Full text
PDF
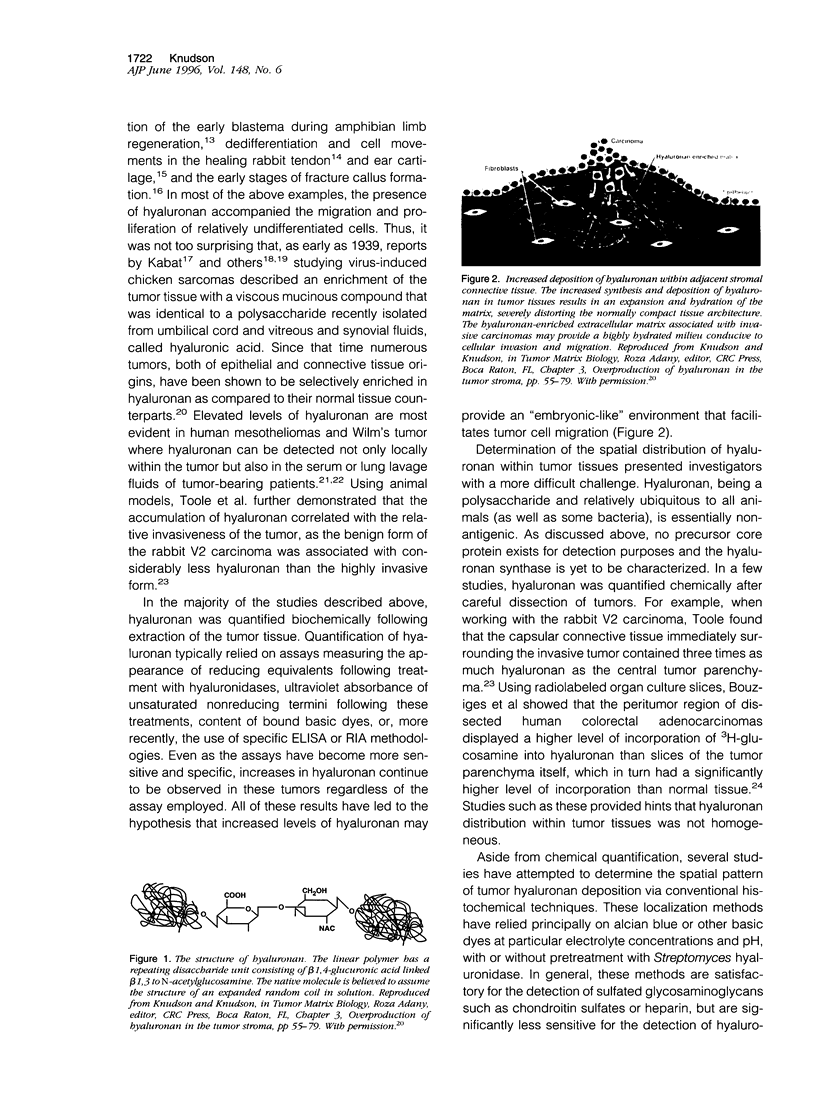




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson C. B., Meier S. Effect of hyaluronidase treatment on the distribution of cranial neural crest cells in the chick embryo. J Exp Zool. 1982 Jul 1;221(3):329–335. doi: 10.1002/jez.1402210308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antonopoulos C. A., Engfeldt B., Gardell S., Hjertquist S. O., Solheim K. Isolation and identification of the glycosaminoglycans from fracture callus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Jul 1;101(2):150–156. doi: 10.1016/0926-6534(65)90045-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aruffo A., Stamenkovic I., Melnick M., Underhill C. B., Seed B. CD44 is the principal cell surface receptor for hyaluronate. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1303–1313. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90694-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertolotto A., Giordana M. T., Magrassi M. L., Mauro A., Schiffer D. Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) in human cerebral tumors. Part 1. Biochemical findings. Acta Neuropathol. 1982;58(2):115–119. doi: 10.1007/BF00691651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouziges F., Simon-Assmann P., Leberquier C., Marescaux J., Bellocq J. P., Haffen K., Kedinger M. Changes in glycosaminoglycan synthesis and in heparan sulfate deposition in human colorectal adenocarcinomas. Int J Cancer. 1990 Aug 15;46(2):189–197. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910460208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahl I. M., Solheim O. P., Erikstein B., Müller E. A longitudinal study of the hyaluronan level in the serum of patients with malignant mesothelioma under treatment. Hyaluronan as an indicator of progressive disease. Cancer. 1989 Jul 1;64(1):68–73. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19890701)64:1<68::aid-cncr2820640112>3.0.co;2-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeAngelis P. L., Papaconstantinou J., Weigel P. H. Molecular cloning, identification, and sequence of the hyaluronan synthase gene from group A Streptococcus pyogenes. J Biol Chem. 1993 Sep 15;268(26):19181–19184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delpech B., Maingonnat C., Girard N., Chauzy C., Maunoury R., Olivier A., Tayot J., Creissard P. Hyaluronan and hyaluronectin in the extracellular matrix of human brain tumour stroma. Eur J Cancer. 1993;29A(7):1012–1017. doi: 10.1016/s0959-8049(05)80214-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derby M. A. Analysis of glycosaminoglycans within the extracellular environments encountered by migrating neural crest cells. Dev Biol. 1978 Oct;66(2):321–336. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(78)90241-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARRIS R. J., MALMGREN H., SYLVEN B. The polysaccharides of Rous sarcoma No. 1. Br J Cancer. 1954 Mar;8(1):141–146. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1954.11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasty K. A., Smith G. N., Jr, Kang A. H. Studies on glycosaminoglycans of regenerating rabbit ear cartilage. Dev Biol. 1981 Aug;86(1):198–205. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(81)90330-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellström S., Tengblad A., Johansson C., Hedlund U., Axelsson E. An improved technique for hyaluronan histochemistry using microwave irradiation. Histochem J. 1990 Dec;22(12):677–682. doi: 10.1007/BF01047452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knudson C. B., Knudson W. Hyaluronan-binding proteins in development, tissue homeostasis, and disease. FASEB J. 1993 Oct;7(13):1233–1241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knudson C. B., Munaim S. I., Toole B. P. Ectodermal stimulation of the production of hyaluronan-dependent pericellular matrix by embryonic limb mesodermal cells. Dev Dyn. 1995 Oct;204(2):186–191. doi: 10.1002/aja.1002040209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knudson W., Biswas C., Toole B. P. Stimulation of glycosaminoglycan production in murine tumors. J Cell Biochem. 1984;25(4):183–196. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240250402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar S., West D. C., Ponting J. M., Gattamaneni H. R. Sera of children with renal tumours contain low-molecular-mass hyaluronic acid. Int J Cancer. 1989 Sep 15;44(3):445–448. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910440311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindqvist U., Chichibu K., Delpech B., Goldberg R. L., Knudson W., Poole A. R., Laurent T. C. Seven different assays of hyaluronan compared for clinical utility. Clin Chem. 1992 Jan;38(1):127–132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwald R. R., Funderberg F. M., Bernanke D. H. Glycosaminoglycans: potential determinants in cardiac morphogenesis. Tex Rep Biol Med. 1979;39:253–270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer F. A. Macromolecular basis of globular protein exclusion and of swelling pressure in loose connective tissue (umbilical cord). Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Feb 22;755(3):388–399. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(83)90242-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orkin R. W., Toole B. P. Hyaluronidase activity and hyaluronate content of the developing chick embryo heart. Dev Biol. 1978 Oct;66(2):308–320. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(78)90240-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pauli B. U., Knudson W. Tumor invasion: a consequence of destructive and compositional matrix alterations. Hum Pathol. 1988 Jun;19(6):628–639. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(88)80168-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pratt R. M., Larsen M. A., Johnston M. C. Migration of cranial neural crest cells in a cell-free hyaluronate-rich matrix. Dev Biol. 1975 Jun;44(2):298–305. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(75)90400-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid T., Flint M. H. Changes in glycosaminoglycan content of healing rabbit tendon. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1974 Apr;31(2):489–495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. N., Jr, Toole B. P., Gross J. Hyaluronidase activity and glycosaminoglycan synthesis in the amputated newt limb: comparison of denervated, nonregenerating limbs with regenerates. Dev Biol. 1975 Apr;43(2):221–232. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(75)90022-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toole B. P., Biswas C., Gross J. Hyaluronate and invasiveness of the rabbit V2 carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6299–6303. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toole B. P. Hyaluronate turnover during chondrogenesis in the developing chick limb and axial skeleton. Dev Biol. 1972 Nov;29(3):321–329. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(72)90071-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toole B. P., Trelstad R. L. Hyaluronate production and removal during corneal development in the chick. Dev Biol. 1971 Sep;26(1):28–35. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(71)90104-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turley E. A., Austen L., Vandeligt K., Clary C. Hyaluronan and a cell-associated hyaluronan binding protein regulate the locomotion of ras-transformed cells. J Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;112(5):1041–1047. doi: 10.1083/jcb.112.5.1041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang C., Tammi M., Guo H., Tammi R. Hyaluronan distribution in the normal epithelium of esophagus, stomach, and colon and their cancers. Am J Pathol. 1996 Jun;148(6):1861–1869. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



