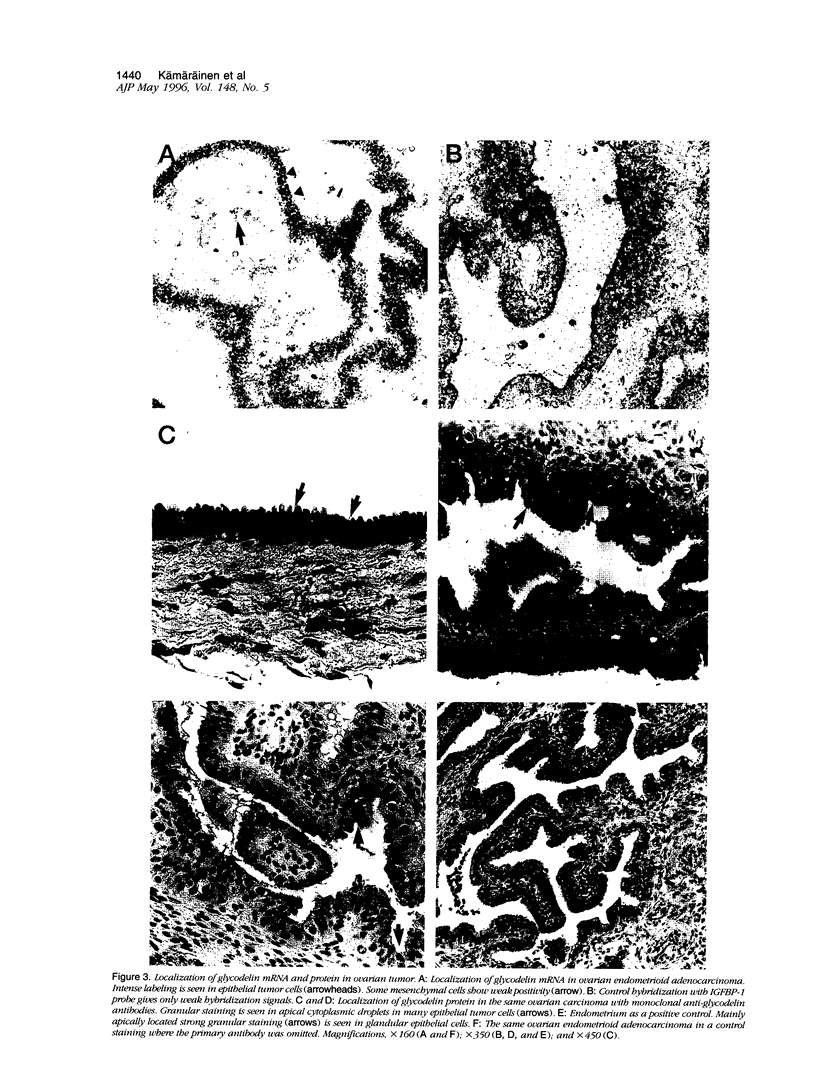



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auffray C., Rougeon F. Purification of mouse immunoglobulin heavy-chain messenger RNAs from total myeloma tumor RNA. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jun;107(2):303–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06030.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Critchley H. O., Chard T., Lieberman B. A., Buckley C. H., Anderson D. C. Serum PP14 levels in a patient with Turner's syndrome pregnant after frozen embryo transfer. Hum Reprod. 1990 Apr;5(3):250–254. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.humrep.a137082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Critchley H. O., Chard T., Olajide F., Davies M. C., Hughes S., Wang H. S., Lieberman B. A., Anderson D. C. Role of the ovary in the synthesis of placental protein-14. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1992 Jul;75(1):97–100. doi: 10.1210/jcem.75.1.1619035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dell A., Morris H. R., Easton R. L., Panico M., Patankar M., Oehniger S., Koistinen R., Koistinen H., Seppala M., Clark G. F. Structural analysis of the oligosaccharides derived from glycodelin, a human glycoprotein with potent immunosuppressive and contraceptive activities. J Biol Chem. 1995 Oct 13;270(41):24116–24126. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.41.24116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Davis G. E., Dickerson K., Ruoslahti E., Varon S., Manthorpe M. Mapping of domains in human laminin using monoclonal antibodies: localization of the neurite-promoting site. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 1):2457–2465. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He J., Furmanski P. Sequence specificity and transcriptional activation in the binding of lactoferrin to DNA. Nature. 1995 Feb 23;373(6516):721–724. doi: 10.1038/373721a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hjerpe A., Boon M. E., Kok L. P. Microwave stimulation of an immunological reaction (CEA/anti-CEA) and its use in immunohistochemistry. Histochem J. 1988 Jun-Jul;20(6-7):388–396. doi: 10.1007/BF01002733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue M., Fujita M., Enomoto T., Morimoto H., Monden T., Shimano T., Tanizawa O. Immunohistochemical analysis of p53 in gynecologic tumors. Am J Clin Pathol. 1994 Nov;102(5):665–670. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/102.5.665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwamura M., Abrahamsson P. A., Benning C. M., Cockett A. T., di Sant'Agnese P. A. Androgen receptor immunostaining and its tissue distribution in formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded sections after microwave treatment. J Histochem Cytochem. 1994 Jun;42(6):783–788. doi: 10.1177/42.6.8189040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson M. R., Brooks A., Norman-Taylor J. Q., Grudzinskas J. G., Wren M. E., Murugni P., Chard T., Abdalla H. Serum placental protein 14 concentrations in the first trimester of ovum donation pregnancies. Hum Reprod. 1993 Mar;8(3):485–487. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.humrep.a138076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julkunen M., Apter D., Seppälä M., Stenman U. H., Bohn H. Serum levels of placental protein 14 reflect ovulation in nonconceptional menstrual cycles. Fertil Steril. 1986 Jan;45(1):47–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julkunen M., Koistinen R., Sjöberg J., Rutanen E. M., Wahlström T., Seppälä M. Secretory endometrium synthesizes placental protein 14. Endocrinology. 1986 May;118(5):1782–1786. doi: 10.1210/endo-118-5-1782. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julkunen M., Koistinen R., Suikkari A. M., Seppälä M., Jänne O. A. Identification by hybridization histochemistry of human endometrial cells expressing mRNAs encoding a uterine beta-lactoglobulin homologue and insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-1. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 May;4(5):700–707. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-5-700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julkunen M., Rutanen E. M., Koskimies A., Ranta T., Bohn H., Seppälä M. Distribution of placental protein 14 in tissues and body fluids during pregnancy. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1985 Nov;92(11):1145–1151. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1985.tb03027.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julkunen M., Seppälä M., Jänne O. A. Complete amino acid sequence of human placental protein 14: a progesterone-regulated uterine protein homologous to beta-lactoglobulins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8845–8849. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julkunen M., Wahlström T., Seppälä M., Koistinen R., Koskimies A., Stenman U. H., Bohn H. Detection and localization of placental protein 14-like protein in human seminal plasma and in the male genital tract. Arch Androl. 1984;12 (Suppl):59–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kämäräinen M., Julkunen M., Seppälä M. HinfI polymorphism in the human progesterone associated endometrial protein (PAEP) gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Sep 25;19(18):5092–5092. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.18.5092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kämäräinen M., Leivo I., Julkunen M., Seppälä M. Localization of progesterone-associated endometrial protein mRNA by in-situ hybridization in human pregnancy decidua, endometriosis and borderline endometrioid adenoma. J Mol Endocrinol. 1993 Feb;10(1):71–77. doi: 10.1677/jme.0.0100071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kämäräinen M., Riittinen L., Seppälä M., Palotie A., Andersson L. C. Progesterone-associated endometrial protein--a constitutive marker of human erythroid precursors. Blood. 1994 Jul 15;84(2):467–473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrow D. M., Xiong N., Getty R. R., Ratajczak M. Z., Morgan D., Seppala M., Riittinen L., Gewirtz A. M., Tykocinski M. L. Hematopoietic placental protein 14. An immunosuppressive factor in cells of the megakaryocytic lineage. Am J Pathol. 1994 Dec;145(6):1485–1495. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oehninger S., Coddington C. C., Hodgen G. D., Seppala M. Factors affecting fertilization: endometrial placental protein 14 reduces the capacity of human spermatozoa to bind to the human zona pellucida. Fertil Steril. 1995 Feb;63(2):377–383. doi: 10.1016/s0015-0282(16)57372-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto N., Uchida A., Takakura K., Kariya Y., Kanzaki H., Riittinen L., Koistinen R., Seppälä M., Mori T. Suppression by human placental protein 14 of natural killer cell activity. Am J Reprod Immunol. 1991 Dec;26(4):137–142. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0897.1991.tb00713.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riittinen L., Julkunen M., Seppälä M., Koistinen R., Huhtala M. L. Purification and characterization of endometrial protein PP14 from mid-trimester amniotic fluid. Clin Chim Acta. 1989 Sep 15;184(1):19–29. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(89)90253-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riittinen L., Närvänen O., Virtanen I., Seppälä M. Monoclonal antibodies against endometrial protein PP14 and their use for purification and radioimmunoassay of PP14. J Immunol Methods. 1991 Jan 24;136(1):85–90. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(91)90253-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riittinen L., Stenman U. H., Alfthan H., Suikkari A. M., Bohn H., Seppälä M. Time-resolved immunofluorometric assay for placental protein 14. Clin Chim Acta. 1989 Aug 15;183(2):115–123. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(89)90327-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suikkari A. M., Leivo I., Kämäräinen M., Holthöfer H., Seppälä M., Julkunen M., Koistinen R. Expression of insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1 mRNA in human fetal kidney. Kidney Int. 1992 Sep;42(3):749–754. doi: 10.1038/ki.1992.343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Niekerk C. C., Ramaekers F. C., Hanselaar A. G., Aldeweireldt J., Poels L. G. Changes in expression of differentiation markers between normal ovarian cells and derived tumors. Am J Pathol. 1993 Jan;142(1):157–177. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahlström T., Huhtaniemi I., Hovatta O., Seppälä M. Localization of luteinizing hormone, follicle-stimulating hormone, prolactin, and their receptors in human and rat testis using immunohistochemistry and radioreceptor assay. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1983 Oct;57(4):825–830. doi: 10.1210/jcem-57-4-825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]