Figure 1. Mutant strains of Salmonella deficient in expression of FliC andFljB flagellin proteins differentially activate NF-κB in HEK293 cells.
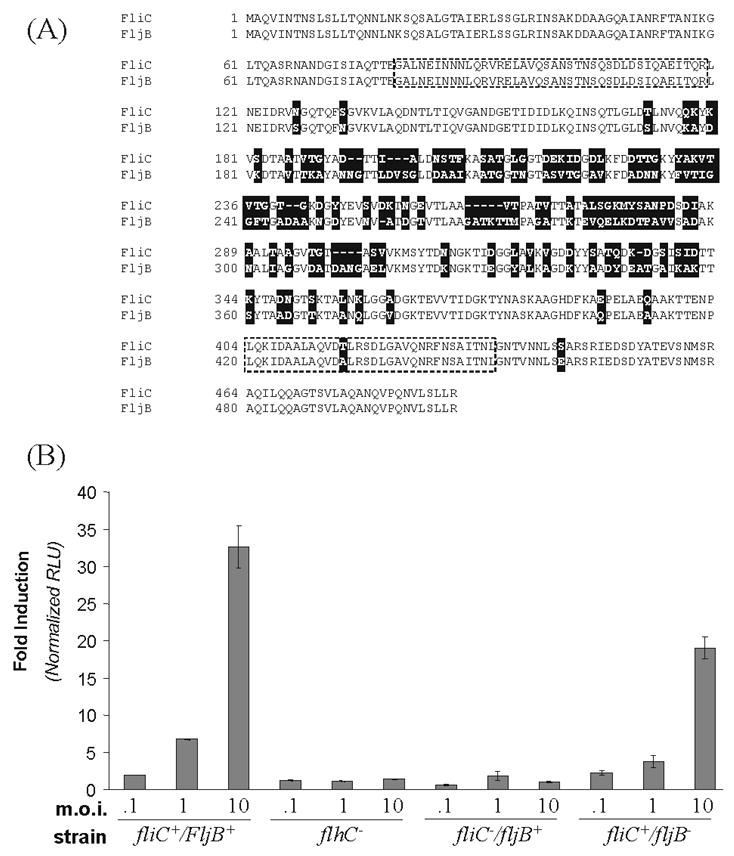
A. The Salmonella typhimurium FliC and FljB proteins were aligned using the SIM alignment software (http://www.expasy.ch/tools/sim-prot.html). Nonconserved residues are denoted with a shaded box. The TLR5 recognition site [17] is indicated by the dashed line. B. Human HEK293 cells stably transformed with a firefly luciferase reporter gene under control of the NF-κB promoter were infected in triplicate with wild-type Salmonella typhimurium (fliC+/fljB+), a FliC (flagellin 1) deficient strain (fliC−/fljB+), a FljB (flagellin 2) deficient strain (fliC+/fljB−), or the flhC− strain deficient in the global regulator of flagellin production. HEK293 cells were harvested at 4 h after infection and luciferase activity (RLU) determined. Luciferase activity from infected cells is expressed relative to that obtained from uninfected cells.
