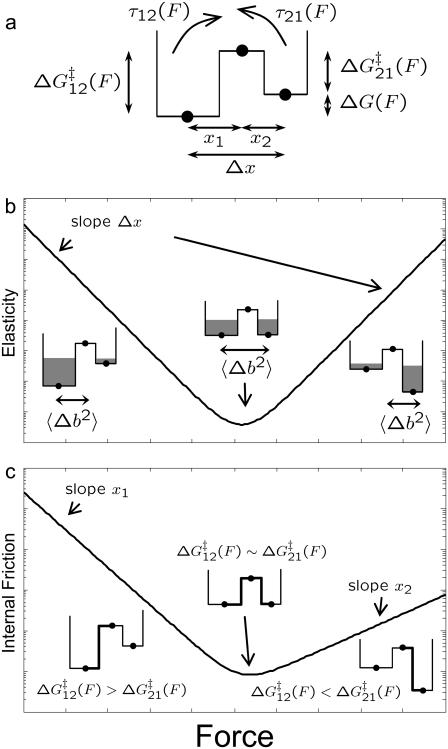
FIGURE 5.
Viscoelastic force spectrum on a discrete bistable landscape. (a) Schematic diagram of the discrete free energy landscape used to calculate the elastic and internal friction force spectra (Eqs. 6 and 7). (b) Elasticity force spectrum on a discrete bistable landscape; force controls free energy difference ΔG(F) = ΔG0 − FΔx and hence spread 〈Δb2〉 and elastic constant κ12(F) = kBT/〈Δb2〉) (shaded regions indicate relative populations of two states). Elasticity is entropic in nature as the elastic constant decreases in direction of increasing entropy of monomers. (c) Internal friction force spectrum for a discrete bistable landscape; force controls activation barrier heights (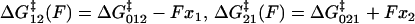 ), and therefore also the internal friction. Hence, at a given force, internal friction is dominated by the activation barrier that is largest, as indicated by the thick lines in diagrams.
), and therefore also the internal friction. Hence, at a given force, internal friction is dominated by the activation barrier that is largest, as indicated by the thick lines in diagrams.