Figure 4.
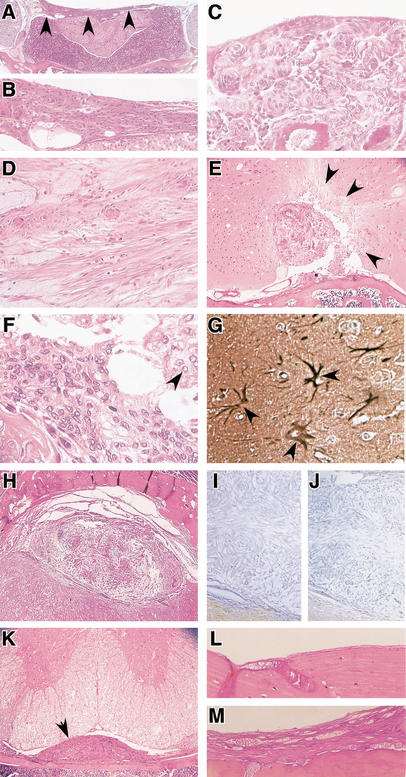
Meningiomas in mice show histological hallmarks of human meningiomas. Histology of meningiomas in adCre-injected Nf2flox2/flox2 (A,B,D–K) and Nf2flox2/flox2;p53+/− (C) mice. Sections are stained with haematoxilin and eosin. (A) Transitional meningioma (arrowheads) on the diaphragma sellae; (B) magnification of the tumor in A; (C) meningothelial meningioma in the supra trigeminal nerve region. Tumor cells form lobules, which are surrounded by thin collagenous septae. Numerous concentric onion bulb structures and whorl formation are observed; (D) fibroblastic meningioma with fascicular arrangements. Spindle-shaped cells form parallel and interlacing bundles on a matrix abundant in collagen and reticulin; (E) menigothelial meningioma. Irregular calcified and ossified masses are present. Arrows indicate areas of brain invasion with (F) typical meningothelial tumor cells infiltrating the adjacent cerebral parenchyma. Cells are largely uniform with oval nuclei that on occasion show central clearing (arrowhead); (G) GFAP staining showing reactive astrocytes (arrowheads) in the proximity of tumor invasion; (H) transitional meningioma showing loss of merlin (I) and protein 4.1B (J) expression; (K) intraspinal meningioma (arrowhead) located in the thoracic region; (L) normal meninges at the adlacZ injection site in an Nf2flox2/flox2 mouse, and (M) meningothelial proliferation at the adCre injection site in an Nf2flox2/flox2 littermate.