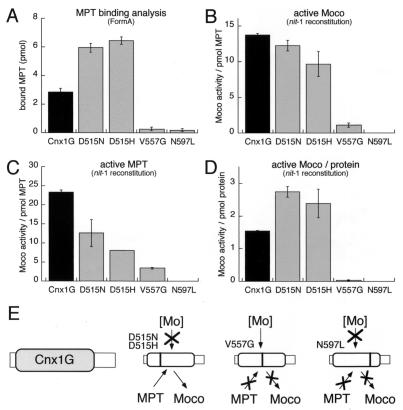
Figure 6.
Binding and stabilization of Moco by Cnx1 G domain. MPT (45 pmol) isolated from xanthine oxidase was incubated with 10 mM sodium molybdate to generate Moco that was supplied for binding to 30 pmol wild-type and mutated Cnx1 G domains or no protein as control. The binding mixture (400 μl) was separated by gel filtration and used for MPT determination (A) by FormA analysis (26) and nit-1 reconstitution in the absence (B and D) or presence (C) of 10 mM sodium molybdate. In all experiments the control (no protein) was subtracted from the measured values. The nit-1 activities determined kinetically by using different amounts of MPT source were plotted either against the MPT amount present in each sample (B and C) or against protein concentration (D) and are expressed in nit-1–nitrate reductase (NR) units per pmol protein-bound MPT (B and C) or nit-1–NR units per pmol protein (D). Standard errors were calculated from triplicates and the nit-1 activity was determined in the linear range of reconstitution by taking three kinetic points of measurement. (E) Model for the different effects of the mutations identified in this work, where both aspartate mutants are defective in Mo insertion and the V557G mutant is impaired in substrate and product binding whereas the N597L mutant has lost all three functional properties of the G domain.