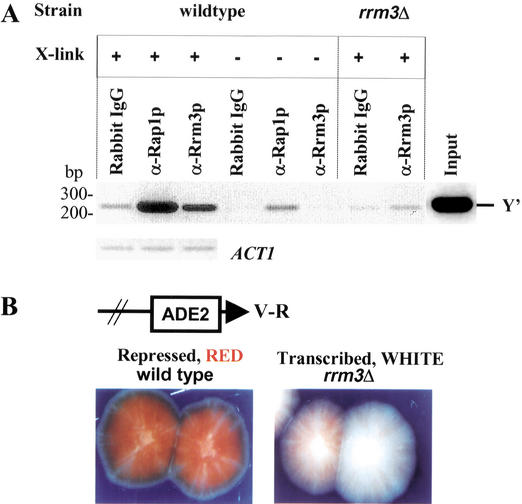
Figure 7.
Rrm3p is associated with telomeric DNA in vivo and has a modest effect on TPE. (A) Chromatin was prepared from otherwise isogenic wild-type or rrm3Δ cells that had been cross-linked (+ cross-link) or not (− cross-link) with formaldehyde in vivo. Immunoprecipitation was carried out using either protein-A-purified preimmune IgG (rabbit IgG), a polyclonal Rap1p antiserum (α-Rap1p; Conrad et al. 1990), or affinity-purified anti-Rrm3p polyclonal antibodies (Ivessa et al. 2000). The DNA in the precipitate was PCR-amplified for 28 cycles using Y‘ primers that detect a 233-bp portion of the subtelomeric Y‘ element that begins 30 bp upstream of the terminal C1–3A/TG1–3 tracts or for 31 cycles using ACT1 primers. The PCR products were separated in a 2.3% agarose gel and visualized by staining with ethidium bromide. PCR amplification of the input DNA with telomeric primers is also shown (Input). Although Rrm3p association with telomeric DNA was eliminated in the absence of in vivo cross-linking, some Rap1p association with telomeric DNA was detected in the no cross-linking control. (B) TPE was measured in a strain with URA3 next to the left telomere of Chromosome VII (Gottschling et al. 1990) and ADE2 next to the right telomere of Chromosome V (Wiley and Zakian 1995). Wild-type or rrm3Δ cells were plated on media containing low amounts of adenine, and the color of the resulting colonies was examined.