Abstract
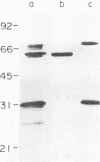
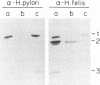
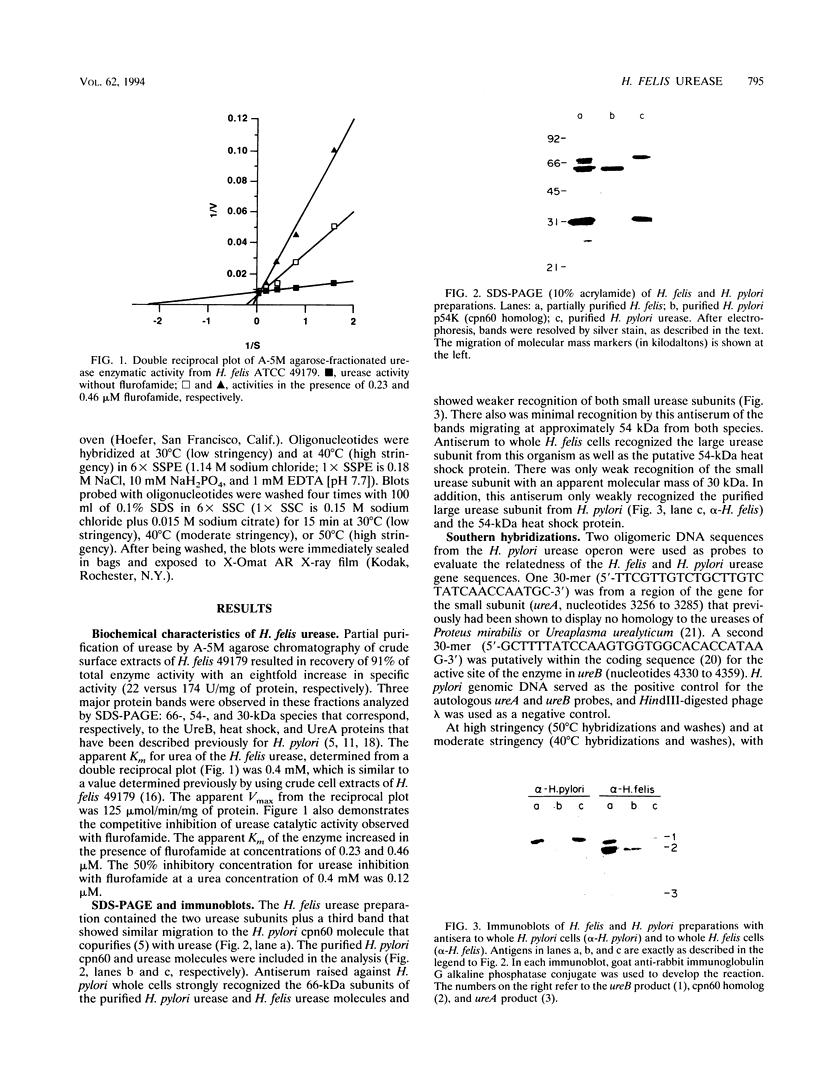
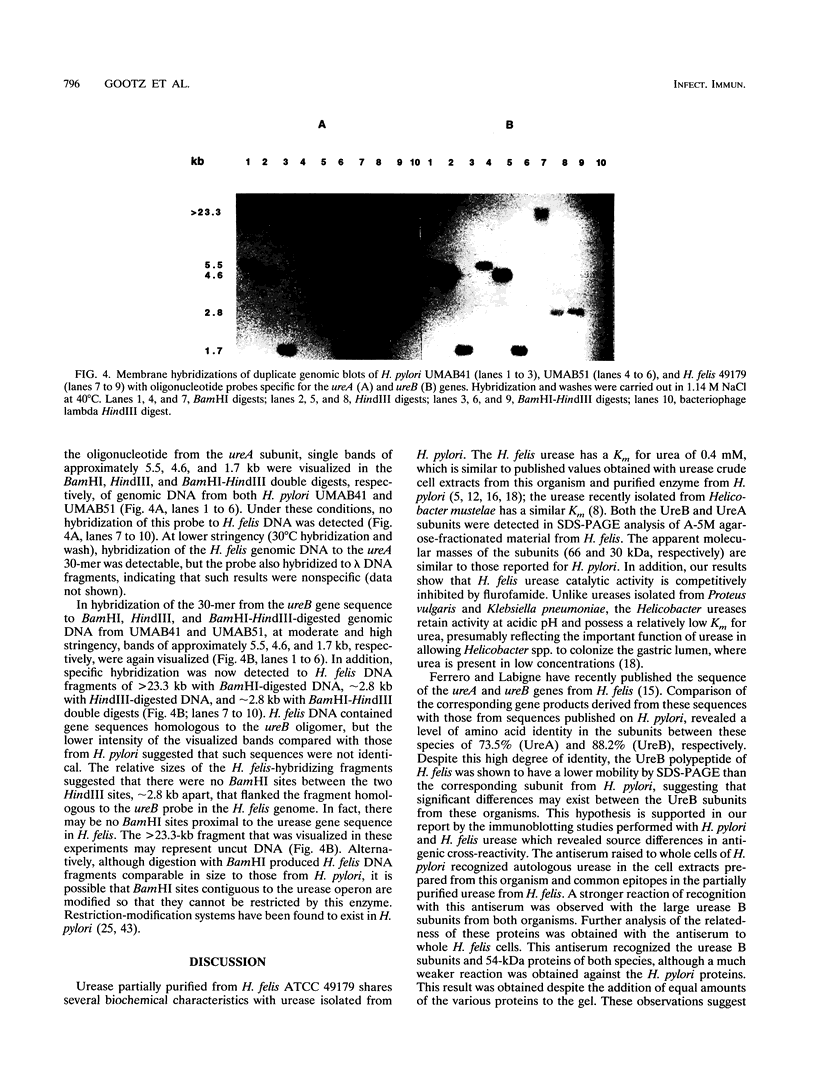
Urease activity has recently been shown to be an important virulence determinant for Helicobacter pylori, allowing it to survive the low pH of the stomach during colonization. Experimental murine infection with Helicobacter felis is now being used as a model for H. pylori infection to study the effects of vaccines, antibiotics, and urease inhibitors on colonization. However, little information comparing the ureases of H. felis and H. pylori is available. Urease was partially purified from the cell surface of H. felis ATCC 49179 by A-5M agarose chromatography, resulting in an eightfold increase in specific activity over that of crude urease. The apparent Km for urea for the partially purified urease was 0.4 mM, and the enzyme was inhibited in a competitive manner by flurofamide (50% inhibitory concentration = 0.12 microM). Antiserum to whole cells of H. pylori recognized both H. pylori and H. felis urease B subunits. Antiserum raised against H. felis whole cells recognized the large and small autologous urease subunits and the cpn60 heat shock molecule in both H. felis and H. pylori. However, this antiserum showed only a weak reaction with the B subunit of H. pylori urease. Two oligomeric DNA sequences were used as probes to evaluate the relatedness of H. felis and H. pylori urease gene sequences. One 30-mer from the ureA sequence, which had been shown previously to be specific for H. pylori, failed to hybridize to H. felis genomic DNA. A probe to the putative coding sequence for the active site of the H. pylori ureB subunit hybridized at low intensity to a 2.8-kb fragment of BamHI-HindIII-digested H. felis DNA, suggesting that the sequences were homologous but not identical, a result confirmed from the recently published sequences of ureA and ureB from H. felis.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blaser M. J. Hypotheses on the pathogenesis and natural history of Helicobacter pylori-induced inflammation. Gastroenterology. 1992 Feb;102(2):720–727. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(92)90126-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton F. J., Hutchinson D. N. Evaluation of three Campylobacter pylori antigen preparations for screening sera from patients undergoing endoscopy. J Clin Pathol. 1989 Jul;42(7):723–726. doi: 10.1136/jcp.42.7.723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buck G. E. Campylobacter pylori and gastroduodenal disease. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1990 Jan;3(1):1–12. doi: 10.1128/cmr.3.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton C. L., Wren B. W., Mullany P., Topping A., Tabaqchali S. Molecular cloning and expression of Campylobacter pylori species-specific antigens in Escherichia coli K-12. Infect Immun. 1989 Feb;57(2):623–629. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.2.623-629.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dent J. C., McNulty C. A., Uff J. S., Gear M. W., Wilkinson S. P. Campylobacter pylori urease: a new serological test. Lancet. 1988 Apr 30;1(8592):1002–1002. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)91827-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn B. E., Campbell G. P., Perez-Perez G. I., Blaser M. J. Purification and characterization of urease from Helicobacter pylori. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 5;265(16):9464–9469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn B. E., Perez-Perez G. I., Blaser M. J. Two-dimensional gel electrophoresis and immunoblotting of Campylobacter pylori proteins. Infect Immun. 1989 Jun;57(6):1825–1833. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.6.1825-1833.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn B. E., Roop R. M., 2nd, Sung C. C., Sharma S. A., Perez-Perez G. I., Blaser M. J. Identification and purification of a cpn60 heat shock protein homolog from Helicobacter pylori. Infect Immun. 1992 May;60(5):1946–1951. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.5.1946-1951.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn B. E., Sung C. C., Taylor N. S., Fox J. G. Purification and characterization of Helicobacter mustelae urease. Infect Immun. 1991 Sep;59(9):3343–3345. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.9.3343-3345.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton K. A., Brooks C. L., Morgan D. R., Krakowka S. Essential role of urease in pathogenesis of gastritis induced by Helicobacter pylori in gnotobiotic piglets. Infect Immun. 1991 Jul;59(7):2470–2475. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.7.2470-2475.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton K. A., Morgan D. R., Krakowka S. Motility as a factor in the colonisation of gnotobiotic piglets by Helicobacter pylori. J Med Microbiol. 1992 Aug;37(2):123–127. doi: 10.1099/00222615-37-2-123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. J., Jr, Evans D. G., Engstrand L., Graham D. Y. Urease-associated heat shock protein of Helicobacter pylori. Infect Immun. 1992 May;60(5):2125–2127. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.5.2125-2127.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. J., Jr, Evans D. G., Kirkpatrick S. S., Graham D. Y. Characterization of the Helicobacter pylori urease and purification of its subunits. Microb Pathog. 1991 Jan;10(1):15–26. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(91)90062-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrero R. L., Labigne A. Cloning, expression and sequencing of Helicobacter felis urease genes. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Jul;9(2):323–333. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01693.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin C. S., Armstrong J. A., Marshall B. J. Campylobacter pyloridis, gastritis, and peptic ulceration. J Clin Pathol. 1986 Apr;39(4):353–365. doi: 10.1136/jcp.39.4.353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu L. T., Mobley H. L. Purification and N-terminal analysis of urease from Helicobacter pylori. Infect Immun. 1990 Apr;58(4):992–998. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.4.992-998.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaltwasser H., Schlegel H. G. NADH-Dependent coupled enzyme assay for urease and other ammonia-producing systems. Anal Biochem. 1966 Jul;16(1):132–138. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(66)90088-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labigne A., Cussac V., Courcoux P. Shuttle cloning and nucleotide sequences of Helicobacter pylori genes responsible for urease activity. J Bacteriol. 1991 Mar;173(6):1920–1931. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.6.1920-1931.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee A., Hazell S. L., O'Rourke J., Kouprach S. Isolation of a spiral-shaped bacterium from the cat stomach. Infect Immun. 1988 Nov;56(11):2843–2850. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.11.2843-2850.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leunk R. D., Johnson P. T., David B. C., Kraft W. G., Morgan D. R. Cytotoxic activity in broth-culture filtrates of Campylobacter pylori. J Med Microbiol. 1988 Jun;26(2):93–99. doi: 10.1099/00222615-26-2-93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leunk R. D. Production of a cytotoxin by Helicobacter pylori. Rev Infect Dis. 1991 Jul-Aug;13 (Suppl 8):S686–S689. doi: 10.1093/clinids/13.supplement_8.s686. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leying H., Suerbaum S., Geis G., Haas R. Cloning and genetic characterization of a Helicobacter pylori flagellin gene. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Oct;6(19):2863–2874. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01466.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall B. J., Barrett L. J., Prakash C., McCallum R. W., Guerrant R. L. Urea protects Helicobacter (Campylobacter) pylori from the bactericidal effect of acid. Gastroenterology. 1990 Sep;99(3):697–702. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(90)90957-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagata K., Mizuta T., Tonokatu Y., Fukuda Y., Okamura H., Hayashi T., Shimoyama T., Tamura T. Monoclonal antibodies against the native urease of Helicobacter pylori: synergistic inhibition of urease activity by monoclonal antibody combinations. Infect Immun. 1992 Nov;60(11):4826–4831. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.11.4826-4831.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newell D. G., Lee A., Hawtin P. R., Hudson M. J., Stacey A. R., Fox J. Antigenic conservation of the ureases of spiral- and helical-shaped bacteria colonising the stomachs of man and animals. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1989 Nov;53(1-2):183–186. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(89)90388-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura A., Stemmermann G. N., Chyou P. H., Kato I., Perez-Perez G. I., Blaser M. J. Helicobacter pylori infection and gastric carcinoma among Japanese Americans in Hawaii. N Engl J Med. 1991 Oct 17;325(16):1132–1136. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199110173251604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pallen M. J., Clayton C. L. Vaccination against Helicobacter pylori urease. Lancet. 1990 Jul 21;336(8708):186–187. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)91716-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsonnet J., Friedman G. D., Vandersteen D. P., Chang Y., Vogelman J. H., Orentreich N., Sibley R. K. Helicobacter pylori infection and the risk of gastric carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 1991 Oct 17;325(16):1127–1131. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199110173251603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez-Perez G. I., Dworkin B. M., Chodos J. E., Blaser M. J. Campylobacter pylori antibodies in humans. Ann Intern Med. 1988 Jul 1;109(1):11–17. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-109-1-11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez G. I., Hopkins J. A., Blaser M. J. Antigenic heterogeneity of lipopolysaccharides from Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter fetus. Infect Immun. 1985 May;48(2):528–533. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.2.528-533.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Pérez G. I., Olivares A. Z., Cover T. L., Blaser M. J. Characteristics of Helicobacter pylori variants selected for urease deficiency. Infect Immun. 1992 Sep;60(9):3658–3663. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.9.3658-3663.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauws E. A., Langenberg W., Houthoff H. J., Zanen H. C., Tytgat G. N. Campylobacter pyloridis-associated chronic active antral gastritis. A prospective study of its prevalence and the effects of antibacterial and antiulcer treatment. Gastroenterology. 1988 Jan;94(1):33–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidebotham R. L., Batten J. J., Karim Q. N., Spencer J., Baron J. H. Breakdown of gastric mucus in presence of Helicobacter pylori. J Clin Pathol. 1991 Jan;44(1):52–57. doi: 10.1136/jcp.44.1.52. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smoot D. T., Mobley H. L., Chippendale G. R., Lewison J. F., Resau J. H. Helicobacter pylori urease activity is toxic to human gastric epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1990 Jun;58(6):1992–1994. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.6.1992-1994.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. E., Eaton M., Chang N., Salama S. M. Construction of a Helicobacter pylori genome map and demonstration of diversity at the genome level. J Bacteriol. 1992 Nov;174(21):6800–6806. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.21.6800-6806.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turbett G. R., Høj P. B., Horne R., Mee B. J. Purification and characterization of the urease enzymes of Helicobacter species from humans and animals. Infect Immun. 1992 Dec;60(12):5259–5266. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.12.5259-5266.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unidentified curved bacilli on gastric epithelium in active chronic gastritis. Lancet. 1983 Jun 4;1(8336):1273–1275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willshaw G. A., Smith H. R., McConnell M. M., Gaastra W., Thomas A., Hibberd M., Rowe B. Plasmid-encoded production of coli surface-associated antigen 1 (CS1) in a strain of Escherichia coli serotype O139.H28. Microb Pathog. 1990 Jul;9(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(90)90035-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt J. I., Rathbone B. J., Dixon M. F., Heatley R. V. Campylobacter pyloridis and acid induced gastric metaplasia in the pathogenesis of duodenitis. J Clin Pathol. 1987 Aug;40(8):841–848. doi: 10.1136/jcp.40.8.841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]